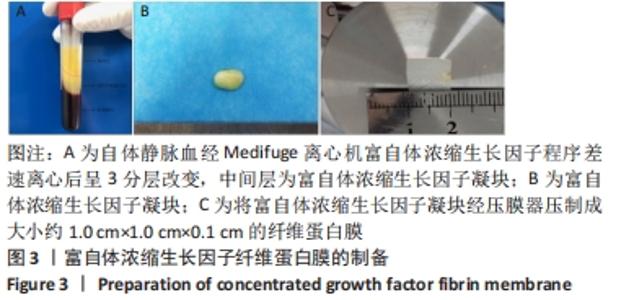
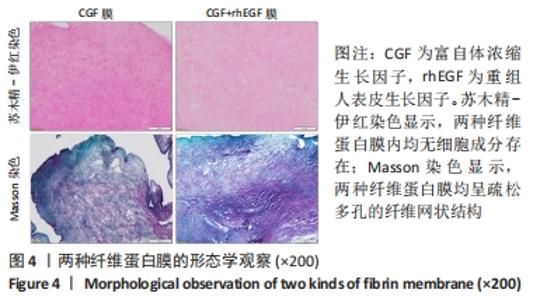
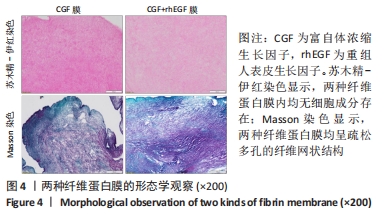
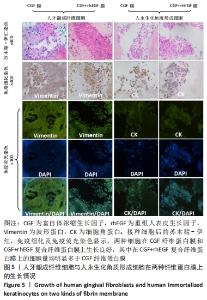
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1848-1855.doi: 10.12307/2023.101
Previous Articles Next Articles
Repairing equivalent injury of oral mucosa with concentrated growth factor fibrin membrane combined with recombinant human epidermal growth factor active protein polypeptide complex
He Ruya1, 2, Liu Yunling1, 2, Nie Minhai1, 2, Liu Xuqian1, 2
- 1Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-09-07Accepted:2021-10-28Online:2023-04-28Published:2022-07-30 -
Contact:Liu Xuqian, Associate professor, Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:He Ruya, Master, Physician, Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Planning Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Department, No. 2020YJ0387 (to LXQ); Key Project of Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation between Luzhou Municipal People's Government of Sichuan Province and Southwest Medical University, No. 2019LZXNYDZ10 (to LXQ); Sichuan Provincial Cadre Health Popularization Application Project, No. 2022-2101 (to LXQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Ruya, Liu Yunling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Repairing equivalent injury of oral mucosa with concentrated growth factor fibrin membrane combined with recombinant human epidermal growth factor active protein polypeptide complex[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1848-1855.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

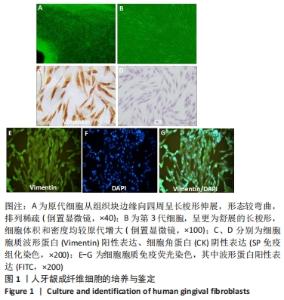
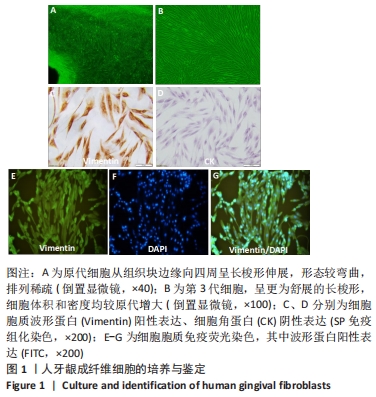
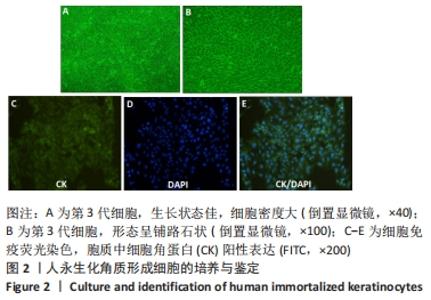
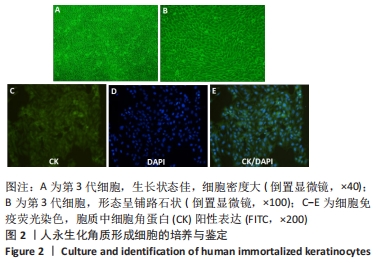
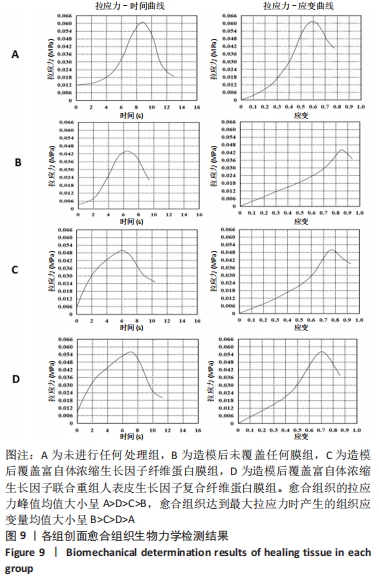
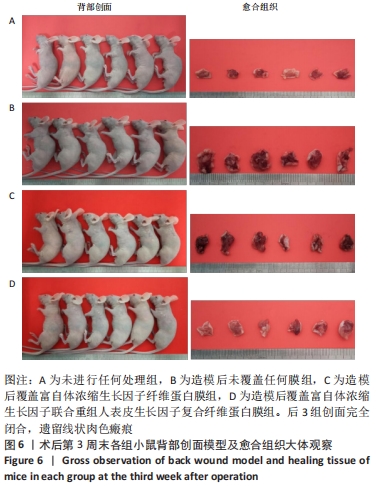
2.3 动物实验结果 2.3.1 实验动物术后情况及创面大体观察情况 术后第2天,各组创面处缝线固定在位,大部分创面周围皮肤稍红,但未见异常分泌物;饮食量及昼夜活动量均较A组少。除A组外,其余3组观察到明显的动物聚集现象,伴精神稍差。术后第7天,部分缝线脱落,脱落部位的创面遗留粉色宽线状未闭合区,4组裸鼠的饮食量及昼夜活动量趋近,精神恢复同术前。术后第14天,大部分缝线已完全脱落,术区皮肤颜色由粉色转变为与周围皮肤颜色接近的淡粉白色,伴局部皮肤轻度皱缩,未闭合区的面积均较前1周缩小,剩余未闭合区面积大小在整体上呈现出B组>C组>D组的规律。术后第21天,缝线均脱落,创面完全闭合,遗留线状肉色瘢痕,见图6。整个实验过程中,各组均未观察到明显的植入物排异反应。"

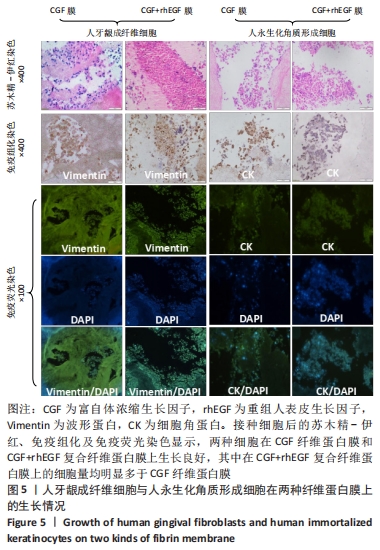
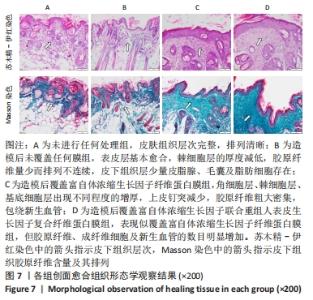
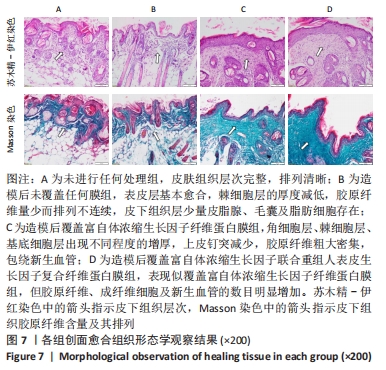
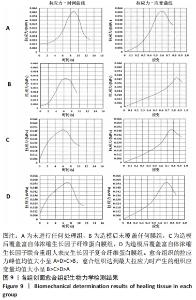
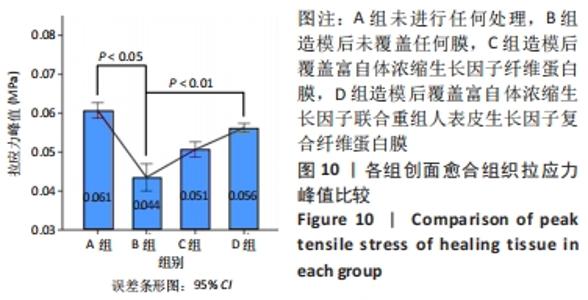
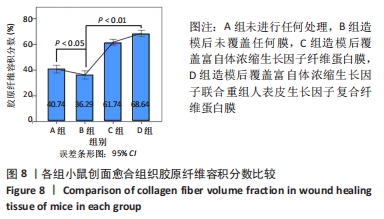
苏木精-伊红染色显示,A组皮肤组织层次完整,基底膜连续,胶原纤维与基底膜紧密相连,不同细胞及皮肤附属器丰富而排列规律;B组表皮层基本愈合,棘细胞层的厚度减低,胶原纤维量少而排列不连续,皮下组织层少量皮脂腺、毛囊及脂肪细胞存在;C组角细胞层、棘细胞层、基底细胞层出现不同程度的增厚,上皮钉突减少,胶原纤维粗大密集,包绕新生血管;D组表现似 C组,但胶原纤维、成纤维细胞及新生血管的数目明显增加。 Masson染色显示,A、B组表皮层细胞及毛囊均呈现透明度较高的红色,胶原纤维呈蓝染状态,皮脂腺腺泡细胞的胞质呈淡粉白色、胞核红染固缩而偏向边缘,血管中的红细胞呈橘黄色;C、D组皮肤附属器明显丧失,大量蓝染胶原纤维排列紧密,仍可见少量橘黄色的血管内红细胞。蓝染的胶原纤维在数量、排列密集程度及连续性等方面呈D组>C组>A组>B组的趋势。A组含皮肤附属器的数量最多,B、D、C组均较A组减少,该3组间差别不明显。 2.3.3 各组创面胶原纤维半定量分析结果 A-D组创面胶原纤维容积分数分别为(40.74±3.61)%,(36.29±3.82)%,(61.74±2.66)%,(68.64±2.81)%,见图8。 "
| [1] MATICHESCU A, ARDELEAN LC, RUSU LC, et al. Advanced Biomaterials and Techniques for Oral Tissue Engineering and Regeneration-A Review. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(22):5303. [2] LI W, WANG F, DONG F, et al. CGF Membrane Promotes Periodontal Tissue Regeneration Mediated by hUCMSCs through Upregulating TAZ and Osteogenic Differentiation Genes. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021: 6644366. [3] XU F, QIAO L, ZHAO Y, et al. The potential application of concentrated growth factor in pulp regeneration: an in vitro and in vivo study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):134. [4] WANG F, SUN Y, HE D, et al. Effect of Concentrated Growth Factors on the Repair of the Goat Temporomandibular Joint. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(3):498-507. [5] BOZKURT DOGAN S, ONGOZ DEDE F, BALL U, et al. Concentrated growth factor in the treatment of adjacent multiple gingival recessions: a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42: 868-875. [6] BEN AMARA H, THOMA DS, SCHWARZ F, et al. Healing kinetics of oral soft tissue wounds treated with recombinant epidermal growth factor: Translation from a canine model. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(1):105-117 [7] TIAN S, WANG J, DONG F, et al. Concentrated Growth Factor Promotes Dental Pulp Cells Proliferation and Mineralization and Facilitates Recovery of Dental Pulp Tissue. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:10016-10028. [8] 张诗韵,赖光云,汪俊.浓缩生长因子与血凝块诱导根管内组织再生的对比研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2020,40(10):1365-1370. [9] 田巍,田丹,胡芳.rhEGF及清创术对口腔颌面部外伤患者血清EGF及炎症因子水平的影响[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(6):105-108. [10] 奉水华,黄新灵,周忠志.rhEGF凝胶在肌皮瓣修复深度电击烧伤创面中的应用[J].中国美容医学,2020,29(4):83-86. [11] 龚博林,方圆文.浓缩生长因子治疗复发性口腔溃疡的疗效观察[J].中国老年保健医学,2013,11(6):48-49. [12] BOATENG JS, MATTHEWS KH, STEVENS HN, et al. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A review. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(8):2892-2923. [13] CHONG DLW, TRINDER S, LABELLE M, et al. Platelet-derived transforming growth factor-β1 promotes keratinocyte proliferation in cutaneous wound healing. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(4):645-649. [14] 吕丹丹,蒙艳丽,安秋霞,等.表皮生长因子促组织损伤修复的研究进展[J].黑龙江中医药,2016,45(5):78-79. [15] ANDASARI V, LÜ D, SWAT M, et al. Computational model of wound healing: EGF secreted by fibroblasts promotes delayed re-epithelialization of epithelial keratinocytes. Integr Biol (Camb). 2018; 10(10):605-634. [16] 李佳,安恒庆,王峰,等.组织块法与酶消化法培养大鼠毛囊干细胞的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(1):91-95. [17] CHEVALIER C, NICOLAS JF, PETIT AC. Preparation and Delivery of 4-Hydroxy-Tamoxifen for Clonal and Polyclonal Labeling of Cells of the Surface Ectoderm, Skin, and Hair Follicle. Methods Mol Biol. 2014; 1195:239-245. [18] NIKOLOUDAKI G, CREBER K, HAMILTON DW. Wound healing and fibrosis: a contrasting role for periostin in skin and the oral mucosa. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318(6):C1065-C1077. [19] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223. [20] AHANGAR P, MILLS SJ, SMITH LE, et al. Human gingival fibroblast secretome accelerates wound healing through anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic mechanisms. NPJ Regen Med. 2020;5(1):24. [21] WILSON VG. Growth and differentiation of HaCaT keratinocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1195:33-41. [22] ALVI SA, HAMILL CS, LEPSE JP, et al. Outcomes after free tissue transfer for composite oral cavity resections involving skin. Head Neck. 2018; 40(5):973-984. [23] WOLFF KD, RAU A, KOLK A. Perforator flaps from the lower leg for intraoral reconstruction: Experience of 131 flaps. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(2):338-345. [24] ZHOU M, CHEN X, QIU Y, et al. Study of tissue engineered vascularised oral mucosa-like structures based on ACVM-0.25% HLC-I scaffold in vitro and in vivo. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020; 48(1):1167-1177. [25] BETKER JL, ANCHORDOQUY TJ. Assessing the effect of a nude mouse model on nanoparticle-mediated gene delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017;7(1):162-167. [26] ZHANG M, ZHANG T, TANG Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor inhibits UVA-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts via the MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(7):BSR20193566. [27] AMATO B, FARINA MA, CAMPISI S, et al. CGF Treatment of Leg Ulcers: a Randomized Controlled Trial. Open Med (Wars). 2019;14:959-967. [28] TONE T, SHIMIZU Y, SAITO H, et al. In vivo behavior of untreated and compressed concentrated growth factors as biomaterials in rabbits. Dent Mater J. 2021;40(1):8-15. [29] CALABRISO N, STANCA E, ROCHIRA A, et al. Angiogenic Properties of Concentrated Growth Factors (CGFs): The Role of Soluble Factors and Cellular Components. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(5):635. [30] KAMAL A, SALMAN B, RAZAK NHA, et al. A Comparative Clinical Study between Concentrated Growth Factor and Low-Level Laser Therapy in the Management of Dry Socket. Eur J Dent. 2020;14(4):613-620. [31] ZHAO QM, GAO J, HUANG XX, et al. Concentrated Growth Factors Extracted from Blood Plasma Used to Repair Nasal Septal Mucosal Defect After Rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020;44(2):511-516. [32] AKCAN SK, ÜNSAL B. Gingival recession treatment with concentrated growth factor membrane: a comparative clinical trial. J Appl Oral Sci. 2020;28:e20190236. [33] WANG X, WANG G, ZHAO X, et al. Short-Term Evaluation of Guided Bone Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh Membranes and CGF Membranes in Immediate Implantation of Anterior Maxillary Tooth. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:4754078. [34] KABILAMURTHI RS, ABHINAV RP, THIYANESWARAN N, et al. Effectiveness of Concentrated Growth Factor on Surgical Wound Healing: A Pilot Study. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2021;31(3):27-32. [35] LEE HM, SHEN EC, SHEN JT, et al. Tensile strength, growth factor content and proliferation activities for two platelet concentrates of platelet-rich fibrin and concentrated growth factor. J Dent Sci. 2020; 15(2):141-146. [36] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360. [37] SCHULTZ G, ROTATORI DS, CLARK W. EGF and TGF-alpha in wound healing and repair. J Cell Biochem. 1991;45(4):346-352. [38] THROM AM, LIU WC, LOCK CH, et al. Development of a cell-derived matrix: effects of epidermal growth factor in chemically defined culture. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(2):533-541. [39] GARCIA-ORUE I, GAINZA G, GUTIERREZ FB, et al. Novel nanofibrous dressings containing rhEGF and Aloe vera for wound healing applications. Int J Pharm. 2017;523(2):556-566. [40] KAO CC, HUANG SY, CHIANG CH, et al. Microencapsulated rhEGF to facilitate epithelial healing and prevent scar formation of cesarean wound: A randomized controlled trial. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021; 60(3):468-473. [41] YANG Q, ZHANG Y, YIN H, et al. Topical Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 ;62:442-451. [42] ESQUIROL CAUSSA J, HERRERO VILA E. Epidermal growth factor, innovation and safety. Med Clin (Barc). 2015;145(7):305-312. [43] SANTANA H, GARCÍA G, VEGA M, et al. Stability Studies of a Freeze-Dried Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor Formulation for Wound Healing. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2015;69(3):399-416. [44] ESQUIROL-CAUSSA J, HERRERO-VILA E. Human recombinant epidermal growth factor in skin lesions: 77 cases in EPItelizando project. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019;30(1):96-101. [45] SANTANA H, SOTOLONGO J, GONZÁLEZ Y, et al. Stabilization of a recombinant human epidermal growth factor parenteral formulation through freeze-drying. Biologicals. 2014;42(6):322-333. [46] ZHANG L, AI H. Concentrated growth factor promotes proliferation, osteogenic differentiation, and angiogenic potential of rabbit periosteum-derived cells in vitro. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):146. [47] STANCA E, CALABRISO N, GIANNOTTI L, et al. Analysis of CGF Biomolecules, Structure and Cell Population: Characterization of the Stemness Features of CGF Cells and Osteogenic Potential. Int J Mol Sci.2021;22(16):8867. [48] 胡亚暖,姚永明,张泽敏,等.不同浓度EGF对兔ADSCs体外诱导分化为表皮细胞的实验研究[J].中国美容医学,2016,25(7):47-50. [49] WEI S, WANG W, LI L, et al. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor combined with vacuum sealing drainage for wound healing in Bama pigs. Mil Med Res. 2021;8(1):18. |
| [1] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [2] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [3] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [4] | Li Yue, Lyu Yan, Feng Wanying, Song Yang, Yan Yu, Guan Yongge. Preparation of hyperoside nanoparticles to repair endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 360-366. |
| [5] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [6] | Zhan Yi, Wang Biao, Ma Yuli, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun. Biomechanical comparison between a novel bone cement screw system and common surgical methods for the treatment of Kummell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 385-390. |
| [7] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| [8] | . Chinese expert consensus on neurorestorative therapy with cerebrospinal fluid administration (2022) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2780-2788. |
| [9] | Ma Yujiu, Zhang Xudong, Tan Jichun. Application status and prospect of menstrual blood-derived stem cells and their exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2427-2434. |
| [10] | Liu Dongyue, Wang Xianyun, Wang Le, Zheng Mingqi, Yin Yajuan, Yang Jiawei, Ding Lini, Liu Gang. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome transplantation for ischemic heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2435-2442. |
| [11] | Cheng Chunfang, Wan Juan, Ding Kaizhi, Song Jiahao, Tang Shan, Gong Yanchun, Yao Lihua. Regulatory mechanism of myoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2200-2206. |
| [12] | Song Kunxiu, Wang Limin, Ma Rongxing, Hu Yongcheng. Application of patent literature in the study of allogenic demineralized bone matrix [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2229-2233. |
| [13] | Zhou Yingying, Zhang Xuehui. Calcined antler cancellous bone/collagen composite scaffolds promote bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1938-1943. |
| [14] | Li Xiaoxue, Hou Xiaowei. Finite element analysis of maxillary defect reconstruction based on polyetheretherketone meshes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1805-1810. |
| [15] | Li Ying, Chen Yingxin, Gao Minghong. Therapeutic efficacy of amniotic membrane transplantation in different stages and degrees of ocular alkali chemical burns [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1772-1779. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||