Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (35): 5596-5602.doi: 10.12307/2023.889
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunoregulatory mechanism of choline acetyltransferase/alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
Li Yutong, Liu Jingshu, Li Zhen
- College of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-01Accepted:2022-12-12Online:2023-12-18Published:2023-06-01 -
Contact:Li Zhen, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Yutong, Master candidate, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81904034 (to LZ); Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine Doctoral Start-up Fund Project, No. 2020BK02 (to LZ); Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine Outstanding Young Scientist Cultivation Project, No. 2021PY-QN-04 (to LZ); Shanxi Province Key Laboratory Open Fund for Inflammatory Response-based Innovative Drugs for Major Diseases, No. 2021sxcxyw01 (to LZ); Scientific Research Plan of Shanxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2023ZYYC058 (to LZ); Postgraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021CX015 (to LYT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yutong, Liu Jingshu, Li Zhen. Immunoregulatory mechanism of choline acetyltransferase/alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5596-5602.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

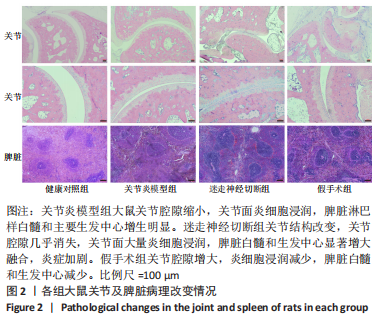
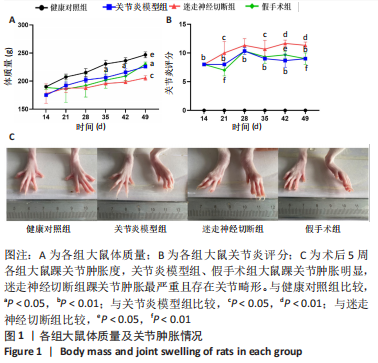
2.1 实验动物数量分析 造模过程中无大鼠死亡,纳入的32只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠体质量及关节肿胀观察结果 各组大鼠体质量和关节肿胀情况,见图1。与健康对照组相比,关节炎模型组大鼠体质量降低(P < 0.05),关节炎评分显著增高(P < 0.01),踝关节显著肿胀;与关节炎模型组相比,迷走神经切断组大鼠体质量降低(P < 0.05),关节炎评分(极)显著升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),踝关节显著肿胀,并存关节变形畸形;与迷走神经切断组相比,假手术组大鼠体质量增高(P < 0.05),关节炎评分(极)显著下降(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),踝关节肿胀度减轻。"

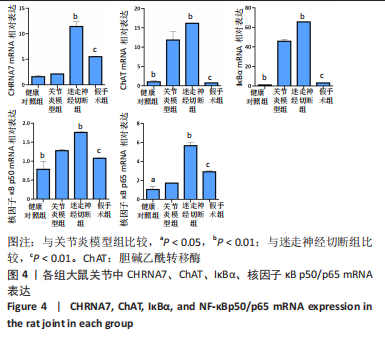
qRT-PCR检测结果显示,与健康对照组相比,关节炎模型组大鼠关节CHRNA7 mRNA表达轻度增高,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65 mRNA表达(极)显著增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与关节炎模型组相比,迷走神经切断组大鼠关节CHRNA7、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65 mRNA表达(极)显著增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与迷走神经切断组相比,假手术组大鼠关节CHRNA7、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65 mRNA表达极显著降低(P < 0.01)。 2.6 各组大鼠关节中α7nAChR、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65蛋白表达 见图5。"
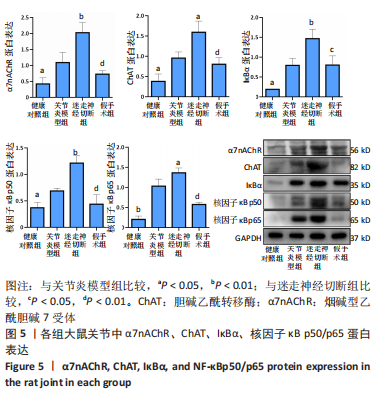

Western blot检测结果显示,与健康对照组相比,关节炎模型组大鼠关节α7nAChR、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65表达(极)显著增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与关节炎模型组相比,迷走神经切断组大鼠关节α7nAChR、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65表达(极)显著增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与迷走神经切断组相比,假手术组大鼠关节α7nAChR、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65表达(极)显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。 2.7 各实验组大鼠关节中α7nAChR、ChAT、IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65免疫组化分析 见图6。"

| [1] FIRESTEIN GS, BUDD RC, GABRIEL SE. 凯利风湿病学[M].10版.栗占国等,译.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2020:1. [2] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):ITC1-ITC16. [3] LV J, JI X, LI Z, et al. The role of the cholinergic anti‐inflammatory pathway in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Scand J Immunol. 2021; 94(4):e13092. [4] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part I. Headache. 2016;56(1):71-78. [5] BUTT MF, ALBUSODA A, FARMER AD, et al. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J Anat. 2020;236(4): 588-611. [6] VAN MAANEN MA, VERVOORDELDONK MJ, TAK PP. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: towards innovative treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(4):229-232. [7] DI LASCIO S, FORNASARI D, BENFANTE R. The Human-Restricted Isoform of the α7nAChR, CHRFAM7A: A Double-Edged Sword in Neurological and Inflammatory Disorders . Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7): 3463. [8] Winick-Ng W, Caetano FA, Winick-Ng J, et al. 82-kDa choline acetyltransferase and SATB1 localize to β-amyloid induced matrix attachment regions. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1-17. [9] 王东岩,杨海永,董旭,等.针刺调控 α7nAchR 激活胆碱能抗炎通路的研究现状[J].上海针灸杂志,2020,39(1):116-122. [10] 殷勤,吴义金.基于胆碱能抗炎通路对炎症治疗及其相关信号机制研究[J].中国药物经济学,2020,15(7):119-123. [11] 樊文香,张锦璐,徐驰.α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在中枢神经系统性疾病中作用的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2021,26(9): 1065-1072. [12] 秦雨涵,侯宏卫,胡清源.α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在胆碱能抗炎通路中的作用机制及应用现状[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2022,38(10):1304-1310. [13] EBERHARDSON M, TARNAWSKI L, CENTA M, et al. Neural control of inflammation: bioelectronic medicine in treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020;10(3): a034181. [14] LI T, ZUO X, ZHOU Y, et al. The vagus nerve and nicotinic receptors involve inhibition of HMGB1 release and early pro-inflammatory cytokines function in collagen-induced arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 2010; 30(2):213-220. [15] RASMUSSEN SE, PFEIFFER-JENSEN M, DREWES AM, et al. Vagal influences in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(1):1-11. [16] LI Z, HAO H, GAO Y, et al. Expression and localization analyses of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and α7nAchR in different tissues of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Histochem. 2019;121(6):742-749. [17] SEYEDABADI M, RAHIMIAN R, GHIA JE. The role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in inflammatory bowel disease: involvement of different cellular pathways. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(2):161-176. [18] 张艳艳,刘伟,张超,等.基于胆碱能抗炎通路的类风湿关节炎治疗机制与中医药作用机制研究进展 [J].山东中医杂志,2018,37(12): 1038-1040. [19] IMAMURA M, MUKAINO A, TAKAMATSU K, et al. Ganglionic acetylcholine receptor antibodies and autonomic dysfunction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1332. [20] MURRAY K, REARDON C. The cholinergic anti‐inflammatory pathway revisited. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30(3):10.1111/nmo.13288. [21] FERREIRA-VIEIRA TH, GUIMARAES IM, SILVA FR, et al. Alzheimer’s disease: targeting the cholinergic system. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016; 14(1):101-115. [22] HAJIASGHARZADEH K, KHABBAZI A, MOKHTARZADEH A, et al. Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and connective tissue diseases. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29(4):975-986. [23] 项水英,丛文娟,刘自兵.胆碱能抗炎通路及其在中医药抗炎效应中的研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2018,20(2):140-143. [24] PRESCOTT SL, LIBERLES SD. Internal senses of the vagus nerve Neuron. 2022;110(4):579-599. [25] BUTT MF, ALBUSODA A, FARMER AD, et al. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J Anat. 2020;236(4): 588-611. [26] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part I. Headache. 2016;56(1):71-78. [27] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part II. Headache. 2016;56(2):259-266. [28] CHAVAN SS, TRACEY KJ. Essential neuroscience in immunology. J Immunol. 2017;198(9):3389-3397. [29] COURTIES A, BERENBAUM F, SELLAM J. Vagus nerve stimulation in musculoskeletal diseases. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88(3):105149. [30] LEVINE YA, FALTYS M, CHERNOFF D. Harnessing the inflammatory reflex for the treatment of inflammation-mediated diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020;10(1):a034330. [31] HOOVER DB. Cholinergic modulation of the immune system presents new approaches for treating inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 179:1-16. [32] VALENTINE G, SOFUOGLU M. Cognitive effects of nicotine: recent progress. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(4):403-414. [33] CHEUNG TT, MCINNES IB. Future therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(4):487-500. [34] KOOPMAN FA, STOOF SP, STRAUB RH, et al. Restoring the balance of the autonomic nervous system as an innovative approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol med. 2011;17(9):937-948. [35] 张胜凯,李红兵,张程,等.胆碱能系统对脓毒症炎症与免疫调控机制的研究进展[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2021,29(10):132-140. [36] WU Y, WANG L, JI C, et al. The role of α7nAChR-mediated cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in immune cells. Inflammation. 2021;44(3): 821-834. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [7] | Liu Ying, Liu Yalei, Liu Yu. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in adriamycin-induced myocardial injury antagonized with daisy leaf gentianone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4121-4128. |
| [8] | Li Jiale, Luo Dasheng, Zheng Liujie, Liu Wei, Yao Yunfeng. Human osteoarthritic chondrocytes up-regulate the expression of osteoprotegerin in osteoblasts via the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4194-4201. |
| [9] | Yang Qipei, Chen Feng, Cui Wei, Zhang Chi, Wu Ruiqi, Song Zhenheng, Meng Xin. Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4242-4249. |
| [10] | Liu Gang, Zeng Jie, Zhao Yalin, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhang Yaqi, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Shujin Jiannao Prescription alleviates inflammation in the cerebral cortex of rats with hypoxic-ischemic cerebral palsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3674-3679. |
| [11] | Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Han Jiaheng, Liu Jiang, Zhang Yan, Lu Zhencao, Ding Yu. Mechanism by which interleukin-1beta regulates the expression of Semaphorin 3A to induce intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3680-3685. |
| [12] | Wu Ruiqi, Zhou Yi, Xia Tian, Zhang Chi, Yang Qipei, Zhang Xuan, Zhang Yazhong, Cui Wei. Mendelian randomization study on the association between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis and bone mineral density [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3715-3721. |
| [13] | Han Jie, Peng Qinglin, Xu Zhiwei, Wu Yukun, Ren Guowu, Xie Xiaozhong, Jin Wanqing, Yang Ling. Active ingredients of Panax notoginseng regulate signaling pathways related to steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3751-3758. |
| [14] | Wang Xin, Wubulikasimu·Mijiti, Huang Jinyong, Xie Zengru. Regulation of bone tissue cells by tumor necrosis factor-alpha [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3400-3406. |
| [15] | Xiong Wanqi, Li Zhenhao, Cui Yan, Liu Jiahe, Li Chenzhi, Wu Mingjian, Li Yancheng, Yang Fan, Liu Baoyi. Effects of biomechanics on biological characteristics of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3407-3412. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||