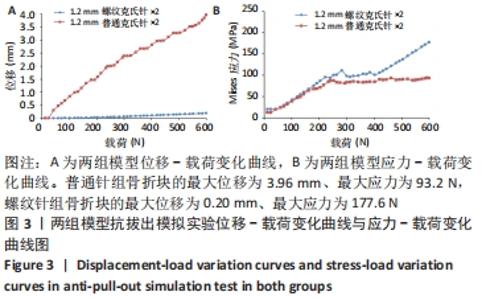
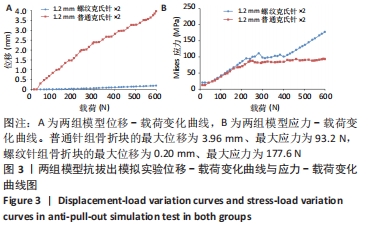
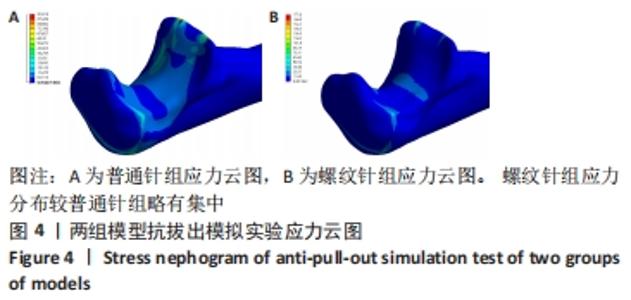
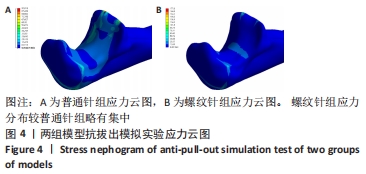
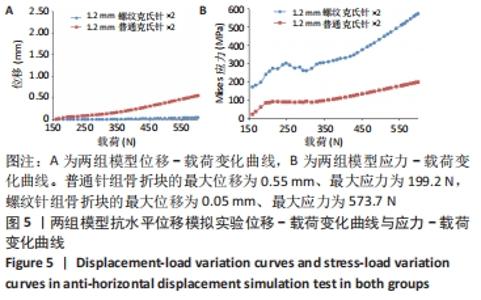
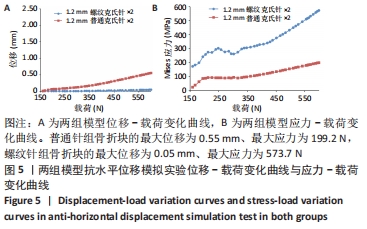
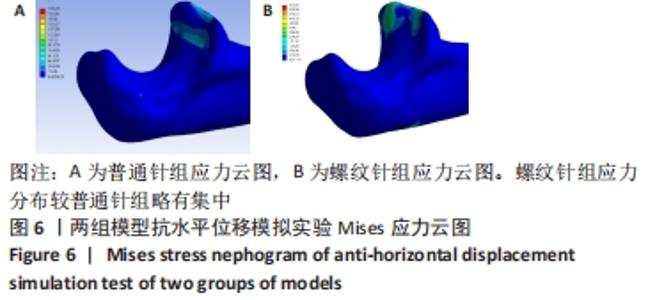
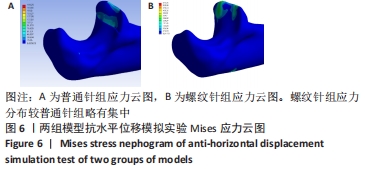
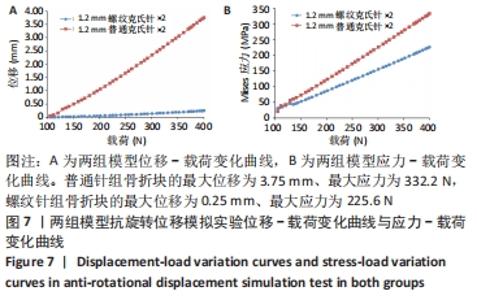
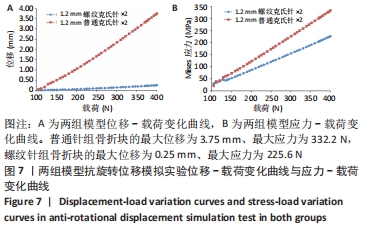
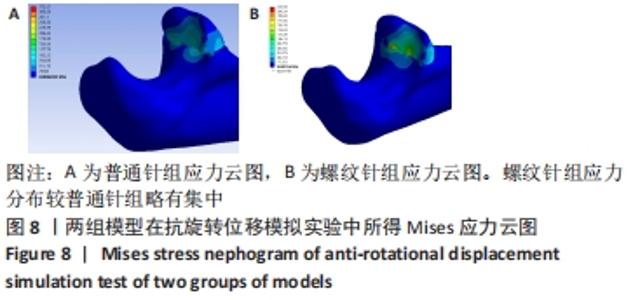
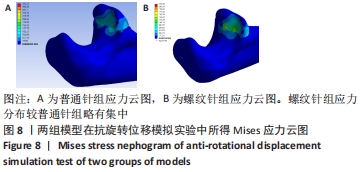
[1] ZHAO S, ZENG C, YUAN S, et al. Reconstruction of coronoid process of the ulna: a literature review. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(4):1-10.
[2] NI Q, YANG X, PAN Z, et al. The pronator teres and the flexor carpi radialis interval approach for operative fixation of ulna coronoid process fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(2):102610.
[3] 鲁谊,张海龙,林坤志,等.2.0 mm和2.5 mm直径螺钉固定钛合金尺骨冠突假体稳定性的有限元分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(1): 46-51.
[4] LOR KK, TOON DH, WEE AT. Buttress plate fixation of coronoid process fractures via a medial approach. Chin J Traumatol. 2019;22(5).255-260.
[5] GRAF DN, FRITZ B, BOUAICHA S, et al. Elbow Instability. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2021;25(4):574-579.
[6] RING D, HORST TA. Coronoid Fractures. Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(10): 437-440.
[7] 王烨明,刘俊阳,田旭,等.锁定钢板治疗尺骨冠状突骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2017,33(1):6-9.
[8] LEE SH, LIM KH, KIM JW. Case Series of All-Arthroscopic Treatment for Terrible Triad of the Elbow: Indications and Clinical Outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(2):431-440.
[9] THAYER MK, SWENSON AK, HACKETT DJ, et al. Classifications in Brief: Regan-Morrey Classification of Coronoid Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(7):1540-1543.
[10] 陈金,王光勇,周廷玉,等.肘前入路经尺骨隧道“T”形钛板钢丝内固定治疗O’DriscollⅡ、Ⅲ型尺骨冠状突骨折[J].中华创伤杂志, 2020,36(7):643-646.
[11] 葛建华,阳运康,魏代清,等.自制袢钢板治疗尺骨冠状突骨折的初步临床应用[J].中华手外科杂志,2017,33(1):10-11.
[12] ZHAO S, ZENG C, YUAN S, et al. Reconstruction of coronoid process of the ulna: a literature review. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(4):1-10.
[13] 姜健.改良螺纹克氏针治疗尺骨冠突骨折的三维有限元分析[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2019.
[14] 吴国林,陈红卫,季向荣,等.尺骨冠状突骨折治疗的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(10):957-960.
[15] 王鹏飞,庄岩,魏教,等.袢钢板治疗Regan-Morry I型冠状突骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(4):277-281.
[16] CHEN HW, TENG XF. A comparative study on the validity and reliability of anterior, medial, and posterior approaches for internal fixation in the repair of fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. Eur J Med Res. 2018;23(1):40.
[17] CHEN HW, HE HH, GAO BL. Efficacy of internal fixation with mini plate and internal fixation with hollow screw for Regan-Morrey type II and III ulna coronoid fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):194.
[18] FENG D, ZHANG X, JIANG Y, et al. Plate fixation through an anterior approach for coronoid process fractures: A retrospective case series and a literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(36):e12041.
[19] RAUSCH V, HACKL M, SEYBOLD D, et al. Plate osteosynthesis of the coronoid process of the ulna. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2020;32(1):35-46.
[20] GIANNICOLA G, POLIMANTI D, GUMINA S, et al. Use of fine-threaded K-wires in the treatment of coronoid fractures in complex elbow instability. Orthopedics. 2013;36(10):e1233-1238.
[21] CHEN HW, TENG XF. A comparative study on the validity and reliability of anterior, medial, and posterior approaches for internal fxation in the repair of fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. Eur J Med Res. 2018;23(1):40.
[22] WANG G, ZHANG L, ZHANG Y. Treatment of ulnar coronoid process fracture via a modified anteromedial approach. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(7):826-830.
[23] YANG X, CHANG W, CHEN W, et al. A novel anterior approach for the fixation of ulnar coronoid process fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(6):899-904.
[24] JUNG HS, JANG YH, LEE HI, et al. comparison of the over-the-top and flexor carpi ulnaris split approaches for the treatment of anteromedial facet fracture of the coronoid process. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021; 30(8):1750-1758.
[25] SHEN JJ, QIU QM, GAO YB, et al. Direct anterior approach for mini plate fixation of Regan-Morrey type II comminuted ulnar coronoid process fracture. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(1):2309499018825223.
[26] 赵宝成,袁天祥,马信龙,等.肘前侧入路治疗尺骨冠突骨折的解剖与临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(8):859-864.
[27] 王俊,刘好源,叶志扬,等.肘关节镜辅助下治疗尺骨冠突骨折的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(12):1132-1136.
[28] 覃芙,王剑青,鲍昌珅,等.改良肘关节前内侧入路微型钢板治疗尺骨冠状突骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2019(2):90-92.
[29] ARRIGONI P, CUCCHI D, GUERRA E, et al. No neurovascular damage after creation of an accessory anteromedial portal for arthroscopic reduction and fixation of coronoid fractures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(1):314-318.
[30] 吴光宇,陈林,贺世雄,等.改良前侧入路手术治疗O’Driscoll Ⅱ型尺骨冠状突骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019, 34(7):760-761.
[31] COWAL LS, PASTOR RF. Dimensional variation in the proximal ulna: evaluation of a metric method for sex assessment. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2008;135(4):469-478.
[32] 敖荣广,禹宝庆,苑双洪.尺骨近端的临床解剖学研究进展[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2016,4(4):251-254.
[33] 董新利,孙强,刘晗,等.克氏针治疗尺骨冠突骨折的基础研究[J].当代医学,2020,26(8):32-34.
|