Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 3351-3356.doi: 10.12307/2022.643
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characterization of chitosan-modified polyetheretherketone and its effect on MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion and proliferation
Feng Le, Qiu Peng, Liu Min, Zhou Hui
- Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-08-24Accepted:2021-11-04Online:2022-07-28Published:2022-01-27 -
Contact:Zhou Hui, Master, Physician, Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Feng Le, Master candidate, Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Research Project of Sichuan Province, No. S19023 (to LM); Science and Technology Plan Project of Luzhou City, No. 2018-JYJ-39 (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Le, Qiu Peng, Liu Min, Zhou Hui. Characterization of chitosan-modified polyetheretherketone and its effect on MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion and proliferation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3351-3356.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
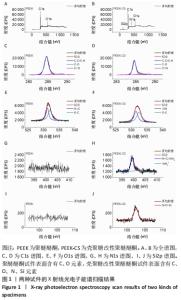
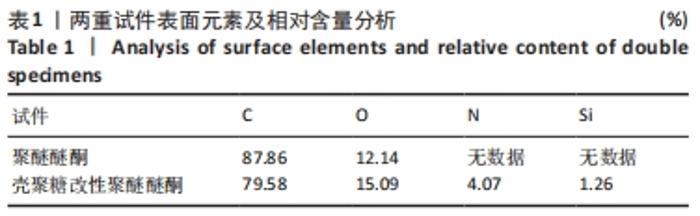
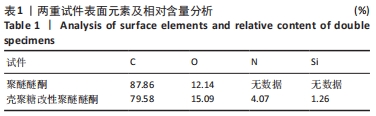
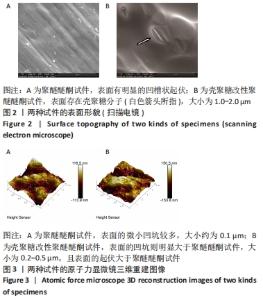
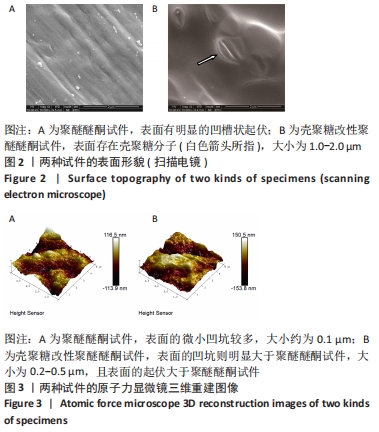
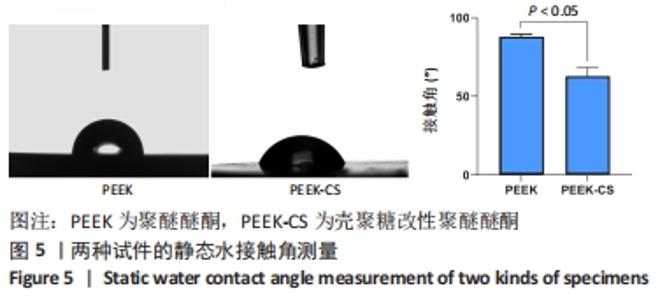
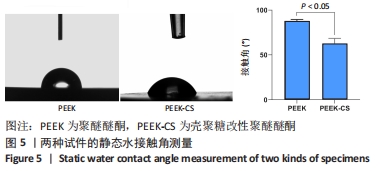
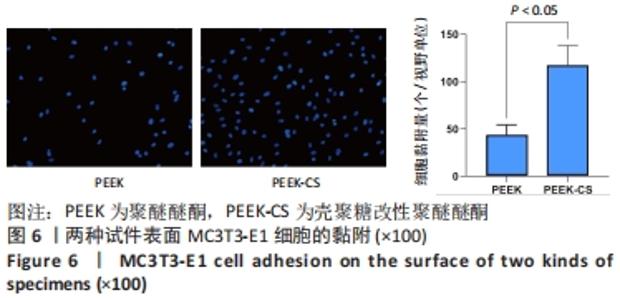
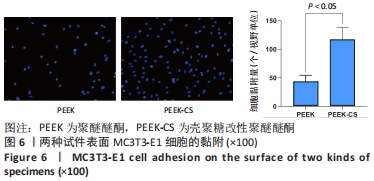
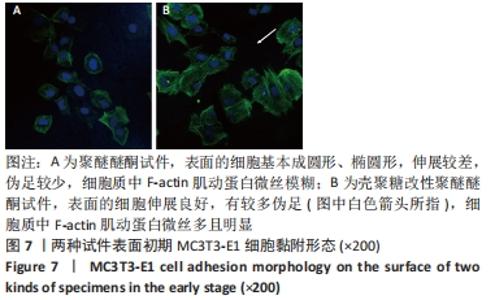
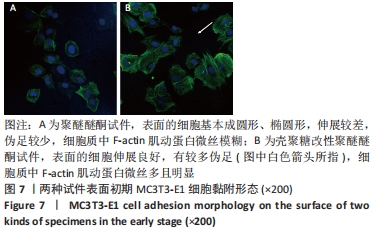
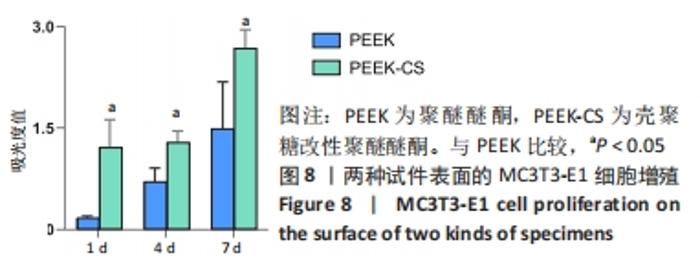
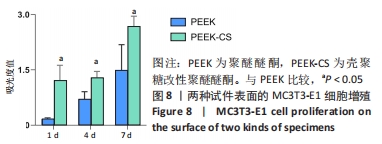
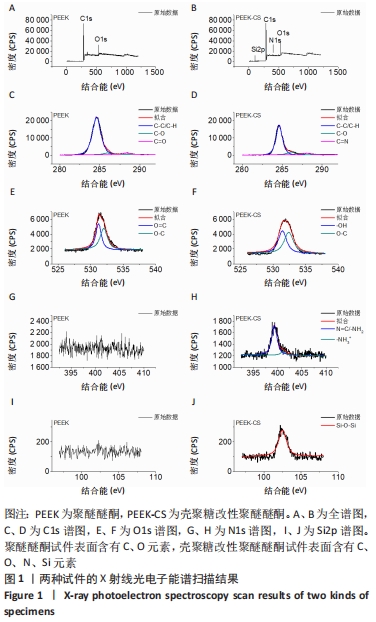
原始聚醚醚酮试件表面扫描范围内检测到了C、O元素,相对含量分别为87.86%,12.14%,未检测出N、Si元素;壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮试件表面扫描范围内检测到了C、O、N、Si元素,相对含量分别为79.58%,15.09%,4.07%,1.26%。 两种试件的X射线电子能谱分析如图1所示。图1A,B为两种试件的全谱图,可见聚醚醚酮组表面只扫描到了C1s和O1s峰,而壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮组表面扫描到了C1s、O1s、N1s和Si2p峰。图1C,D为两种试件的C1s谱图,可见聚醚醚酮组在284.8 eV处有C-C/C-H峰,在286.0 eV处有C-O峰,在287.2 eV处有C=O峰;壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮组不仅有284.8 eV处的C-C/C-H峰和286.0 eV处的C-O峰,还出现了287.7 eV处的C=N峰,没有287.2 eV处的C=O峰。图1E,F为两种试件的O1s谱图,可见聚醚醚酮组在531.5 eV处的O=C峰和533.5 eV处的O-C峰,壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮组在532.2 eV处的-OH峰和533.5 eV处的O-C峰。图1G,H为两种试件的N1s谱图,可见聚醚醚酮组内没有N元素的相关峰,壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮组在399.5 eV处出现了N=C峰和-NH2,在401.4 eV处出现了-NH3+峰(质子化或形成氢键的氨基)。图I,J为两种试件的Si2p谱图,可见聚醚醚酮组内没有Si元素的相关峰,壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮组出现了3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷的特征Si-O-Si峰。 "
| [1] 陈贤明,周王峰.聚醚醚酮在口腔医学领域的应用[J].中国标准化,2020 (S01):354-358. [2] PANAYOTOV IV, ORTI V, CUISINIER F, et al. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for medical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(7):118. [3] TSUNEO S, MIYUKI H. Radiation deterioration of several aromatic polymers under oxidative conditions. Elsevier. 1987;28(11):694-699. [4] LI HM, FOURACRE RA, GIVEN MJ, et al. The effects on polyetheretherketone and polyethersulfone of electron and /spl gamma/irradiation. IEEE T DIELECT EL IN. 1999;6(3):295-303. [5] 陈井春雨,蓝菁.聚醚醚酮材料表面形态和骨结合原理研究进展[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021,37(2):259-262. [6] ABDULLAH MR, GOHARIAN A, ABDUL KADIR MR, et al. Biomechanical and bioactivity concepts of polyetheretherketone composites for use in orthopedic implants-a review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3689-3702. [7] 刘吕花,熊成东,张丽芳,等.聚醚醚酮表面接枝聚丙烯酸及其成骨细胞相容性[J].塑料工业,2021,49(7):1591-1563. [8] SAROT JR, CONTAR CM, CRUZ AC, et al. Evaluation of the stress distribution in CFR-PEEK dental implants by the three-dimensional finite element method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(7):2079-2085. [9] FEERICK EM, KENNEDY J, MULLETT H, et al. Investigation of metallic and carbon fibre PEEK fracture fixation devices for three-part proximal humeral fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(6):712-722. [10] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, GITTENS RA, SCHNEIDER JM, et al. Osteoblasts exhibit a more differentiated phenotype and increased bone morphogenetic protein production on titanium alloy substrates than on poly-ether-ether-ketone. Spine J. 2012;12(3):265-272. [11] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, SLOSAR PJ, et al. Implant materials generate different peri-implant inflammatory factors: poly-ether-ether-ketone promotes fibrosis and microtextured titanium promotes osteogenic factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(6):399-404. [12] MUXIKA A, ETXABIDE A, URANGA J, et al. Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: Processing, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;105(Pt 2): 1358-1368. [13] PATRULEA V, OSTAFE V, BORCHARD G, et al. Chitosan as a starting material for wound healing applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97(Pt B):417-426. [14] 毛誉蓉,孙佳敏,周雄,等.医用特种高分子聚醚醚酮植入体及其表面界面工程[J].功能高分子学报,2021,34(2):144-160. [15] MA R, TANG T. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5426-5445. [16] ABDULKAREEM MH, ABDALSALAM AH, BOHAN AJ. Influence of chitosan on the antibacterial activity of composite coating (PEEK /HAp) fabricated by electrophoretic deposition. Prog Org Coat. 2019;130:251-259. [17] 陈睿超,孙辉,许国志.PEEK的表面改性和表征[J].中国塑料,2011,25(5): 17-23. [18] 刘焕萍,孙辉,高艺菡.聚醚醚酮表面壳聚糖的固定[J].中国塑料,2014, 28(6):52-56. [19] XU A, ZHOU L, DENG Y, et al. A carboxymethyl chitosan and peptide-decorated polyetheretherketone ternary biocomposite with enhanced antibacterial activity and osseointegration as orthopedic/dental implants. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(10):1878-1890. [20] BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT JR, DILLON MR, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(8):852-857. [21] AZZAWI ZGM, HAMAD TI, KADHIM SA, et al. Osseointegration evaluation of laser-deposited titanium dioxide nanoparticles on commercially pure titanium dental implants. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(7):96. [22] GUADARRAMA BELLO D, FOUILLEN A, BADIA A, et al. A nanoporous titanium surface promotes the maturation of focal adhesions and formation of filopodia with distinctive nanoscale protrusions by osteogenic cells. Acta Biomater. 2017;60:339-349. [23] FARAWATI FA, NAKAPARKSIN P. What is the Optimal Material for Implant Prosthesis? Dent Clin North Am. 2019;63(3):515-530. [24] 鲁晨,陶璐,项闫颜,等.聚醚醚酮改性及在口腔种植领域的应用研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(5):819-824. [25] 潘硕,郭晓恒.聚醚醚酮在口腔种植体及义齿修复领域的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019,19(84):40-42+44. [26] MASSIA SP, STARK J. Immobilized RGD peptides on surface-grafted dextran promote biospecific cell attachment. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;56(3):390-309. [27] 陈兰花,盛道鹏.X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)表征技术研究及其应用[J].教育现代化,2018,5(1):180-182+92. [28] LIEDER R, DARAI M, THOR MB, et al. In vitro bioactivity of different degree of deacetylation chitosan, a potential coating material for titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(12):3392-3399. [29] GALLI C, PIEMONTESE M, LUMETTI S, et al. The importance of WNT pathways for bone metabolism and their regulation by implant topography. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:46-59. [30] LV L, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. The nanoscale geometry of TiO2 nanotubes influences the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by modulating H3K4 trimethylation. Biomaterials. 2015;39:193-205. [31] BAN S, IWAYA Y, KONO H, et al. Surface modification of titanium by etching in concentrated sulfuric acid. Dent Mater. 2006;22(12):1115-1120. [32] DE SOUZA FERREIRA SB, DE ASSIS DIAS BR, OBREGON CS, et al. Microparticles containing propolis and metronidazole: in vitro characterization, release study and antimicrobial activity against periodontal pathogens. Pharm Dev Technol. 2014;19(2):173-180. [33] MAMALIS AA, MARKOPOULOU C, VROTSOS I, et al. Chemical modification of an implant surface increases osteogenesis and simultaneously reduces osteoclastogenesis: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(6): 619-626. [34] BANG SM, MOON HJ, KWON YD, et al. Osteoblastic and osteoclastic differentiation on SLA and hydrophilic modified SLA titanium surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(7):831-837. [35] 李雪菁,邱小亥,赵宝红.亲水种植体促进骨整合机制研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(8):501-505. [36] CONTI M, DONATI G, CIANCIOLO G, et al. Force spectroscopy study of the adhesion of plasma proteins to the surface of a dialysis membrane: role of the nanoscale surface hydrophobicity and topography. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;61(3):370-379. [37] AMARAL IF, LAMGHARI M, SOUSA SR, et al. Rat bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and fibronectin adsorption on chitosan membranes: the effect of the degree of acetylation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(2):387-397. [38] MOURSI AM, GLOBUS RK, DAMSKY CH. Interactions between integrin receptors and fibronectin are required for calvarial osteoblast differentiation in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1997;110(Pt 18):2187-2196. [39] SAENGDEE P, CHAISRIRATANAKUL W, BUNJONGPRU W, et al. Surface modification of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride and titanium oxynitride for lactate dehydrogenase immobilization. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;67:134-138. [40] ZHU X, CHEN J, SCHEIDELER L, et al. Effects of topography and composition of titanium surface oxides on osteoblast responses. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(18):4087-4103. [41] ANSELME K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21(7): 667-681. [42] MARTIN HJ, SCHULZ KH, BUMGARDNER JD, et al. XPS study on the use of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane to bond chitosan to a titanium surface. Langmuir. 2007;23(12):6645-6651. [43] HSIAO SW, THIEN DV, HO MH, et al. Interactions between chitosan and cells measured by AFM. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(5):054117. [44] CAI K, FRANT M, BOSSERT J, et al. Surface functionalized titanium thin films: zeta-potential, protein adsorption and cell proliferation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2006;50(1):1-8. [45] 俞娟,徐俊华,范一民.壳聚糖抗菌性能研究进展[J].林业工程学报, 2018,3(5):20-27. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [5] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [6] | Gao Wenbo, Ma Zongmin, Li Shuxian, Nie Xiuji. Finite element analysis on the effect of implant length and diameter on initial stability under different bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 875-880. |
| [7] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [8] | Li Jian, Bao Zhengqi, Zhou Pinghui, Zhu Ruizhi, Li Zhixiang, Wang Jinzi. Effects of posterior single open-door laminoplasty and anterior cervical corpectomy fusion on cervical sagittal balance parameters in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 949-953. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [11] | Tan Guozhong, Tu Xinran, Guo Liyang, Zhong Jialin, Zhang Yang, Jiang Qianzhou. Biosafety evaluation of three-dimensional printed gelatin/sodium alginate/58S bioactive glass scaffolds for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 521-527. |
| [12] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [13] | Qiu Peng, Fu Qilin, Liu Min, Lan Yuyan, Wang Pin. Comparison of oral micro-adhesion on polyetheretherketone, zirconium dioxide, and pure titanium abutment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 540-545. |
| [14] | Chen Shuo, Xiao Dongqin, Li Xingping, Ran Bin, Shi Feng, Zhang Chengdong, Deng Li, Huang Nanxiang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and characterization of tantalum functional coating on titanium implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 546-552. |
| [15] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||