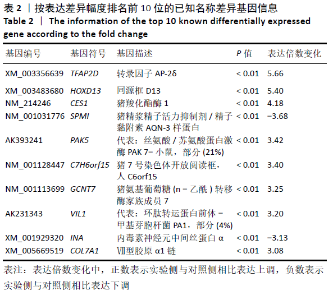
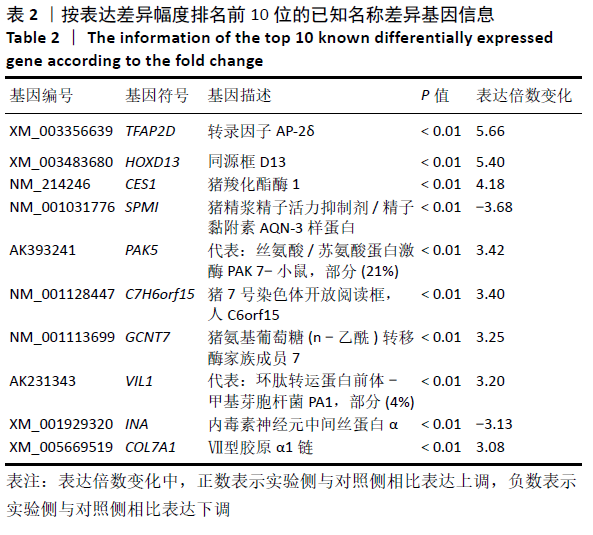
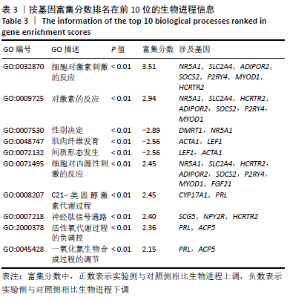
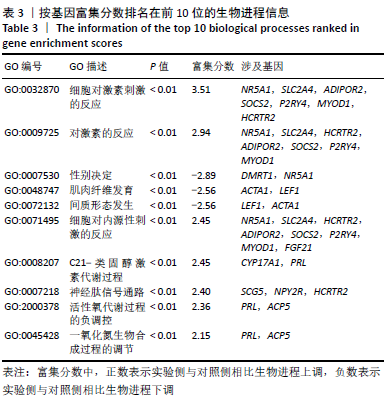
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5109-5115.doi: 10.12307/2021.212
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gene expression profiling of the medial meniscus in a minipig model of varus knee
Fang Yehan, Zhang Jian, Huang Hui, Zhou Gang, Xiong Xiaolong, Lin Jianping
- Orthopedics Center, Hainan General Hospital (Hainan Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University), Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China
-
Received:2020-08-31Revised:2020-09-01Accepted:2020-10-30Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Lin Jianping, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Orthopedics Center, Hainan General Hospital (Hainan Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University), Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Fang Yehan, Master, Associate chief physician, Orthopedics Center, Hainan General Hospital (Hainan Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University), Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Scientific Research and Development Plan of Hainan Province, No. ZDYF2017112 (to LJP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Yehan, Zhang Jian, Huang Hui, Zhou Gang, Xiong Xiaolong, Lin Jianping . Gene expression profiling of the medial meniscus in a minipig model of varus knee[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5109-5115.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] DUBUC J, GIRARD C, RICHARD H, et al. Equine meniscal degeneration is associated with medial femorotibial osteoarthritis. Equine Vet J. 2018;50(1):133-140. [2] RIBITSCH I, PEHAM C, ADE N, et al. Structure-Function relationships of equine menisci. PLoS One. 20189;13(3):e0194052. [3] IIJIMA H, AOYAMA T, ITO A, et al. Destabilization of the medial meniscus leads to subchondral bone defects and site-specific cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(7):1036-1043. [4] FISCHENICH KM, LEWIS J, KINDSFATER KA, et al. Effects of degeneration on the compressive and tensile properties of human meniscus. J Biomech. 2015;48(8):1407-1411. [5] BENDELE AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;1(4):363-376. [6] SUN Y, MAUERHAN DR, STEUERWALD NM, et al. Expression of phosphocitrate-targeted genes in osteoarthritis menisci. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:210469. [7] CHEUNG HS, SALLIS JD, DEMADIS KD, et al. Phosphocitrate blocks calcification-induced articular joint degeneration in a guinea pig model. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2452-2461. [8] KREINEST M, REISIG G, STRÖBEL P, et al. A Porcine Animal Model for Early Meniscal Degeneration - Analysis of Histology, Gene Expression and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Six Months after Resection of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0159331. [9] ZHANG R, FANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Gene expression analyses of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis by microarray. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32356. [10] GOTTERBARM T, BREUSCH SJ, SCHNEIDER U, et al. The minipig model for experimental chondral and osteochondral defect repair in tissue engineering: retrospective analysis of 180 defects. Lab Anim. 2008;42(1):71-82. [11] BOLLEN P, ELLEGAARD L. The Göttingen minipig in pharmacology and toxicology. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997;80 Suppl 2:3-4. [12] ASPDEN RM, YARKER YE, HUKINS DW. Collagen orientations in the meniscus of the knee joint. J Anat. 1985;140(Pt 3):371-380. [13] PAPAGEORGIOU CD, GIL JE, KANAMORI A, et al. The biomechanical interdependence between the anterior cruciate ligament replacement graft and the medial meniscus. Am J Sports Med. 2001;29(2):226-231. [14] KILLIAN ML, ZIELINSKA B, GUPTA T, et al. In vitro inhibition of compression-induced catabolic gene expression in meniscal explants following treatment with IL-1 receptor antagonist. J Orthop Sci. 2011; 16(2):212-220. [15] SHEN C, YAN J, ERKOCAK OF, et al. Nitric oxide inhibits autophagy via suppression of JNK in meniscal cells. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53(6):1022-1033. [16] TAKAHASHI K, HASHIMOTO S, KUBO T, et al. Hyaluronan suppressed nitric oxide production in the meniscus and synovium of rabbit osteoarthritis model. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(3):500-503. [17] HÄFELEIN K, PREUßE-PRANGE A, BEHRENDT P, et al. Selenium Reduces Early Signs of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Induced Meniscal Tissue Degradation. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;177(1):80-89. [18] BEHRENDT P, HÄFELEIN K, PREUSSE-PRANGE A, et al. IL-10 ameliorates TNF-α induced meniscus degeneration in mature meniscal tissue in vitro. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):197. [19] CHOI CJ, CHOI YJ, SONG IB, et al. Characteristics of radial tears in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus compared to horizontal tears. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(2):128-132. [20] ZHANG F, KUMM J, SVENSSON F, et al. Risk factors for meniscal body extrusion on MRI in subjects free of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: longitudinal data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(5):801-806. [21] LANGE AK, FIATARONE SINGH MA, et al. Degenerative meniscus tears and mobility impairment in women with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(6):701-708. [22] ŚLIWIŃSKI L, CEGIEŁA U, PYTLIK M, et al. Effects of fenoterol on the skeletal system depend on the androgen level. Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(2):260-267. [23] MOBLEY CB, MUMFORD PW, KEPHART WC, et al. Effects of testosterone treatment on markers of skeletal muscle ribosome biogenesis. Andrologia. 2016;48(9):967-977. [24] PAULI C, GROGAN SP, PATIL S, et al. Macroscopic and histopathologic analysis of human knee menisci in aging and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(9):1132-1141. [25] DU G, ZHAN H, DING D, et al. Abnormal Mechanical Loading Induces Cartilage Degeneration by Accelerating Meniscus Hypertrophy and Mineralization After ACL Injuries In Vivo. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(3):652-663. [26] SUN Y, ROBERTS A, MAUERHAN DR, et al. Biological activities of phosphocitrate: a potential meniscal protective agent. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:726581. [27] CAMACHO A, SIMÃO M, EA HK, et al. Iron overload in a murine model of hereditary hemochromatosis is associated with accelerated progression of osteoarthritis under mechanical stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):494-502. [28] KATSURAGAWA Y, SAITOH K, TANAKA N, et al. Changes of human menisci in osteoarthritic knee joints. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(9):1133-1143. [29] NEUMANN J, GUIMARAES JB, HEILMEIER U, et al. Diabetics show accelerated progression of knee cartilage and meniscal lesions: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Skeletal Radiol. 2019;48(6):919-930. [30] HENNERBICHLER A, MOUTOS FT, HENNERBICHLER D, et al. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit repair of the porcine meniscus in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(9):1053-1060. [31] STONE AV, LOESER RF, VANDERMAN KS, et al. Pro-inflammatory stimulation of meniscus cells increases production of matrix metalloproteinases and additional catabolic factors involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(2): 264-274. [32] COOK AE, COOK JL, STOKER AM. Metabolic Responses of Meniscus to IL-1β. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(9):834-840. [33] AOKI T, CHONG LC, TAKATA K, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Disease-Defining T-cell Subsets in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(3):406-421. |
| [1] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [2] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [3] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [4] | Zhong Hehe, Jin Ying, Liu Xiuqi, Xiang Kuan, Wu Shuhong, Peng Jiachen, Liu Yi. High tibial osteotomy combined with arthroscopy to treat degenerative tear in the posterior horn of medial meniscus combined with varus deformity of the knee [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3531-3536. |
| [5] | Chen Hao, Wang Rui, Jiang Shaowei, Wu Lei. Correlation of MRI quantitative measurement of medial meniscus extrusion and medial meniscus injury pattern with cartilage damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3567-3572. |
| [6] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Etiological analysis of discoid meniscus based on whole exome sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 192-199. |
| [7] | Xu Zhi, Li Yuwan, Jin Ying, Liu Yi. Effect of partial posterior root tear of medial meniscus on biomechanics of the knee joint during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2824-2830. |
| [8] | Zhou Lanxi, Shao Lu, Dong Shiwu, Yu Zhengwen. Molecular mechanism of angiogenesis promoted by medical metal materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2616-2624. |
| [9] | Yang Jun, Li Peng. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into meniscus fibrochondrocytes induced by transforming growth factor beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2412-2419. |
| [10] | Chen Yiyan, Fan Zhiying, Song Honghui, Lu Aming, Zhou Haibin. Pain intensity influences the movement patterns of patients with lateral meniscus injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5639-5645. |
| [11] | Du Chaozheng, Zhi Jiajia, Wang Yue, Wang Xinjun, Yuan Yinpeng, Wang Yuze. Alternative strategies for tissue engineering repair of meniscus injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5553-5561. |
| [12] | Qian Xiaofen, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Wang Hao, Zhou Shulong, Pan Haida. Screening key genes in synovium of osteoarthritis by a combination of differentially expressed genes and weighted co-expression network analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5342-5349. |
| [13] | Zhang Jingxin, Liu Linfeng, Zhang Shiwen, Lin Jie. Molecular mechanism of magnesium ion promoting bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5384-5392. |
| [14] | Wu Huiting, Zhu Dacheng, Xu Xiaoming, Chang Na. Ethanol extract of toosendan induces apoptosis of leukemia CEM cells through mitochondrial pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4873-4878. |
| [15] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||