Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (23): 3683-3690.doi: 10.12307/2022.668
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening and biological function analysis of inflammation-related circRNAs in synovial tissue of patients with primary knee osteoarthritis
Qiao Linghui1, Yuan Tao1, Han Jie2, Wang Guancheng1, Gu Yanglin1
- 1Wuxi Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Wuxi Clinical College of Nantong University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-24Accepted:2021-08-19Online:2022-08-18Published:2022-02-23 -
Contact:Gu Yanglin, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Associate chief physician, Wuxi Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Qiao Linghui, Master candidate, Physician, Wuxi Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Wuxi Municipal “Double Hundred” Young and Middle-aged Top Talent Training Fund for Medicine and Health, No. BJ2020037 (to GYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiao Linghui, Yuan Tao, Han Jie, Wang Guancheng, Gu Yanglin. Screening and biological function analysis of inflammation-related circRNAs in synovial tissue of patients with primary knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3683-3690.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
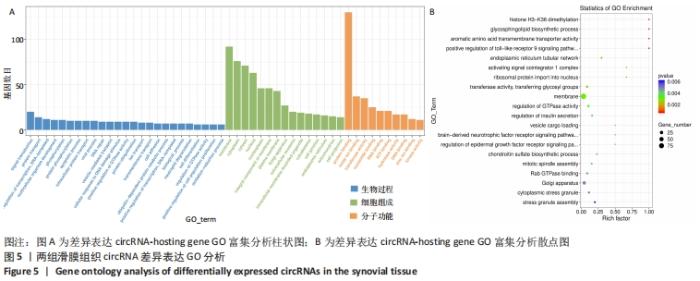
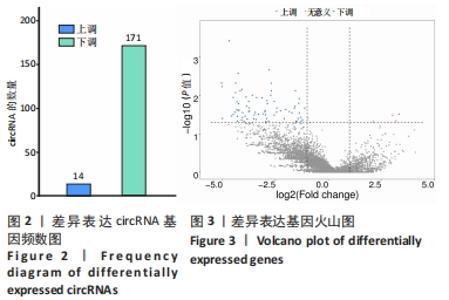
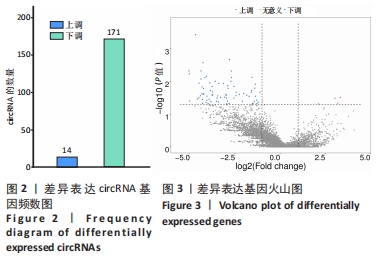
2.3 骨关节炎组和类风湿性关节炎组滑膜组织circRNA差异表达GO分析 GO富集分析结果的直方图反映了针对生物过程、细胞成分和分子功能富集的GO_Term上差异基因的个数分布情况。根据注释到GO_Term的差异基因数目(S gene number)针对3种GO_function从高到低排序,选择Top25、Top15、Top10 GO_Terms进行绘图。如果有多个GO_Terms对应相同数量的基因编号,则随机选择一个GO_Terms进行绘制,见图5A。GO富集分析的结果通过ggplot2以散点图的形式显示。横轴的rich factor代表GO中的差异基因数/位于该GO的总基因数,Rich factor越大,GO富集的程度越高。纵坐标是GO_Term,是GO途径的注解。P值小于 0.05 表示显著富集。GO富集分析散点图是根据富集的显著性(P值)取Top20的Go_term进行绘图,见图5B。"
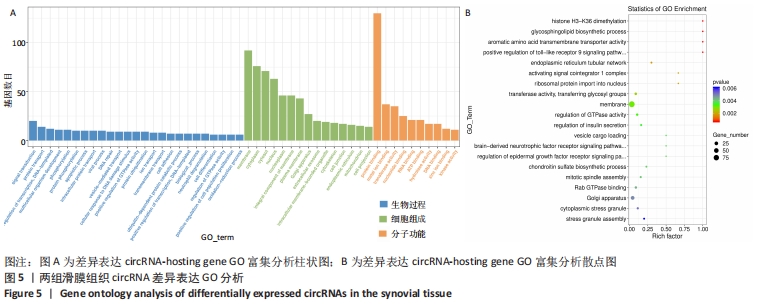
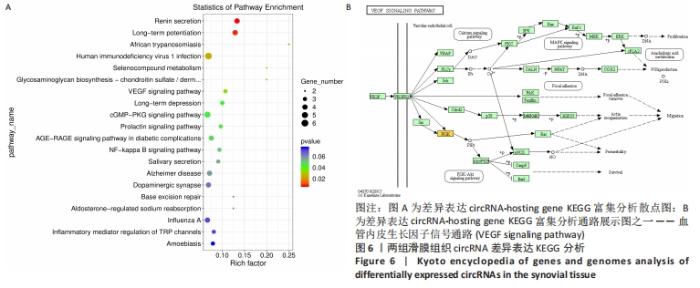
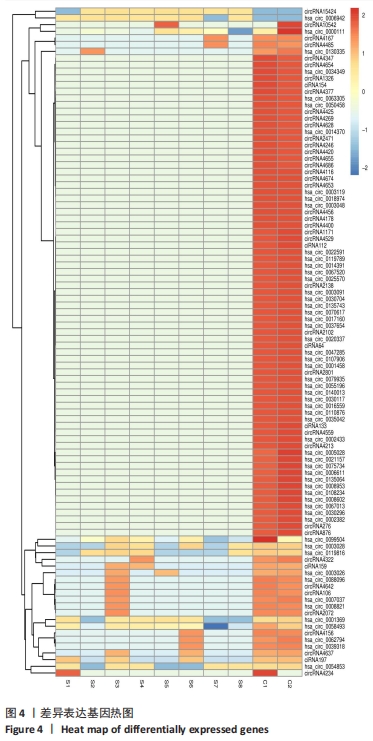
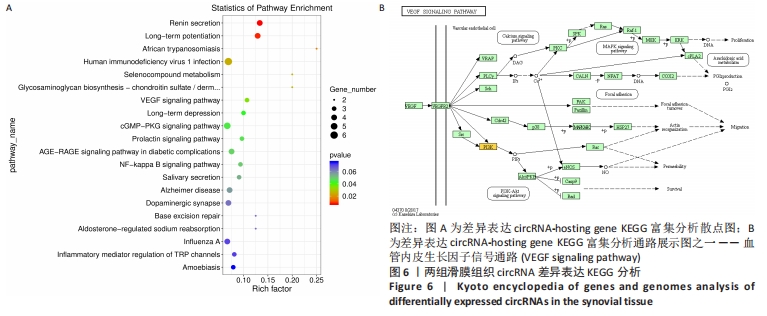
从图上可以看出,在生物过程(Biological Process)层面,骨关节炎组患者滑膜组织差异表达的circRNA主要富集于蛋白 H3-K36 二甲基化、鞘糖脂生物合成过程、Toll样受体9信号通路的正调控、核糖体蛋白导入细胞核、GTP酶活性的调节等过程。在细胞成分(cellular component)层面,骨关节炎组患者滑膜组织差异表达的circRNA主要富集于细胞膜、高尔基体、细胞内膜结合的细胞器、细胞连接、早期内体膜等细胞组分中。在分子功能(molecular_function)层面,钾离子和钠离子逆向转运蛋白活性、内质网管状网络、激活信号协整器 1 复合物、转移酶活性、非跨膜蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶活性等均在骨关节炎组中有明显差异表达。 2.4 骨关节炎组和类风湿性关节炎组滑膜组织circRNA差异表达KEGG分析 KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)是由日本京都大学和东京大学联合开发的数据库,是系统分析基因功能、联系基因组信息和功能信息的知识库,可以用来查询代谢途径、酶(或编码酶的基因)、代谢产物等,也可以通过BLAST比对查询未知序列的代谢途径信息(www.genome.jp/kegg)。 骨关节炎组和类风湿性关节炎组滑膜组织差异表达的circRNA主要参与了肾素分泌、长期增益效应、人类免疫缺陷病毒1型感染、硒化合物代谢、糖胺聚糖生物合成——硫酸软骨素/硫酸皮肤素、血管内皮生长因子信号通路、长期抑郁、cGMP-PKG信号通路、催乳素信号通路等,见图6A。KEGG分析进一步揭示富集circRNA在已知通路中的表达情况。图6B为血管内皮生长因子信号通路(VEGF signaling pathway)富集分析图,黄色代表注释到某个ko节点的显著差异表达基因既有上调也有下调,实心箭头表示生化反应的方向,虚线箭头连接其他的相关代谢途径。"
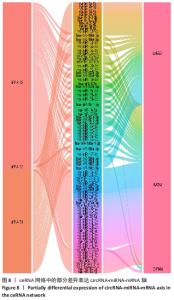
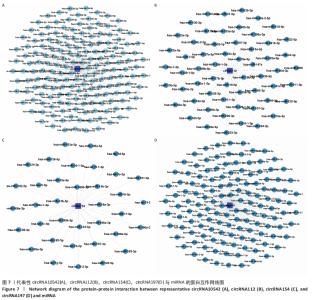
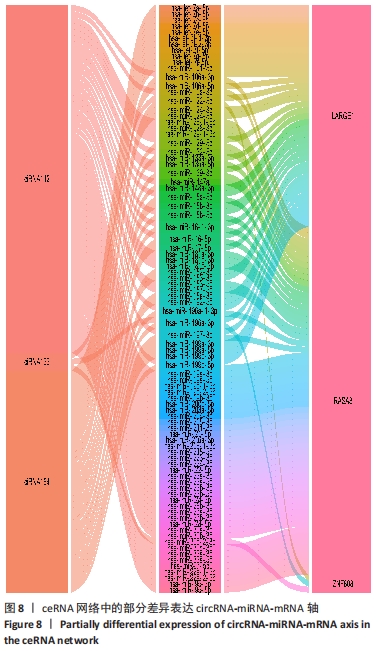
因此,根据以上测序结果创建了一个circRNA-miRNA 相互作用网络,该网络有助于理解差异表达circRNA的作用。在所有185个差异表达的circRNA中,有超过2 000 个miRNA与其产生相互作用并满足包容性标准。最终可视化4个具有代表性的circRNA的相关网络,见图7。 2.6 骨关节炎组和类风湿性关节炎组滑膜组织差异表达 circRNA-miRNA-mRNA轴 circRNA作为内源性竞争性RNA通过碱基互补海绵吸附miRNA的方式来调控下游靶基因。miRNA通过靶向mRNA的3'UTR降低mRNA的稳定性或者抑制mRNA的翻译,进而负向调控靶基因的表达,这类转录后调控模式称作ceRNA假说。ceRNA不仅参与正常细胞的各种生物过程,而且在各类炎症和肿瘤中也发挥重要作用[11]。circRNA-miRNA-mRNA轴在其他疾病中的病理作用得到很多研究,而在骨关节炎及类风湿性关节炎中的研究还较少。由于差异基因靶向的下游mRNA较多,该研究仅将出现频次最高的前3位mRNA位点及其与代表性的3个circRNA形成的circRNA-miRNA-mRNA轴进行可视化,见图8,并针对性的进行相关分析。这些研究将为骨关节炎的发病机制、诊断和治疗提供新的方向。"
| [1] JI Y, FANG QY, WANG SN, et al. Lnc-RNA BLACAT1 regulates differentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting miR-142-5p in osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2893-2901. [2] LIU C, GAO J, SU G, et al. MicroRNA-1202 plays a vital role in osteoarthritis via KCNQ1OT1 has-miR-1202-ETS1 regulatory pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):130. [3] 王银山.类风湿性关节炎的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志,2008,10(10): 131-134. [4] DEY M, CUTOLO M, NIKIPHOROU E. Beverages in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What to Prefer or to Avoid. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3155. [5] CHENG Q, CHEN X, WU H, et al. Three hematologic/immune system-specific expressed genes are considered as the potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis through bioinformatics analysis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):18. [6] ALIVERNINI S, MACDONALD L, ELMESMARI A, et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1295-1306. [7] ZHOU X, ZHAN L, HUANG K, et al. The functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):138. [8] KONG S, TAO M, SHEN X, et al. Translatable circRNAs and lncRNAs: Driving mechanisms and functions of their translation products. Cancer Lett. 2020; 483:59-65. [9] CAO Q, GUO Z, DU S, et al. Circular RNAs in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Life Sci. 2020;255:117837. [10] CHENG Y, SU Y, WANG S, et al. Identification of circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Competitive Endogenous RNA Network as Novel Prognostic Markers for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(8):868. [11] LIU S, SONG A, ZHOU X, et al. ceRNA network development and tumour-infiltrating immune cell analysis of metastatic breast cancer to bone. J Bone Oncol. 2020;24:100304. [12] 康悦,刘洁.环状RNA在间充质干细胞成骨分化中的生物学作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):107-112. [13] LV YS, WANG C, LI LX, et al. Effects of circRNA_103993 on the proliferation and apoptosis of NSCLC cells through miR-1271/ERG signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(16):8384-8393. [14] YANG J, CHENG M, GU B, et al. CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):833. [15] LIU Q, ZHANG X, HU X, et al. Circular RNA Related to the Chondrocyte ECM Regulates MMP13 Expression by Functioning as a MiR-136 ‘Sponge’ in Human Cartilage Degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572. [16] LIU Q, ZHANG X, HU X, et al. Emerging Roles of circRNA Related to the Mechanical Stress in Human Cartilage Degradation of Osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;7:223-230. [17] DAI Q, MA Y, XU Z, et al. Downregulation of circular RNA HECTD1 induces neuroprotection against ischemic stroke through the microRNA-133b/TRAF3 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;264:118626. [18] MA G, LI G, FAN W, Et al. Circ-0005105 activates COL11A1 by targeting miR-20a-3p to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(7):656. [19] ZHOU ZB, DU D, HUANG GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene. 2018;646:203-209. [20] 关鸿,张宏博,邵焱,等.PDZ结构域蛋白1缺失促进骨关节炎软骨细胞衰老[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(2):190-197. [21] HAN D, FANG Y, TAN X, et al. The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(17):9518-9532. [22] CHEN S, LUO Z, CHEN X. Hsa_circ_0044235 regulates the pyroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis via MiR-135b-5p-SIRT1 axis. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(12):1107-1121. [23] LI M, HUA Q, SHAO Y, et al. Circular RNA circBbs9 promotes PM2.5-induced lung inflammation in mice via NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Environ Int. 2020;143:105976. [24] BIERMANN MHC, BOELTZ S, PIETERSE E, et al. Autoantibodies Recognizing Secondary NEcrotic Cells Promote Neutrophilic Phagocytosis and Identify Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2018;9:989. [25] DOBENECKER MW, MARCELLO J, BECKER A, et al. The catalytic domain of the histone methyltransferase NSD2/MMSET is required for the generation of B1 cells in mice. FEBS Lett. 2020;594(20):3324-3337. [26] YANG Y, XING D, WANG Y, et al. A long non-coding RNA, HOTAIR, promotes cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting WIF-1 expression and activating Wnt pathway. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(1):53. [27] ABBASIFARD M, IMANI D, BAGHERI-HOSSEINABADI Z. PTPN22 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gene Med. 2020;22(9):e3204. [28] DEN HOLLANDER W, PULYAKHINA I, BOER C, et al. Annotating Transcriptional Effects of Genetic Variants in Disease-Relevant Tissue: Transcriptome-Wide Allelic Imbalance in Osteoarthritic Cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(4): 561-570. [29] KOFUJI S, SASAKI AT. GTP metabolic reprogramming by IMPDH2: unlocking cancer cells’ fuelling mechanism. J Biochem. 2020;168(4):319-328. [30] HIRSCH L, FLIPPOT R, ESCUDIER B, et al. Immunomodulatory Roles of VEGF Pathway Inhibitors in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Drugs. 2020;80(12):1169-1181. [31] VAN RAEMDONCK K, UMAR S, SHAHRARA S. The pathogenic importance of CCL21 and CCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020; 55:86-93. [32] MURPHY MP, KOEPKE LS, LOPEZ MT, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration by activated skeletal stem cells. Nat Med. 2020;26(10):1583-1592. [33] PIAZZA GA, WARD A, CHEN X, et al. PDE5 and PDE10 inhibition activates cGMP/PKG signaling to block Wnt/β-catenin transcription, cancer cell growth, and tumor immunity. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(8):1521-1527. [34] SIMENTAL-MENDÍA M, SÁNCHEZ-GARCÍA A, VILCHEZ-CAVAZOS F, et al. Effect of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(8):1413-1428. [35] BI X, GUO XH, MO BY, et al. LncRNA PICSAR promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miRNA-4701-5p in rheumatoid arthritis. EBioMedicine. 2019;50:408-420. [36] MAO G, HU S, ZHANG Z, et al. Exosomal miR-95-5p regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage degradation via histone deacetylase 2/8. J Cell Mol Med. 2018; 22(11):5354-5366. [37] DE LUCA L, TRINO S, LAURENZANA I, et al. Knockdown of miR-128a induces Lin28a expression and reverts myeloid differentiation blockage in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(6):e2849. [38] HU S, LI Z, LUTZ H, et al. Dermal exosomes containing miR-218-5p promote hair regeneration by regulating β-catenin signaling. Sci Adv. 2020;6(30): eaba1685. [39] WU B, ZHANG S, GUO Z, et al. RAS P21 Protein Activator 3 (RASA3) Specifically Promotes Pathogenic T Helper 17 Cell Generation by Repressing T-Helper-2-Cell-Biased Programs. Immunity. 2018;49(5):886-898.e5. [40] RIGHINO B, BOZZI M, PIROLLI D, et al. Identification and Modeling of a GT-A Fold in the α-Dystroglycan Glycosylating Enzyme LARGE1. J Chem Inf Model. 2020;60(6):3145-3156. |
| [1] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [6] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [7] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [8] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [9] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [10] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [11] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [12] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [14] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [15] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||