Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (26): 4121-4128.doi: 10.12307/2024.346
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening and analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in adriamycin-induced myocardial injury antagonized with daisy leaf gentianone
Liu Ying1, Liu Yalei2, Liu Yu1
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Biology, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 2Experimental Center, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-14Accepted:2023-06-10Online:2024-09-18Published:2023-09-28 -
Contact:Liu Yu, Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Biology, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Liu Ying, Master candidate, Department of Biochemistry and Biology, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81500317 (to LY); Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, H2017423033 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Ying, Liu Yalei, Liu Yu. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in adriamycin-induced myocardial injury antagonized with daisy leaf gentianone[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4121-4128.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
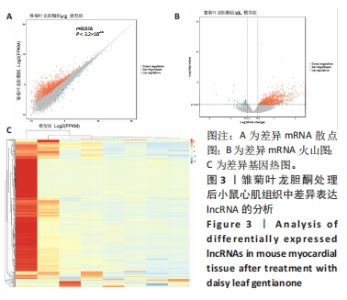
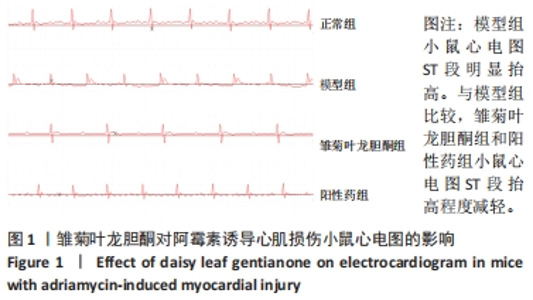
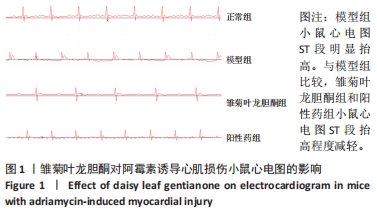
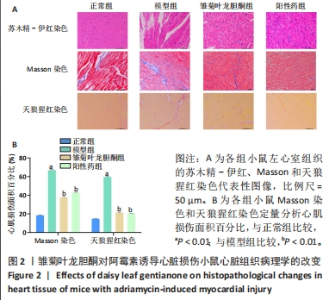
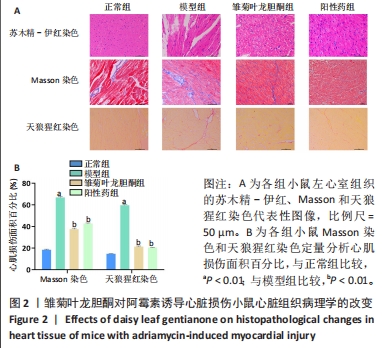
2.2.3 心肌组织Masson染色结果 正常组小鼠心肌组织形态完整、清晰,镜下视野呈紫红色,蓝色的胶原组织少量;与正常组相比,模型组小鼠心肌组织排列紊乱,紫红色心肌组织减少,蓝色胶原纤维增多(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠心肌组织以紫红色心肌细胞为主,蓝色胶原纤维减少(P < 0.05),见图2。证明雏菊叶龙胆酮可改善心肌组织纤维化。 2.2.4 心肌组织天狼星红染色结果 天狼猩红是一种阴离子强酸染料,容易与胶原纤维中的碱性基团发生反应,因此,苦酸狼猩红染料溶液可以使胶原纤维特异性染成猩红色,而非胶原纤维部分看不到猩红色背景。正常组小鼠心肌组织可见少量猩红色胶原组织;与正常组相比,模型组小鼠心肌组织排列紊乱,猩红色胶原纤维增加(P < 0.05);与模型组小鼠相比,雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠心肌组织猩红色胶原纤维减少(P < 0.05),见图2。证明雏菊叶龙胆酮可改善阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌组织纤维化。 以上结果显示,雏菊叶龙胆酮可显著改善阿霉素诱导心肌损伤小鼠的心功能。 2.3 雏菊叶龙胆酮处理后小鼠心肌组织中差异表达 lncRNA的筛选 通过高通量测序分析,识别雏菊叶龙胆酮组与模型组小鼠心肌组织中差异表达的 lncRNA,见图3。以差异倍数> 2.0为筛选条件,与模型组相比,雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠心肌组织识别出差异表达基因共408个,其中表达上调的基因有385个,表达下调的基因有23个;其中表达上调9倍以上的基因有7个,分别为Foxa1、Foxj1、Cyp2a5、Krt15、Scnn1b、Muc5b、Reg3g;表达下调2倍以上的lncRNA有5个,分别是Gm49320、Gm45717、Gm17021、Gm20634、Cd207。"
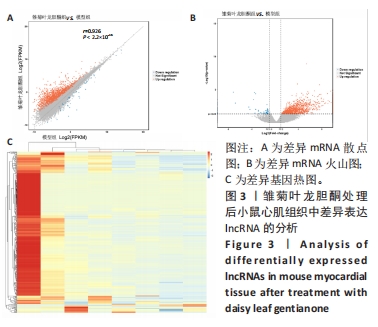
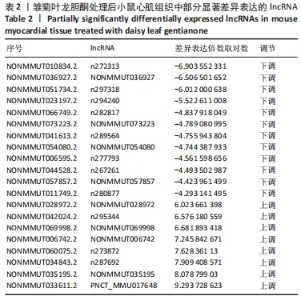
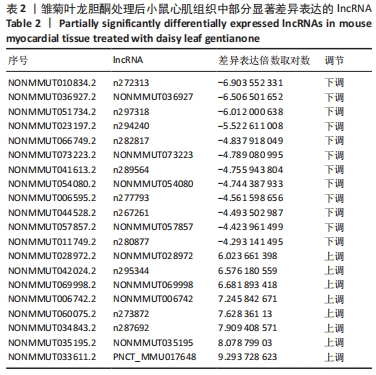
与模型组相比,雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠心肌组织识别出差异表达的lncRNA共270个,其中表达上调的lncRNA有165个,表达下调的lncRNA有105个;表达上调7倍以上的lncRNA有9个,分别为NONMMUT014305、n268869、NONMMUT002554、Sfta3-ps、Gm43085、Gm47720、n297229、ensembl、n270971;表达下调5倍以上的lncRNA有11个,分别是n295844、NONMMUT069998、n295344、n288833、n280108、NONMMUT028972、NR_027905、n288679、NONMMUT064356、n279956、NONMMUT066251。表2展示了部分差异表达显著的lncRNA。"
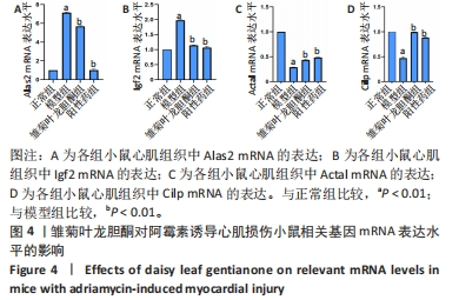
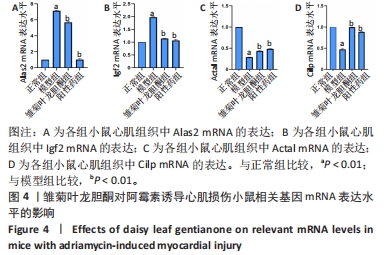
经过分析此部分实验结果并查阅相关文献,最终获得3条LncRNA(NONMMUT149833.1、NONMMUT003237.2、ENSMUST00000219015)及4个相关mRNAs(Alas2、Igf2、Acta1、Cilp)。其中,Alas2、Igf2为上升基因,Acta1、Cilp为下降基因,并通过RT-PCR验证了其表达水平,与预期结果相一致。 2.4 差异表达基因的验证 经过分析差异性大小及查阅相关文献,挑选出3个差异表达的 lncRNAs 和4个mRNAs,通过RT-PCR 验证高通量测序分析结果,与正常组比较,模型组Actal、Cilp mRNA表达下调(P < 0.01),Alas2、Igf2 mRNA表达上调(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,雏菊叶龙胆酮组、阳性药组Alas2、Igf2 mRNA表达下调(P < 0.01),Actal、Cilp mRNA表达上调(P < 0.01)。结果与高通量测序预测的结果相一致,见图4。因此,将所有差异表达的基因均列入后续分析。"
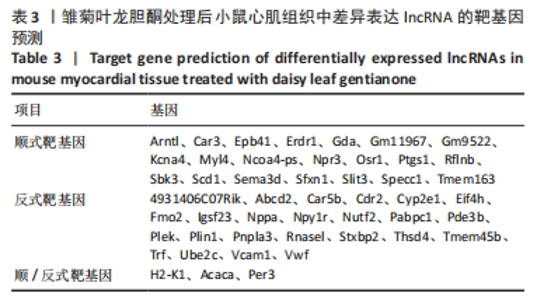
2.5 差异表达显著的 lncRNA 顺式(cis-)作用和反式(trans-)作用的靶基因预测 lncRNA与mRNA的相互作用关系分为顺式(cis-)与反式(trans-),这种与lncRNA发生相互作用关系的mRNA被称为lncRNA的靶基因。cis靶基因预测是寻找基因组上位于lncRNA上下游100 kb范围内的mRNA作为lncRNA的靶基因。trans靶基因预测是基于序列互补配对原则,使用blast比对得到与lncRNA相互补的mRNA,再利用RNAplex软件计算lncRNA与mRNA互补配对后其热动力学参数值,选择软件阈值范围之上的结果作为lncRNA的靶基因。 通过对差异表达明显的lncRNA进行靶基因预测,结果表明49个lncRNAs具有靶基因,其中21个通过顺式(cis-)作用对靶基因进行调控,靶基因分别是Arntl、Car3、Kcna4、Rflnb、Scd1和Tmem163等;24个是通过反式(trans-)作用来对靶基因进行调控,靶基因分别是 Abcd2、Cyp2e1、Igsf23、Pabpc1、Rnasel和Vcam1等;另3个可同时通过顺式和反式两种作用方式来对靶基因进行调控,靶基因分别为H2-K1、Acaca和Per3,见表3。"
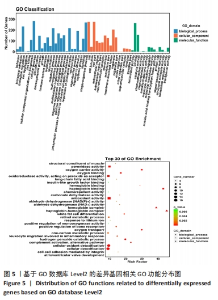
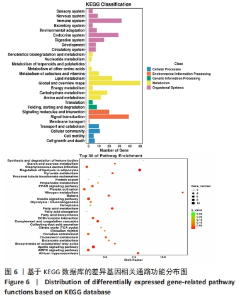
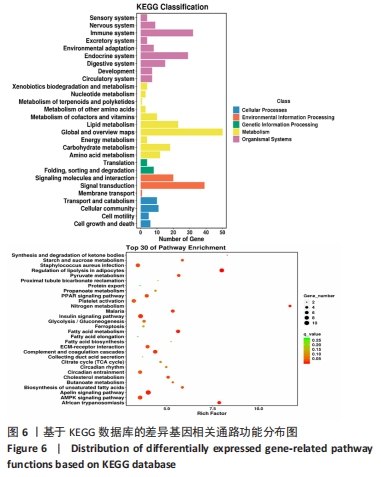
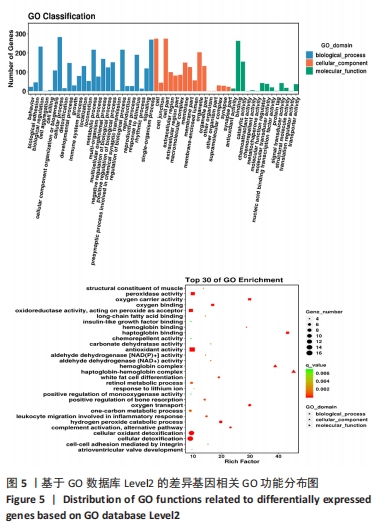
2.6 GO富集与KEGG信号通路分析 为了明晰基因在体内或细胞中行使的生物学功能及参与的信号通路等,对每一个基因进行基于GO及KEGG数据库的注释[12-13]。在总体上,此次研究倾向于差异基因往往集中行使某些生物学功能或在某些信号通路中表现活跃,从而使得生物体呈现出区别于他体的表型。使用基于GO和KEGG数据库的差异基因富集分析就是为了找出差异基因主要相关的生物学功能及信号通路。从细胞组成、生物过程和分子功能3个方面对差异表达lncRNA预测的靶基因进行GO富集分析。 通过对差异表达显著 lncRNA 的靶基因从细胞成分、生物学过程和分子功能3个方面进行GO富集分析,结果显示:GO富集的细胞成分主要为细胞器部分、膜部分、细胞外区域部分、细胞连接、大分子复合物及突触部分等,生物学过程主要为代谢过程、免疫防御过程、参与突触前的化学传递过程、生物过程的正向调节、对刺激的反应及多细胞生物过程等,分子功能主要为催化活性、信号传感器活动、分子功能调节剂、转录因子活性、抗氧化活性、化学诱导活性及分子伴侣等,见图5。"
| [1] SIMONA GG, JOSEPH D, JOHANNES H, et al. European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) 2022 Guidance Paper for Carcinoid Syndrome and Carcinoid Heart Disease. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022;34(7):e13146. [2] CARRIE L, DAVID H, SLINDSEY D, et al.Current Practice in Carcinoid Heart Disease and Burgeoning Opportunities. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022;23(12):1793-1803. [3] BASNET P, KADOTA S, SHIMIZU M, et al. Bellidifolin:apotent hypoglycemic agent in streptozotocin(STZ)-induced diabetic rats from Swertia japonica. Planta Med. 1994;60(6):507-511. [4] DIJANA KM, NEVENA B, TEODORA J, et al. Gentianella lutescens subsp. carpatica J. Holub.: Shoot propagation in vitro and effect of sucrose and elicitors on xanthones production. Plants (Basel). 2021;10(8):1651. [5] URBAIN A, MARSTON A, GRILO LS, et al. Xanthones from Gentianella amarella ssp. acuta with acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities. J Nat Prod. 2008;71(5):895-897. [6] LI Y, LUO YL, LI CH, et al. Bellidifolin Inhibits Proliferation of A549 Cells by Regulating STAT3/COX-2 Expression and Protein Activity. J Oncol. 2020;2020: 1723791. [7] ZHAO ZY, GAO YY, GAO L, et al. Protective effects of bellidifolin in hypoxia-induced in pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) and underlying mechanisms. Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017;80(22):1187-1192. [8] REN K, GONG X, ZHANG RF, et al. Protective effect of bellidifolin on H2O2- induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte injury. J Med Pharm Chin Minor. 2020;26:31-35. [9] LI SQ, HUANG CY, LI X, et al. Bellidifolin from Gentianella acuta (Michx.) Hulten protects H9c2 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury via the PI3K-Akt signal pathway. Toxicol Rep. 2022;9:1655-1665. [10] GAO F, CHEN ZY, ZHOU L, et al. Preparation, characterization and in vitro study of bellidifolin nano-micelles. RSC Adv. 2022;12(34):21982-21989. [11] ALLISON BH, DIMITRIOS T, MYRIAM G, et al. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell. 2022;82(12):2252-2266. [12] KELLY MA, DOUGLAS MA. LncRNAs at the heart of development and disease. Mamm Genome. 2022;33(2):354-365. [13] WANG SX, DUAN J, LIAO JQ, et al. LncRNA H19 inhibits ER stress induced apoptosis and improves diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(16):6809-6828. [14] 赵希坤,闫鹏,陈红娟,等.消退素E1在阿霉素心脏毒性中的保护作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(8):932-934. [15] ANJA K, JAVID M, RUDOLF AB, et al. Cardio-onco-metabolism: metabolic remodelling in cardiovascular disease and cancer. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(6): 414-425. [16] ORLY L, GABRIELA H, KATYA R, et al. Cardiovascular Disease in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2022;4(2):166-182. [17] CAPPETTA D, ROSSI F, PIEGARI E, et al. Doxorubicin targets multiple players:A new view of an old problem. Pharmacol Res. 2018;127:4-14. [18] BANKE A, FOSBØL EL, MØLLER JE, et al.Long-term effect of epirubicin on incidence of heart failure in women with breast cancer:Insight from a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20(10):1447-1453. [19] TEBBI CK, LONDON WB, FRIEDMAN D, et al. Dexrazoxaneassociated risk for acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome and other secondary malignancies in pediatric Hodgkin’s disease. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(5):493-500. [20] 武海军,李旻辉,张海涛,等.Bellidifolin对麻醉大鼠心电图的影响[J].包头医学院学报,2011,27(1):22. [21] 任凯,龚雪,张瑞芬,等.蒙药尖叶假龙胆中雏菊叶龙胆酮对H2O2诱导H9c2细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J].中国民族医药杂志,2020,26(2):31-35. [22] 吴江立,贾玉涛,田雨卿,等.雏菊叶龙胆酮通过调节Nrf2/HO-1和caspase-3 通路减轻阿霉素诱导的H9c2心肌细胞损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2023,39(1):103-109. [23] PAPAIT R, KUNDERFRANCO P, STIRPARO GG, et al. Long noncoding RNA: a new player of heart failure? J Cardiovasc Transl Res Dec. 2013;6(6):876-883. [24] YANG G, LU X, YUAN L. LncRNA: a link between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(11):1097-1109. [25] MARYAM K, BAHRAM MS, MOHAMED N, et al. The conserved long non-coding RNA CARMA regulates cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cardiovasc Res. 2022; 118(10):2339-2353. [26] MILAD AF, NAVID R, ALAN PK, et al. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in pancreatic cancer progression. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27(8):2181-2198. [27] HUANG ZY, WANG ZS, XIA HM, et al. Long noncoding RNA HAND2-AS1: A crucial regulator of malignancy. Clin Chim Acta. 2023;539:162-169. [28] SUN ZP, TAN ZG, PENG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01419 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy by mediating miR-485-5p/LSM4 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022;38(9):826-838. [29] JING DH, ZHU FQ, XU Z, et al. The role of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) in immune diseases. Transpl Immunol. 2022;75:101716. [30] LIU YQ, CHENG X, LI HL, et al.Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Regulators of Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:908076. [31] DENISE B, REINIER AB, RIO PJ, et al. The multifaceted actions of the lncRNA H19 in cardiovascular biology and diseases. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136(15):1157-1178. [32] FAN H, SHAO H, GAO XY, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTTIP is Elevated in Patients with Sepsis and Promotes Cardiac Dysfunction. Immunol Invest. 2022; 51(7):2086-2096. [33] GONG Y, ZHONG Q, XIA YF, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 sponges miR-30c to promote the calcification of human vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating Runx2. Ren Fail. 2023;45(1):2204953. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [3] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [7] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [8] | Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin. SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4447-4454. |
| [9] | Zhai Sheng, Aikeremujiang • Aerken, Zhang Zheng, Rixiati • Paerhati, Hao Feihu. CircCDR1as/miR-7-5p/RAF1 axis promotes autophagy levels in steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4455-4460. |
| [10] | Tian Yong, Zhou Ying, Gu Yongxiang, Yang Guohui. Metformin pretreatment induces cardiac autophagy to reduce myocardial injury in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4469-4476. |
| [11] | Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497. |
| [12] | Li Shudong, Liang Xuezhen, Luo Di, Li Jiacheng, Yan Bozhao, Li Gang. Identification of biomarkers associated with ferroptosis and pyroptosis for the potential diagnosis of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4511-4515. |
| [13] | Zhang Tiandong, Peng Qingping, Liu Huan, Feng Jianguo, Yi Qian, Huang Wenhua. Semen cuscutae in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4516-4521. |
| [14] | Liu Jing, Liang Fangyuan, Li Jia, Wang Hua. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea based on proteomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4129-4136. |
| [15] | Li Jiale, Luo Dasheng, Zheng Liujie, Liu Wei, Yao Yunfeng. Human osteoarthritic chondrocytes up-regulate the expression of osteoprotegerin in osteoblasts via the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4194-4201. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||