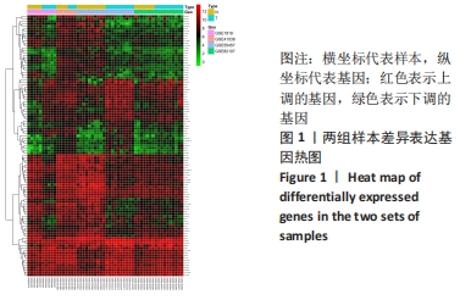
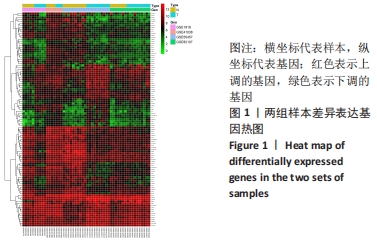
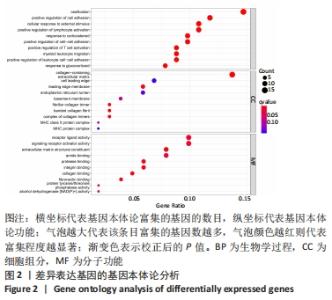
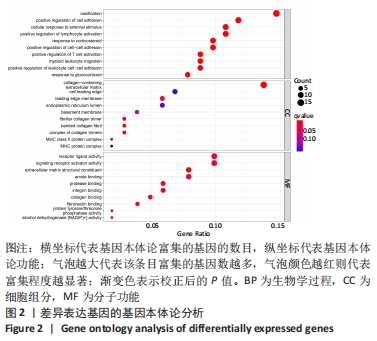
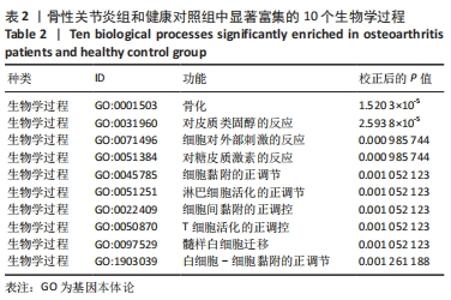
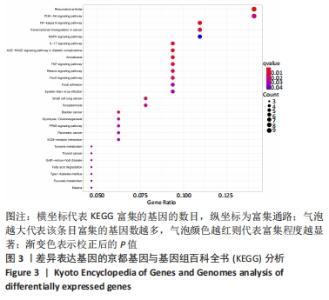
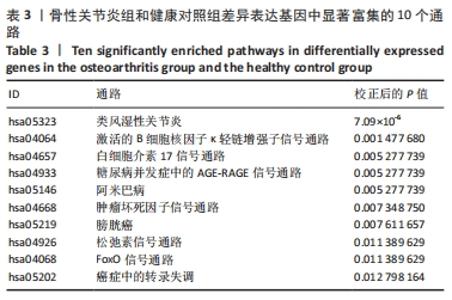
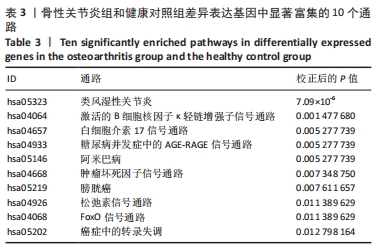
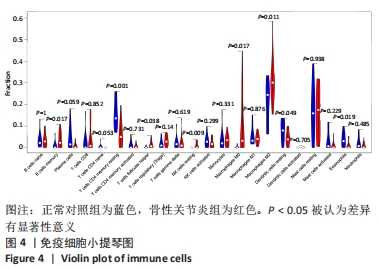
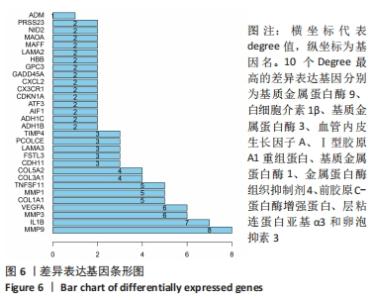
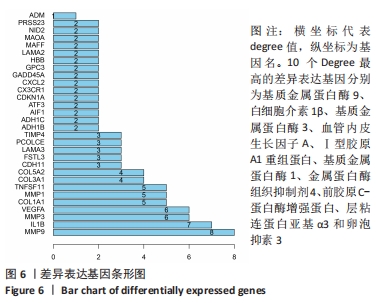
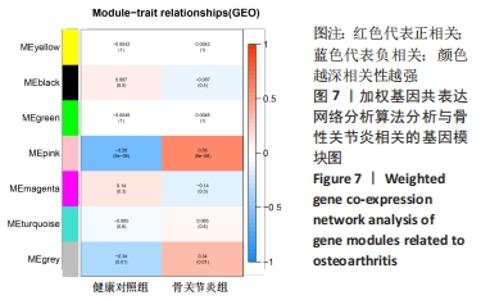
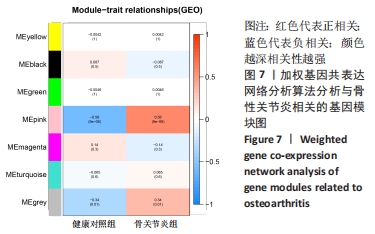
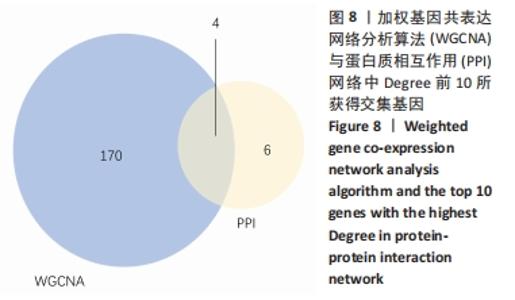
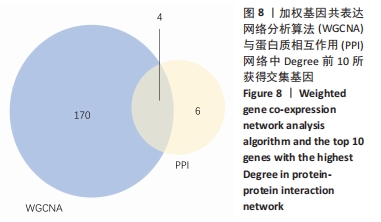
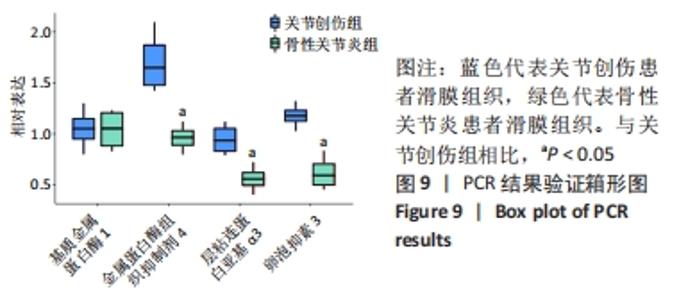
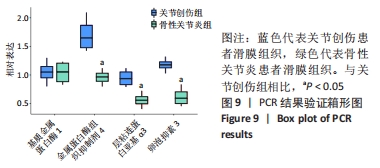
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1907-1914.doi: 10.12307/2022.515
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening of differentially expressed genes in osteoarthritis by gene chip technique and verification using quantitative real-time PCR
Chen Cai1, Zeng Ping2, Liu Jinfu1, Qian Xiaofen1, Lu Guanyu1, Xiong Bo1, Chen Lihua1, Huang Yue1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-04-26Revised:2021-04-27Accepted:2021-06-15Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Zeng Ping, MD, Professor, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Cai, Master candidate, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960876 (to ZP); College-level Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2017ZD002 (to ZP); Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology Development and Promotion Project, No. GZSY21-14 (to ZP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Cai, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Qian Xiaofen, Lu Guanyu, Xiong Bo, Chen Lihua, Huang Yue. Screening of differentially expressed genes in osteoarthritis by gene chip technique and verification using quantitative real-time PCR[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1907-1914.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [2] FRANK M, BWEMERO J, KALUNGA D, et al. OA60 Public health and palliative care mix; a ccpmedicine approach to reverse the overgrowing burden of non-communicable diseases in tanzania. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2015;5 Suppl 1:A19. [3] CHANG MC, CHIANG PF, KUO YJ, et al. Hyaluronan-Loaded Liposomal Dexamethasone-Diclofenac Nanoparticles for Local Osteoarthritis Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):665. [4] WANG X, HUNTER DJ, JIN X, et al. The importance of synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis: current evidence from imaging assessments and clinical trials. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(2): 165-174. [5] RIM YA, JU JH. The Role of Fibrosis in Osteoarthritis Progression. Life (Basel). 2020;11(1):3. [6] LIU W, JIAO Y, TIAN C, et al. Gene Expression Profiling Studies Using Microarray in Osteoarthritis: Genes in Common and Different Conditions. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2020;68(5):28. [7] TANG J, LIU T, WEN X, et al. Estrogen-related receptors: novel potential regulators of osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):5. [8] 罗磊, 龚宝成, 刘福囝. GSE74602芯片数据中直肠癌关键基因与治疗药物的生物信息学筛选[J] .中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(4):457-467. [9] MARTEL-PELLETIER J. Pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998;6(6):374-376. [10] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Eph-Ephrin Signaling Mediates Cross-Talk Within the Bone Microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 598612. [11] NISHIMURA R, MORIYAMA K, YASUKAWA K, et al. Combination of interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors induces differentiation and activation of JAK-STAT and MAP kinase pathways in MG-63 human osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(5):777-785. [12] GARCIA JP, UTOMO L, RUDNIK-JANSEN I, et al. Association between Oncostatin M Expression and Inflammatory Phenotype in Experimental Arthritis Models and Osteoarthritis Patients. Cells. 2021;10(3):508. [13] 刘金富, 曾平, 农焦, 等. 整合多组微阵列芯片分析骨关节炎患者滑膜中生物标志物和治疗靶点[J] . 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23): 3690-3696. [14] MYNGBAY A, MANARBEK L, LUDBROOK S, et al. The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2426. [15] HU Q, ECKER M. Overview of MMP-13 as a Promising Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1742. [16] 卢文豪, 周雪灵, 任义昆, 等. 电针上调Cezanne表达抑制NF-κB信号通路介导的大鼠脑缺血/再灌注炎性损伤[J] . 第三军医大学学报,2021,43(4):283-294. [17] HAN S, LI Z, HAN F, et al. ROR alpha protects against LPS-induced inflammation by down-regulating SIRT1/NF-kappa B pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019;668:1-8. [18] NEES TA, ROSSHIRT N, REINER T, et al. Die Rolle der Inflammation bei Arthroseschmerzen [Inflammation and osteoarthritis-related pain]. Schmerz. 2019;33(1):4-12. [19] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4): 400-409. [20] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914. [21] VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN DEN BERG WB. Chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis: role in initiation and progression of cartilage degeneration? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(3):223-232. [22] WU J, ZOU M, PING A, et al. MicroRNA-449a upregulation promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105:940-946. [23] SRIVASTAVA RK, DAR HY, MISHRA PK. Immunoporosis: Immunology of Osteoporosis- Role of T Cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:657. [24] SUN Y, ZUO Z, KUANG Y. An Emerging Target in the Battle against Osteoarthritis: Macrophage Polarization. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22): 8513. [25] NAKAJIMA H, WATANABE S, HONJOH K, et al. Expression Analysis of Susceptibility Genes for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine in Human OPLL-related Tissues and a Spinal Hyperostotic Mouse (ttw/ttw). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020; 45(22):E1460-E1468. [26] CAO J, HAN X, QI X, et al. miR‑204‑5p inhibits the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting Runx2. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 42(5):2560-2568. [27] CHEN CL, ZHANG L, JIAO YR, et al. miR-134 inhibits osteosarcoma cell invasion and metastasis through targeting MMP1 and MMP3 in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett. 2019;593(10):1089-1101. [28] GUO Y, JIA X, CUI Y, et al. Sirt3-mediated mitophagy regulates AGEs-induced BMSCs senescence and senile osteoporosis. Redox Biol. 2021; 41:101915. [29] WYATT LA, NWOSU LN, WILSON D, et al. Molecular expression patterns in the synovium and their association with advanced symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(4):667-675. [30] GENG R, XU Y, HU W, et al. The association between MMP-1 gene rs1799750 polymorphism and knee osteoarthritis risk. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5):BSR20181257. [31] STACK J, MCCARTHY GM. Cartilage calcification and osteoarthritis: a pathological association? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(10):1301-1302. [32] SAKAMURI SSVP, WATTS R, TAKAWALE A, et al. Absence of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-4 (TIMP4) ameliorates high fat diet-induced obesity in mice due to defective lipid absorption. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6210. [33] OZEN G, BOUMIZA S, DESCHILDRE C, et al. Inflammation increases MMP levels via PGE2 in human vascular wall and plasma of obese women. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019;43(9):1724-1734. [34] ZHAO H, LIU S, MA C, et al. Estrogen-Related Receptor γ Induces Angiogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis in Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1290. [35] WANG F, LIU J, CHEN X, et al. IL-1β receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) combined with autophagy inducer (TAT-Beclin1) is an effective alternative for attenuating extracellular matrix degradation in rat and human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):171. [36] WANG J, AN F, CAO Y, et al. Association of TIMP4 gene variants with steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the population of northern China. Peer J. 2019;7:e6270. [37] 蒋锐, 於子卫.细胞外基质在周围神经修复组织工程学中应用的研究进展[J] .听力学及言语疾病杂志,2018,26(5):556-560. [38] ABERKANE A, ESSAHIB W, SPITS C, et al. Expression of adhesion and extracellular matrix genes in human blastocysts upon attachment in a 2D co-culture system. Mol Hum Reprod. 2018;24(7):375-387. [39] LI Z, MENG D, LI G, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-210 promotes chondrocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting HIF-3α in osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2769-2776. [40] GANG X, SUN Y, LI F, et al. Identification of key genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis with bioinformatics approach. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(31):e7673. [41] MACDONALD IJ, LIU SC, SU CM, et al. Implications of Angiogenesis Involvement in Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2012. [42] VADALÀ G, RUSSO F, MUSUMECI M, et al. Targeting VEGF-A in cartilage repair and regeneration: state of the art and perspectives. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018;32(6 Suppl. 1):217-224. [43] TAKANO S, UCHIDA K, INOUE G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and their action in the synovial membranes of patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):204. [44] WANG YH, KUO SJ, LIU SC, et al. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2020;9(3):594. [45] OLDKNOW KJ, SEEBACHER J, GOSWAMI T, et al. Follistatin-like 3 (FSTL3) mediated silencing of transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling is essential for testicular aging and regulating testis size. Endocrinology. 2013;154(3):1310-1320. [46] CHRUŚCIK A, GOPALAN V, LAM AK. The clinical and biological roles of transforming growth factor beta in colon cancer stem cells: A systematic review. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018;97(1):15-22. [47] WANG Q, ZHOU C, LI X, et al. TGF-β1 promotes gap junctions formation in chondrocytes via Smad3/Smad4 signalling. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2): e12544. [48] SUN PF, KONG WK, LIU L, et al. Osteopontin accelerates chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis rats through the NF-κb signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2836-2842. [49] ZHU H, DAI L, LI X, et al. Role of the long noncoding RNA H19 in TGF-β1-induced Tenon’s capsule fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition. Exp Cell Res. 2020;387(2):111802. |
| [1] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [4] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [5] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [6] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [7] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [8] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [9] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [10] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [11] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [12] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [13] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| [14] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Changes in kinematic parameters after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 390-396. |
| [15] | Wang Chong, Zhang Meiying, Zhou Jian, Lao Kecheng. Early gait changes after total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach and posterolateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 359-364. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||