[1] CHEN X, SANDHU HS, VARGAS CASTILLO J, et al. The association between pain scores and disc height change following discectomy surgery in lumbar disc herniation patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(11):3265-3277.
[2] ROBERTO VL, NEVES VE, SUÁREZ HJE, et al. Hérnia discal lombar. Rev Bras Ortop. 2010;45(1):17-22.
[3] DI GIAMPAOLO L, CANO E, MISTICONI GF, et al. Lumbar discopathies: correlation between pathology, work eligibility and recognition of technopathy. G Ital Med Lav Ergon. 2021;43(2):118-125.
[4] AMIN RM, ANDRADE NS, NEUMAN BJ. Lumbar Disc Herniation. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(4):507-516.
[5] BENZAKOUR T, IGOUMENOU V, MAVROGENIS AF, et al. Current concepts for lumbar disc herniation. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):841-851.
[6] 李建华, 朱清广, 房敏,等. 脊柱微调手法联合导引功法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床观察[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(2):999-1001.
[7] 陈志伟, 张钰敏, 占超,等. 脊柱微调手法结合四维牵引调曲治疗腰椎间盘突出症100例[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(2):358-359.
[8] 李民, 董竑麟, 汪桂珍,等. 有限元分析不同牵伸时长相邻腰椎节段和椎间盘应力及位移的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(21):3281-3286.
[9] ZHONG ZC, WEI SH, WANG JP, et al., Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(1):90-98.
[10] MO ZJ, ZHAO YB, WANG LZ, et al. Biomechanical effects of cervical arthroplasty with U-shaped disc implant on segmental range of motion and loading of surrounding soft tissue. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(3):613-621.
[11] DU HG, LIAO SH, JIANG Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of press-extension technique on degenerative lumbar with disc herniation and staggered facet joint. Saudi Pharm J. 2016;24(3):305-311.
[12] 黄学成, 叶林强, 梁德,等. 三维有限元模型分析旋转手法中旋转方向对颈椎间盘位移和椎间孔容积的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(3):404-408.
[13] LEE SH, IM YJ, KIM KT, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed- and mobile-core artificial disc replacement: a finite element analysis. Spine. 2011;36(9):700-708.
[14] MO Z, ZHAO Y, DU C, et al. Does location of rotation center in artificial disc affect cervical biomechanics? Spine. 2015;40(8):E469-E475.
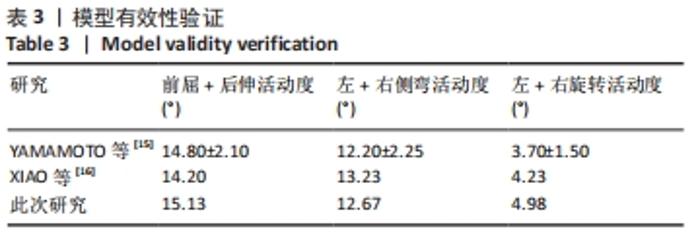
[15] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[16] XIAO Z, WANG L, GONG H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three surgical scenarios of posterior lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2012;11:31.
[17] 徐海涛,李松,刘澜,等.腰椎斜扳手法时椎间盘的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2335-2338.
[18] 赵文韬, 向俊宜, 李具宝. 不同牵引力对腰椎间盘突出症生物力学效应的三维有限元分析[J]. 山西医药杂志,2018,47(24):2907-2909.
[19] HARRIS A, WILKENING M, MARRACHE M, et al. Adult Lumbar Disk Herniation: Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications, Outcomes, and Evidence-Based Data for Patient and Health Professional Counseling. Instr Course Lect. 2020;69:607-624.
[20] CHENG ZX, ZHENG YJ, FENG ZY, et al. Chinese Association for the Study of Pain: Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment for lumbar disc herniation. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(9):2058-2067.
[21] 钟士元. 脊柱相关疾病治疗学[M]. 3 版. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2011.
[22] 苟亚博, 黄国松. 脊椎手疗法图解[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2009.
[23] 沈国权.脊柱推拿的理论与实践——脊柱微调手法体系[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2016:723
[24] XIE Y, WANG X, JIAN Q, et al. Three dimensional finite element analysis used to study the influence of the stress and strain of the operative and adjacent segments through different foraminnoplasty technique in the PELD: Study protocol clinical trial (SPIRIT Compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99(15):e19670.
[25] CAO S, CHEN Y, ZHANG F, et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of “Three-Dimensional Balanced Manipulation” in the Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy by Finite Element Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5563296.
[26] BERRA LV, DI RITA A, LONGHITANO F, et al. Far lateral lumbar disc herniation part 1: Imaging, neurophysiology and clinical features. World J Orthop. 2021; 12(12):961-969.
[27] TAKAMATSU N, YAMASHITA K, SUGIURA K, et al. Successful Full Endoscopic Surgery for L5 Radiculopathy Due to L4-5 Discal Cyst and Disc Herniation in a Professional Baseball Player. NMC Case Rep J. 2021;8(1):189-194.
[28] FG A, HS B, SA A, et al. Internal load-sharing in the human passive lumbar spine: Review of in vitro and finite element model studies-Science Direct. J Biomech. 2020;102:109441.
|