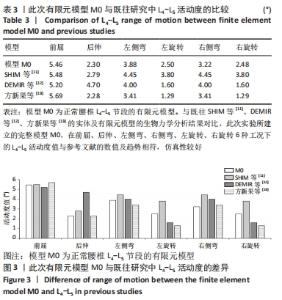
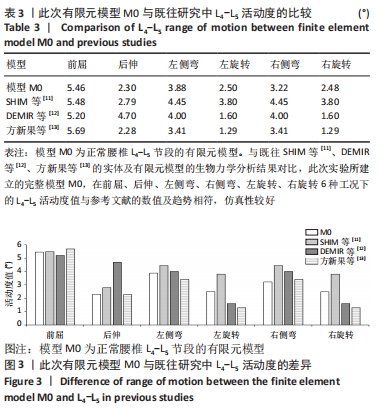
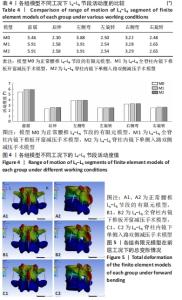
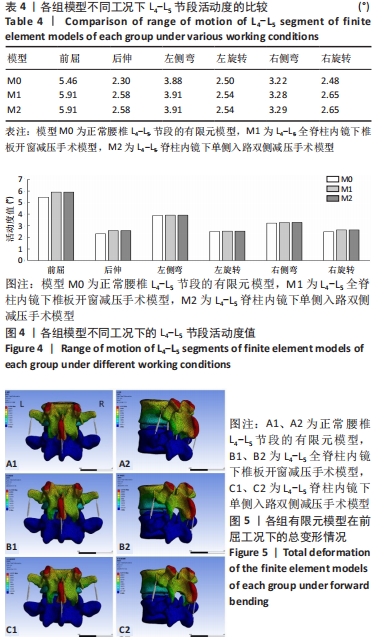
[1] 李子全,余可谊,王以朋,等.经皮椎间孔入路脊柱内镜下单侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症临床疗效及非手术侧下肢症状观察研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(7):831-836.
[2] LURIE J, TOMKINS-LANE C. Management of lumbar spinal stenosis. BMJ. 2016;352:h6234-6234.
[3] 丁宇,张建军,卢正操,等.腰椎管狭窄症后路内镜减压手术策略研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2021,14(4):285-291.
[4] SIEPE CJ, SAUER D, MICHAEL MAYER H. Full endoscopic, bilateral over-the-top decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(S4):563-565.
[5] 李翔,司建炜.脊柱结核病灶清除术中单节段短椎弓根钉固定的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4552-4557.
[6] ZHAO X B, MA H J, GENG B, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic unilateral laminotomy and bilateral decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):641-650.
[7] 肖广润,杨建东,林升元,等.有限元分析在脊柱外科中的应用及研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2020,41(6):347-351.
[8] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104-110.
[9] SHI Y, XIE Y, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593-605.
[10] 代云磊,魏亚,吴昌兵,等.有限元模拟脊柱内镜下椎间孔成形对腰椎生物力学的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(1): 127-132.
[11] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine. 2008;33(22):E820-E827.
[12] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al. Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420.
[13] 方新果,赵改平,王晨曦,等.基于CT图像腰椎L4~L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2014,33(4):487-492.
[14] 王坤,梅伟.腰椎管狭窄症的治疗进展[J].骨科,2019,10(3):248-252.
[15] 巴根,贾长青,梁峰,等.老年退变性腰椎管狭窄症的个体化手术治疗及临床疗效观察[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2015,34(1):22-26.
[16] ARMIN SS, HOLLY LT, KHOO LT. Minimally invasive decompression for lumbar stenosis and disc herniation. Neurosurg Focus. 2008;25(2): E11-E14.
[17] MCGRATH LB, WHITE-DZURO GA, HOFSTETTER CP. Comparison of clinical outcomes following minimally invasive or lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;30(4):491-499.
[18] JIANG Q, DING Y, LU Z, et al. Comparative analysis of non-full and full endoscopic spine technique via interlaminar approach for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: A retrospective, single institute, propensity score-matched study. Global Spine J. 2021;21925682211039181. doi: 10.1177/21925682211039181.
[19] YOSHIKANE K, KIKUCHI K, OKAZAKI K. Clinical outcomes of selective single-level lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis and risk factors of reoperation. Global Spine. 2021;21925682211033575. doi: 10.1177/21925682211033575.
[20] 黄开,杨金华.单侧入路双侧减压术和全椎板切除减压术治疗腰椎管狭窄症的临床疗效[J].江苏医药,2016,42(14):1576-1578.
[21] O’LEARY SA, PASCHOS NK, LINK JM, et al. Facet joints of the spine: structure-function relationships, problems and treatments, and the potential for regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;20:145-170.
[22] KIM H, CHOI S, SHIM D, et al. Advantages of new endoscopic unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression (ULBD) over conventional microscopic ULBD. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):330-336.
[23] 陈小龙,海涌,关立,等.有限元分析在腰椎人工椎间盘生物力学研究中的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(4):327-331.
[24] 蒋强,丁宇,刘金玉,等.有限元模拟全内镜下精准椎板开窗减压术及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1891-1896.
|