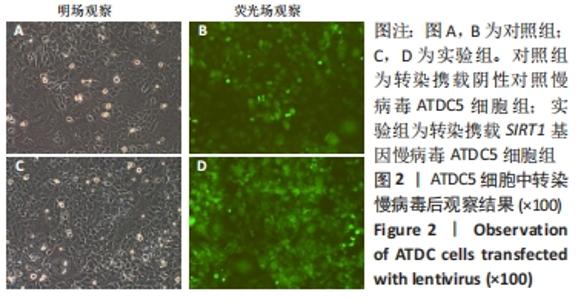
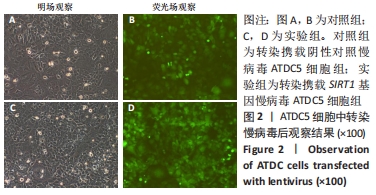
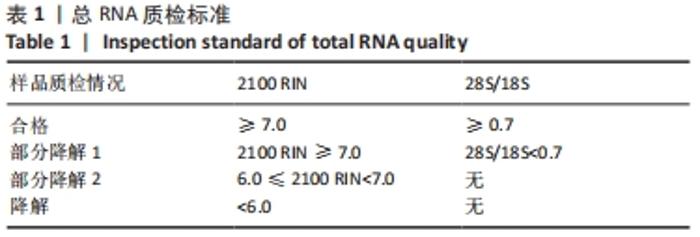
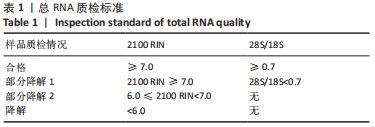
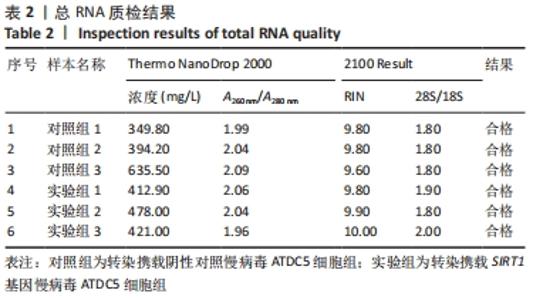
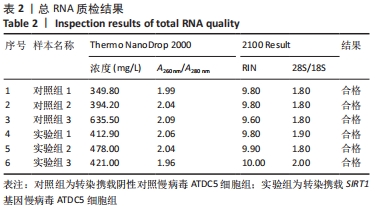
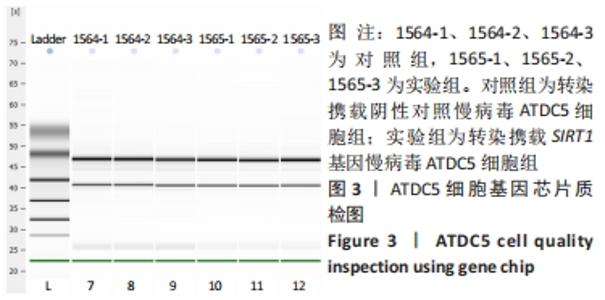
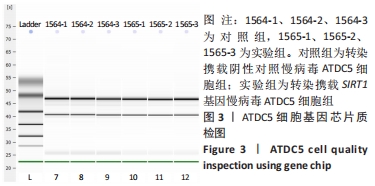
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5112-5118.doi: 10.12307/2022.849
Previous Articles Next Articles
Activation of chondrocyte degeneration related signaling pathways and expression of differential factors in ATDC5 mouse cells after silent information regulator 1 knockdown
Xie Xiaochen1, 2, Yang Qi3, Weng Jian1, 2, Zeng Hui1, 2, Kang Bin1, 2, Liu Pei1, 2, Zhong Huage4, Yu Fei1, 2
- 1Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, 3Department of Medical Ultrasound, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; 2National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; 4Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Guangxi Medical University Affiliated Tumor Hospital, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-08-30Accepted:2021-10-15Online:2022-11-18Published:2022-05-12 -
Contact:Yu Fei, MD, Physician, Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xie Xiaochen, Associate chief physician, Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82102568 (to YF); the Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund of Guangdong Province, Nos. 2021A1515012586 and 2019A1515110983 (both to YF); Bethune · CSPC Osteoporosis Scientific Research Fund Project, No. G-X-2020-1107-21 (to YF); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82102076 (to YQ); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82172432 (to ZH); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund, No. 2019A1515011290 (to ZH); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82001319 (to WJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Xiaochen, Yang Qi, Weng Jian, Zeng Hui, Kang Bin, Liu Pei, Zhong Huage, Yu Fei. Activation of chondrocyte degeneration related signaling pathways and expression of differential factors in ATDC5 mouse cells after silent information regulator 1 knockdown[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5112-5118.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] KRYCH AJ, SARIS DBF, STUART MJ, et al. Cartilage Injury in the Knee: Assessment and Treatment Options. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020; 28(22):914-922. [2] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43. [3] CORYELL PR, DIEKMAN BO, LOESER RF. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):47-57. [4] CHEN DH, ZHENG G, ZHONG XY, et al. Oroxylin A attenuates osteoarthritis progression by dual inhibition of cell inflammation and hypertrophy. Food Funct. 2021;12(1):328-339. [5] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [6] YU H, YAO S, ZHOU C, et al. Morroniside attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritic development by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;266:113447. [7] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249. [8] TSINGAS M, OTTONE OK, HASEEB A, et al. Sox9 deletion causes severe intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by apoptosis, matrix remodeling, and compartment-specific transcriptomic changes. Matrix Biol. 2020;94:110-133. [9] WANG J, ROBERTS S, KUIPER JH, et al. Characterization of regional meniscal cell and chondrocyte phenotypes and chondrogenic differentiation with histological analysis in osteoarthritic donor-matched tissues. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21658. [10] YU F, YUAN Y, LI D, et al. The Effect of Lentivirus-mediated SIRT1 Gene Knockdown in the ATDC5 Cell Line via inhibition of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cell Signal. 2019;53:80-89. [11] 于斐,曾晖,雷鸣,等.SIRT1基因敲除对骨关节炎小鼠VEGF/AKT信号通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(1):31-37. [12] 袁昊,曾晖,肖德明,等.白藜芦醇通过NF-κB信号通路抑制软骨细胞炎症因子的表达[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1):75-79. [13] SUN K, LUO J, JING X, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine. 2021; 80:153387. [14] ZHANG L, SUI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Knockdown of hsa_circ_0134111 alleviates the symptom of osteoarthritis via sponging microRNA-224-5p. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(11):1052-1066. [15] DAI J, ZHANG Y, CHEN D, et al. Glabridin inhibits osteoarthritis development by protecting chondrocytes against oxidative stress, apoptosis and promoting mTOR mediated autophagy. Life Sci. 2021; 268:118992. [16] BATSHON G, ELAYYAN J, QIQ O, et al. Serum NT/CT SIRT1 ratio reflects early osteoarthritis and chondrosenescence. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(10):1370-1380. [17] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388. [18] WANG FS, KUO CW, KO JY, et al. Irisin Mitigates Oxidative Stress, Chondrocyte Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Development through Regulating Mitochondrial Integrity and Autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(9):810. [19] YAO Y, ZHANG T, CHEN H, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis in a coculture system with genetically manipulated dedifferentiated chondrocytes and ATDC5 cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(10):3173-3181. [20] ZHAO J, DUAN L, WANG R, et al. Roflumilast prevents lymphotoxin α (TNF-β)-induced inflammation activation and degradation of type 2 collagen in chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(12):1191-1199. [21] 于斐,曾晖,翁鉴,等.慢病毒介导SIRT1基因表达降低的ATDC5细胞模型建立[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(2):154-158. [22] PAN XH, LIN QK, YAO X, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect thymus structure and function in aged C57 mice by downregulating aging-related genes and upregulating autophagy- and anti-oxidative stress-related genes. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(17): 16899-16920. [23] ZEMEL MB. Modulation of Energy Sensing by Leucine Synergy with Natural Sirtuin Activators: Effects on Health Span. J Med Food. 2020; 23(11):1129-1135. [24] LUO D, FAN H, MA X, et al. miR-1301-3p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Facilitates Cell Cycle Progression via Targeting SIRT1 in Gastric Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:664242. [25] CHEN C, ZHOU M, GE Y, et al. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187:111215. [26] MA S, FENG J, ZHANG R, et al. SIRT1 Activation by Resveratrol Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction via Mitochondrial Regulation in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4602715. [27] ISIDE C, SCAFURO M, NEBBIOSO A, et al. SIRT1 Activation by Natural Phytochemicals: An Overview. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1225. [28] ALVES-FERNANDES DK, JASIULIONIS MG. The Role of SIRT1 on DNA Damage Response and Epigenetic Alterations in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3153. [29] TANG BL. Sirt1 and the Mitochondria. Mol Cells. 2016;39(2):87-95. [30] SINGH V, UBAID S. Role of Silent Information Regulator 1 (SIRT1) in Regulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Inflammation. 2020; 43(5):1589-1598. [31] YU F, ZENG H, LEI M, et al. Effects of SIRT1 Gene Knock-Out via the Activation of SREBP2 Protein Mediated PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway on Osteoarthritis in Mice. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016; 36(5):683-690. [32] YU F, LI M, YUAN Z, et al. Mechanism Research on a Bioactive Resveratrol-PLA-Gelatin Porous Nano-scaffold in Promoting the Repair of Cartilage Defect. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:7845-7858. [33] 刘玉峰, 许肈初, 马海燕. 基因芯片技术在中药现代化研究中的应用进展[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(3):254-262. [34] YIN G, BIE S, GU H, et al. Application of gene chip technology in the diagnostic and drug resistance detection of Helicobacter pylori in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35(8):1331-1339. [35] TONOMURA H, NAGAE M, TAKATORI R, et al. The Potential Role of Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Degenerative Disorders of the Synovial Joint and Spine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8717. [36] SAHU N, AGARWAL P, GRANDI F, et al. Encapsulated Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Microbeads Promote Endogenous Regeneration of Osteoarthritic Cartilage Ex Vivo. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(8): e2002118. [37] SHI L, XU X, MENG B, et al. Neuregulin 4 Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression by Inhibiting Inflammation and Apoptosis of Chondrocytes in Mice. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021.doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00897-2. [38] CINQUE L, DE LEONIBUS C, IAVAZZO M, et al. MiT/TFE factors control ER-phagy via transcriptional regulation of FAM134B. EMBO J. 2020; 39(17):e105696. [39] HALLETT SA, ONO W, ONO N. The hypertrophic chondrocyte: To be or not to be. Histol Histopathol. 2021;18355. [40] KUMAR A, PALIT P, THOMAS S, et al. Osteoarthritis: Prognosis and emerging therapeutic approach for disease management. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(1):49-58. [41] GALDERISI S, CICALONI V, MILELLA MS, et al. Homogentisic acid induces cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix alteration in alkaptonuric cartilage.J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(8):6011-6024. [42] LEE W, NIMS RJ, SAVADIPOUR A, et al. Inflammatory signaling sensitizes Piezo1 mechanotransduction in articular chondrocytes as a pathogenic feed-forward mechanism in osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(13):e2001611118. [43] DING C, ZOU Q, WANG F, et al. HGF and BFGF Secretion by Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Improves Ovarian Function During Natural Aging via Activation of the SIRT1/FOXO1 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(4):1316-1332. [44] GU A, JIE Y, SUN L, et al. RhNRG-1β Protects the Myocardium against Irradiation-Induced Damage via the ErbB2-ERK-SIRT1 Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137337. [45] CHEN CC, KUO CH, LEU YL, et al. Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and β3-AR activation. Pharmacol Res. 2021;164:105291. [46] HESHMATI M, SOLTANI A, SANAEI MJ, et al. Ghrelin induces autophagy and CXCR4 expression via the SIRT1/AMPK axis in lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Cell Signal. 2020; 66:109492. [47] MOTONISHI S, NANGAKU M, WADA T, et al. Sirtuin1 Maintains Actin Cytoskeleton by Deacetylation of Cortactin in Injured Podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(8):1939-1959. |
| [1] | Sun Jinpeng, Liu Jun, Bai Yunfeng, Hua Feng, Wang Haoran, Zheng Hongrui, Wu Tao. Melatonin effect on the activity of mouse ATDC5 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5665-5668. |
| [2] | Tian Tian, Ouyang·Juyan, Li Yu, Miyesai·Ainiwaer, He Juanli, Li Zhenhua, Wang Hong. Mechanism by which echinacoside delays the senescence of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5014-5019. |
| [3] | Zhang Jingying, Li Ziyi, Liu Xiaochuan, Li Dan, Wang Yang, Wu zhuguo. Tail vein injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for repair of skull injury in aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3944-3950. |
| [4] | Geng Yuanwen, Lin Qinqin, Li Ruoming, Tang Shaokai, Wang Baihui, Tian Zhenjun. A single bout of exhaustive exercise induces renal NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome expression in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 190-196. |
| [5] | Wang Quanzhen, Xiao Yingfeng, Wan Shengxiang, Zhang Jian, Zhou Bo, Meng Fanbin, Yu Longbiao, Yu Fei. Effect of connective tissue growth factor on the secretion of type I and III collagen in tenocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2673-2677. |
| [6] | Chen Cai, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Qian Xiaofen, Lu Guanyu, Xiong Bo, Chen Lihua, Huang Yue. Screening of differentially expressed genes in osteoarthritis by gene chip technique and verification using quantitative real-time PCR [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1907-1914. |
| [7] | Fang Yehan, Zhang Jian, Huang Hui, Zhou Gang, Xiong Xiaolong, Lin Jianping . Gene expression profiling of the medial meniscus in a minipig model of varus knee [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5109-5115. |
| [8] | Shen Fu, Kuang Gaoyan, Yang Zhuo, Wen Meng, Zhu Kaimin, Yu Guizhi, Xu Wuji, Deng Bo . Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2183-2191. |
| [9] | Zhang Luyao. Mechanism of action of energy metabolism molecule SIRT1 in improving bone metabolism of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 276-281. |
| [10] | Sui Xiang, Tian Guangzhao, Yang Zhen, Li Xu, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi. Application potential of CD146 positive subpopulation as seed cells for cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 2997-3003. |
| [11] | Chen Hongyu, Han Hao, Chen Wei, Zhang Qiang . Effect of intermittent hydrostatic pressure on early cartilage differentiation of ATDC5 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2153-2157. |
| [12] | Liu Jiao, Wang Daming, An Taixue, Hu Xuesong, Li Nankai, Wang Hongfu, Ma Wen, Nie-He Zhongrong, Xiao Lijia, Zhou Yiwen, Zheng Lei. Expression profile analysis of miRNAs in serumal exosomes as sensitive biomarkers in patients with graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3418-3425. |
| [13] | Xie Miao-miao, Hu Xiao-cong, Wu Bu-ling, Yan Wen-juan. Streptococcus mutans gcp gene knockout strains expression profile gene chip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(33): 5988-5994. |
| [14] | Fang Hang, Zhang Rong-kai, Chen Yu-xian, Song Yan-cheng, Cai Dao-zhang. Expression of mechanical stress related genes in subchondral bone of rat osteoarthritis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(22): 4084-4090. |
| [15] | Jin Bo, Yin Heng-chong, Wang Ling-qing, Bao Li-wen, Li Yan-lin, Zhu Jun, Shi Hai-ming. Expression prolife of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway genes in vascular calcification associated with osteogenic differentiation of smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(20): 3618-3625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||