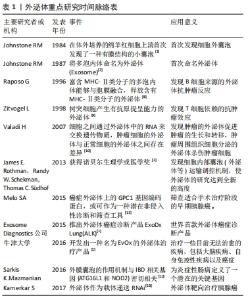
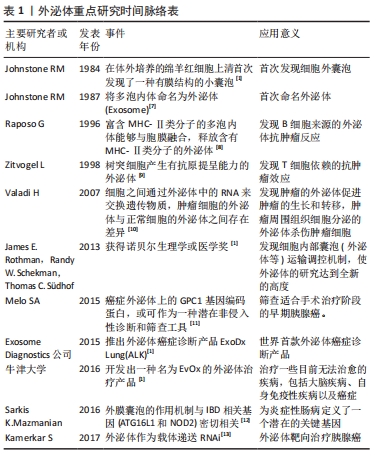
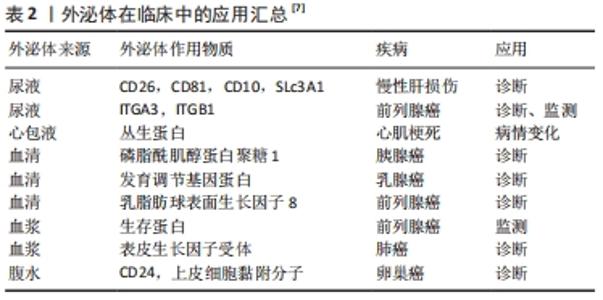
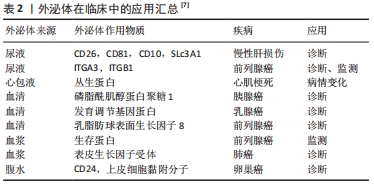
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 3065-3070.doi: 10.12307/2022.387
Previous Articles Next Articles
Important role of exosomes-mediated hypoxia-related signaling pathways in the occurrence and progression of diseases
Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Zhao Wanhua, Lin Yushi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua
- School of Medicine, Xizang Minzu University, Xianyang 712082, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-20Revised:2021-07-21Accepted:2021-07-29Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-29 -
Contact:Li Wenhua, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Medicine, Xizang Minzu University, Xianyang 712082, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Gu Xia, Master candidate, School of Medicine, Xizang Minzu University, Xianyang 712082, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760332 (to LWH); Natural Science Foundation Youth Project of Tibet Autonomous Region Science and Technology Department, No. XZ202001ZR0053G (to WPY); Tibet Autonomous Region Science and Technology Department and School Joint Project, No. XZ202101ZR0100G (to WPY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Zhao Wanhua, Lin Yushi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Important role of exosomes-mediated hypoxia-related signaling pathways in the occurrence and progression of diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3065-3070.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
在低氧相关的炎性疾病中,外泌体促进免疫应答的方式主要是介导促炎反应,且各种间充质干细胞及免疫细胞来源外泌体在低氧相关疾病上表现出优越的治疗潜力[5,16-19];而在肿瘤微环境中,肿瘤细胞来源的外泌体对免疫反应起抑制作用,促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移,加快肿瘤部位的血管生成,创造有利于肿瘤细胞生长和侵袭的微环境[20]。 2.2 低氧相关信号通路 低氧诱导因子信号通路是经典的低氧信号通路。常氧环境下,低氧诱导因子1α由脯氨酸羟化酶及肿瘤抑制蛋白介导降解,因此尽管低氧诱导因子1α在所有哺乳动物细胞内表达,但并不能在所有细胞内观察到。低氧环境下,低氧诱导因子1α顺利进入细胞核并与低氧诱导因子1β形成低氧诱导因子1复合体,从而与基因上的低氧反应原件相互作用,导致下游靶基因表达,从而影响机体内各种重要代谢过程[21-22]。PI3K/Akt作为再灌注损伤救援激酶的经典信号之一,在细胞内广泛存在,参与细胞代谢、炎症和保护过程,调节细胞凋亡、组织重塑等过程[23]。核转录因子κB通常与抑制蛋白I-κB绑定而无法表达,但当I-κB在I-κB激酶的作用下发生磷酸化降解后,核转录因子κB便可成功进入核转位,在炎症和肿瘤疾病中发挥免疫调节功能,维持机体的免疫环境平衡[24]。转化生长因子β是一种细胞活性调节因子,其功能多种多样,激活的转化生长因子β受体使下游的R-Smad(Smad3或Smad4)磷酸化并与之形成复合物,进入核内发挥作用,广泛参与细胞增殖、分化和胚胎发育[25]。各项研究表明,PI3K/Akt、核转录因子κB、转化生长因子β等信号通路在低氧环境下的表达发生变化,且受低氧诱导因子调控,影响疾病的发生发展过程,改变疾病的转归[4,26]。 2.3 外泌体介导低氧相关信号通路调控疾病 "

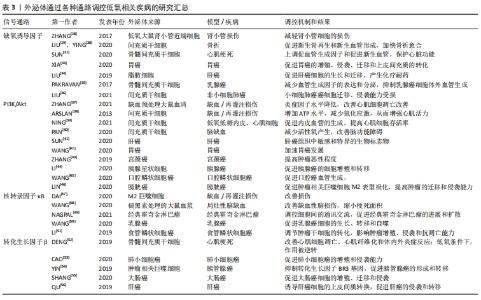
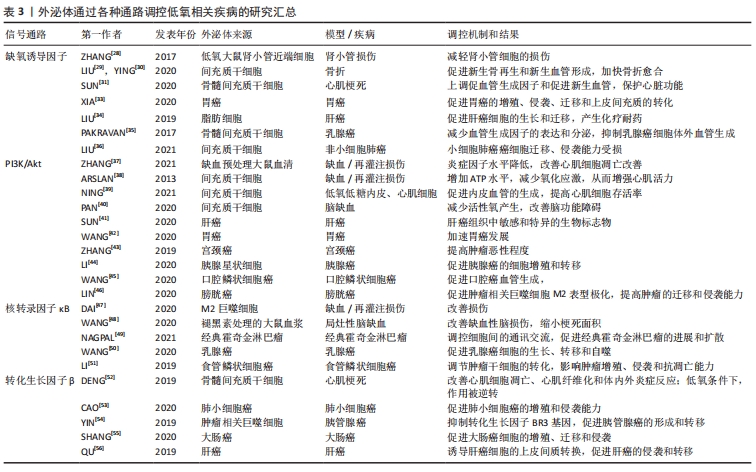
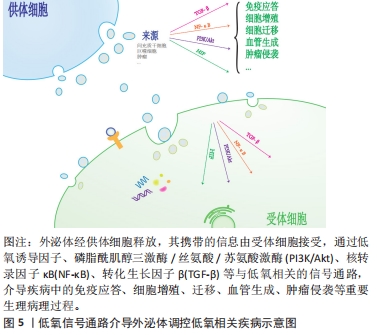
2.3.1 低氧相关疾病中的外泌体与低氧诱导因子信号通路 作为经典的低氧信号通路,低氧诱导因子信号通路与外泌体的关系密切。一些研究表明,低氧诱导因子主要通过增加一些细胞表面受体(如表皮生长因子受体、葡萄糖转运体和转铁蛋白受体等)表达,诱导外泌体形成及随后的分泌[27]。有研究团队构建的低氧大鼠肾小管近端细胞模型中,低氧并不改变肾小管近端细胞分泌的外泌体的平均大小,但以时间依赖性的方式显著增加了外泌体的产量,从而改善肾小管细胞的损伤;而低氧诱导因子1的过表达促进了低氧时外泌体的产生,增强了这种保护作用[28]。 LIU等[29]发现,低氧预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞激活了低氧诱导因子1α信号通路,促进了外泌体miR-126和相关信号通路表达,从而缩短了骨折愈合时间;而低氧诱导因子1α的敲除则导致这一效果大打折扣,此结果可能与外泌体miR-126的显著降低有关。相似的是,YING等[30]发现大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体来源的突变型低氧诱导因子1α对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖起显著促进作用,新生血管形成、新生骨的再生和临界大小骨缺损的修复效率明显提高,其效果优于骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体。低氧诱导因子1α高表达的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体还可通过上调促血管生成因子和促进新生血管,抑制大鼠心肌梗死模型纤维化来维持心脏功能,介导心脏保护[31]。由此可看出,稳定高表达低氧诱导因子1α的骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体具有较高的血管生成能力[32],这在缺血相关疾病的治疗中具有潜在的应用价值。 XIA等[33]的研究结果证实在胃癌低氧微环境中,外泌体介导miR-301-3p在胃癌细胞间传递,并通过脯氨酸羟化酶3抑制低氧诱导因子1α降解,此时低氧诱导因子1α与miR-301-3p协同作用,共同促进胃癌的增殖、侵袭、迁移。LIU等[34]的体外研究表明,在肝癌中,脂肪细胞来源的外泌体miR-23a/b转运到癌细胞中,促进肝癌细胞的生长和迁移,并通过靶向低氧诱导因子信号轴产生化疗耐药。而另一项研究中骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过调节乳腺癌细胞的低氧诱导因子信号轴,降低血管生成因子的表达和分泌水平,抑制乳腺癌细胞体外血管生成,且呈剂量依赖性[35]。LIU等[36]也发现间充质干细胞外泌体miR-204的过表达抑制了低氧诱导因子通路的活性,导致非小细胞肺癌癌细胞迁移、侵袭能力受损,对非小细胞肺癌具有抗肿瘤作用。这种外泌体对肿瘤的生长和迁移产生不同的效应的结果可能是由于不同细胞来源外泌体携带的信号分子不同。 2.3.2 低氧相关疾病中的外泌体与PI3K/Akt信号通路 ZHANG等[37]建立小鼠缺血/再灌注模型,结扎后在小鼠心肌内即刻注射缺血预处理大鼠血清外泌体,观察到小鼠体内PI3K/Akt的蛋白表达升高,而炎症因子表达水平却呈相反趋势;心肌细胞的凋亡率有所减少,心功能也显著提高。因此,缺血预处理大鼠血清外泌体可能通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路减轻心肌损伤,降低心肌梗死面积,改善心功能[37]。ARSLAN等[38]的小鼠缺血/再灌注模型也说明,间充质干细胞外泌体通过激活PI3K/Akt通路,增加心肌缺血/再灌注损伤后ATP水平,恢复了生物能量学,减少氧化应激,从而增强心肌活力,防止心肌的不良重构。而NING等[39]研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体MiRNA-153-3p在低氧低糖内皮细胞和心肌细胞的模型中激活了血管生成因子/PI3K/Akt通路,有利于内皮血管的生成,抑制了低氧对内皮细胞和心肌细胞的损伤并提高其存活率。因此,间充质干细胞外泌体可能是心肌梗死再灌注治疗的潜在佐剂。相似的,PAN等[40]的实验结果也表明,间充质干细胞外泌体过表达miR-132-3p通过调节 PI3K/Akt的水平,极大地减少了缺血/再灌注损伤中活性氧产生,改善了脑功能障碍。可见,PI3K/Akt信号通路在外泌体改善缺血缺氧相关疾病中扮演着至关重要的角色。 肝癌患者血液外泌体中差异表达的环状RNA通过靶向调节血管生成因子/血管生成因子受体、PI3K/Akt信号通路介导肿瘤的大小和分期[41],或可作为诊断肝癌有价值的生物标志物。Wang等[42]称在胃癌中,外泌体RNA LINC0155激活了PI3K/Akt通路,其中PGK 1蛋白得到了上调,PTEN蛋白得到了下调,加速了胃癌的发生发展,或可作为一种潜在的胃癌标志物。而在宫颈癌分泌物外泌体中,PI3K/Akt蛋白水平高于正常人,且PI3K/Akt基因和蛋白水平随着肿瘤恶性程度的增加而增加,提示外泌体介导的PI3K/Akt可为临床提供候选的生物标志物[43]。其他报道也称,胰腺星状细胞来源外泌体携带miR-5703在胰腺癌细胞中传播,过程中激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,在胰腺癌细胞中靶向促进胰腺癌的细胞增殖和转移[44];口腔鳞状细胞癌来源外泌体靶向上调miR-210-3p的表达,从而促进口腔鳞状细胞癌血管生成,参与口腔鳞状细胞癌的发展过程,主要是由PI3K/Akt通路介导的[45];膀胱癌外泌体miR-21也是通过调控PI3K/Akt信号途径,使肿瘤相关巨噬细胞更易向M2表型极化,更导致肿瘤的迁移、侵袭能力大大提高[46]。这些结果表明PI3K/Akt信号通路在外泌体介导肿瘤的发生、发展及侵袭、转移过程发挥着不容忽视的作用。 2.3.3 低氧相关疾病中的外泌体与核转录因子κB通路 近年来许多文献报道过来自于不同细胞的外泌体参与了缺血/再灌注导致心肌损伤这一过程。DAI等[47]在制备M2巨噬细胞来源外泌体和建立新生大鼠心肌细胞体外模型的基础上发现,M2巨噬细胞来源的外泌体miR-148A,通过下调维持氧化还原稳态和抑制核转录因子κB炎症信号通路,极大地改善了缺血/再灌注导致的心肌损伤。WANG等[48]从褪黑素处理的大鼠血浆中提取外泌体并建立了大鼠局灶性脑缺血模型,并分析了神经系统的各项检测指标,发现褪黑素在核转录因子κB通路的介导下促进了血浆外泌体的改善缺血性脑损伤作用,有效地缩小了梗死面积,极大地改善了功能恢复。由此可见,核转录因子κB通路在外泌体改善心肌缺血/再灌注导致损伤的过程中扮演着十分重要的角色。 NAGPAL等[49]的研究表明,在经典霍奇金淋巴瘤中,外泌体介导核转录因子κB通路对细胞间的通讯交流进行调控,并帮助创造了一个支持肿瘤发生发展的微环境,从而促进了经典霍奇金淋巴瘤的进展和扩散。WANG等[50]实验结果证实,乳腺癌细胞来源外泌体miR-1910-3p激活了核转录因子κB信号通路,从而在乳腺癌细胞的生长、转移和自噬的过程中起促进作用。另有实验证明,食管鳞状细胞癌lncRNA被包装成外泌体释放到肿瘤微环境中,调节肿瘤干细胞的转化,从而影响食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖、侵袭和抗凋亡能力,而这一过程依赖于核转录因子κB信号通路[51]。因此,对肿瘤的增殖和侵袭来说,核转录因子κB信号通路可能是一种正性调节因子。 2.3.4 低氧相关疾病中的外泌体与转化生长因子β信号通路 有研究结果表明,脂肪源性骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体在改善心肌细胞凋亡、心肌纤维化、体内外炎症反应和减轻心肌梗死所致的心脏损伤中有明显作用,而这些作用功能主要是通过抑制核转录因子κB和转化生长因子β1的表达介导的;而在低氧条件下,这种作用被逆转[52]。有研究报道称,外泌体细胞骨架调节因子在肺小细胞癌细胞的过表达,显著促进了肺小细胞癌的增殖和侵袭能力,而这些效应可能是通过转化生长因子β通路发挥的[53]。 在胰管腺癌的发展过程中,肿瘤相关巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体miR-501-3p激活了转化生长因子β信号通路,导致肿瘤抑制因子转化生长因子BR3基因受到抑制,从而调节胰管腺癌的发育和细胞活性,最终促进胰腺导管等腺癌的和形成和转移[54]。SHANG等[55]发现了大肠癌来源外泌体circRNA,主要通过介导miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p调节转化生长因子β1的表达,从而对大肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭等过程进行正向调控。同样的,QU等[56]发现肝癌细胞来源的外泌体对受体细胞迁移和侵袭有明显影响,如肝癌细胞系MHCC97H和MHCC97L衍生外泌体是通过转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路发挥生物学效应,诱导肝癌细胞的上皮间质转换,促进肝癌的侵袭和转移的。以上低氧信号通路介导外泌体调控低氧疾病的总结图,见图5。"
| [1] PAN B, TENG K, WU C, et al. Electron Microscopic Evidence for Externalization of the Transferrin Receptor in Vesicular Form in Sheep Reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;101(3):942-948. [2] 张灏,赵立波,叶国栋.外泌体研究、转化和临床应用专家共识[J].转化医学杂志,2018,7(6):321-325. [3] DUAN P, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. Potential role of exosomes in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoxic diseases. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1184-1201. [4] 顾霞,赵敏,王平义,等.低氧诱导因子1α与低氧相关疾病信号通路的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1284-1289. [5] EMANUELI C, SHEARN AIU, ANGELINI GD, et al. Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs in cardiovascular protection and repair. Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;71:24-30. [6] SHAO C, YANG F, MIAO S, et al. Role of hypoxia-induced exosomes in tumor biology. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):120. [7] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [8] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-1172. [9] ZITVOGEL L, REGNAULT A, LOZIER A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5):594-600. [10] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [11] MELO SA, LUECKE LB, KAHLERT C, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523(7559):177-182. [12] CHU H, KHOSRAVI A, KUSUMAWARDHANI IP, et al. Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science. 2016;352(6289):1116-1120. [13] KAMERKAR S, LEBLEU VS, SUGIMOTO H, et al. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;546(7659):498-503. [14] Wu Y, Wang X, Meng L, et al. Changes of miRNA expression profiles from cervical-vaginal fluid-derived exosomes in response to HPV16 infection. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020(17):1-8. [15] BELTING M, CHRISTIANSON HC. Role of exosomes and microvesicles in hypoxia-associated tumour development and cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med. 2015,278(3):251-263. [16] MIZUTA Y, AKAHOSHI T, GUO J, et al. Exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate histone-induced acute lung injury by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):508. [17] LI J, DENG X, JI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reverse acute lung injury through Nrf-2/ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways. Peer J. 2020;8(1):e9928. [18] CAI L, CHAO G, LI W, et al. Activated CD4(+) T cells-derived exosomal miR-142-3p boosts post-ischemic ventricular remodeling by activating myofibroblast. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7380-7396. [19] LI D, ZHANG D, TANG B, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce damage from oxidative stress and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal epithelial cells exposed to oxalate and calcium oxalate monohydrate. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1-10. [20] KUMAR A, DEEP G. Exosomes in hypoxia-induced remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2020;488:1-8. [21] TIRPE AA, GULEI D, CIORTEA SM, et al. Hypoxia: overview on hypoxia-mediated mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF genes. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6140. [22] MCGETTRICK AF, O NEILL LAJ. The role of HIF in immunity and inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):524-536. [23] HOXHAJ G, MANNING BD. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020; 20(2):74-88. [24] 曲畅,吴云红,穆靖洲,等.核转录因子κB在缺氧导致的炎症中的作用[J].生理科学进展,2018,49(1):39-43. [25] TZAVLAKI K, MOUSTAKAS A. TGF-β Signaling. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3): 487. [26] ZHANG Z, YAO L, YANG J, et al. PI3K/Akt and HIF1 signaling pathway in hypoxiaischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3547-3554. [27] CHOUDHRY H, HARRIS AL. Advances in hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 2018;27(2):281-298. [28] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, YAO Q, et al. HIF-1-mediated production of exosomes during hypoxia is protective in renal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;313(4):F906-F913. [29] LIU W, LI L, Rong Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [30] YING C, WANG R, WANG Z, et al. BMSC-exosomes carry mutant hif-1α for improving angiogenesis and osteogenesis in critical-sized calvarial defects. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2020. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.565561. [31] SUN J, SHEN H, SHAO L, et al. HIF-1α overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mediates cardioprotection in myocardial infarction by enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):373. [32] GONZALEZ-KING H, GARCIA N A, ONTORIA-OVIEDO I, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha potentiates jagged 1-mediated angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Stem Cells. 2017;35(7):1747-1759. [33] XIA X, WANG S, NI B, et al. Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2020;39(39):6231-6244. [34] LIU Y, TAN J, OU S, et al. Adipose-derived exosomes deliver miR-23a/b to regulate tumor growth in hepatocellular cancer by targeting the VHL/HIF axis. J Physiol Biochem. 2019;75(3):391-401. [35] PAKRAVAN K, BABASHAH S, SADEGHHIZADEH M, et al. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 2017;40(5):457-470. [36] LIU XN, ZHANG CB, LIN H, et al. microRNA-204 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inhibits the migration and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via the KLF7/AKT/HIF-1alpha axis. Neoplasma. 2021. doi:10.4149/neo_2021_201208N1328. [37] ZHANG J, ZHANG X. Ischaemic preconditioning‐induced serum exosomes protect against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(2):287-295. [38] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312. [39] NING W, LI S, YANG W, et al. Blocking exosomal miRNA-153-3p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates hypoxia-induced myocardial and microvascular damage by targeting the ANGPT1-mediated VEGF/PI3k/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. 2021;77: 109812. [40] PAN Q, KUANG X, CAI S, et al. miR-132-3p priming enhances the effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes on ameliorating brain ischemic injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):260. [41] SUN X, WANG Y, LI G, et al. Serum-derived three-circRNA signature as a diagnostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01302-y. [42] WANG L, BO X, YI X, et al. Exosome-transferred LINC01559 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):723. [43] ZHANG W, ZHOU Q, WEI Y, et al. The exosome-mediated PI3k/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019; 12(7):2474-2484. [44] LI M, GUO H, WANG Q, et al. Pancreatic stellate cells derived exosomal miR-5703 promotes pancreatic cancer by downregulating CMTM4 and activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:20-30. [45] WANG H, WANG L, ZHOU X, et al. OSCC exosomes regulate miR-210-3p targeting EFNA3 to promote oral cancer angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1-13. [46] LIN F, YIN HB, LI XY, et al. Bladder cancer cellsecreted exosomal miR21 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in macrophages to promote cancer progression. Int J Oncol. 2020;56(1):151-164. [47] DAI Y, WANG S, CHANG S, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;142:65-79. [48] WANG K, RU J, ZHANG H, et al. Melatonin enhances the therapeutic effect of plasma exosomes against cerebral ischemia-induced pyroptosis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Front Neurosci. 2020; 14:848. [49] NAGPAL P, DESCALZI MONTOYA DB, LODHI N. The circuitry of the tumor microenvironment in adult and pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma: cellular composition, cytokine profile, EBV, and exosomes. Cancer Rep. 2021;4(2):e1311. [50] WANG B, MAO JH, WANG BY, et al. Exosomal miR-1910-3p promotes proliferation, metastasis, and autophagy of breast cancer cells by targeting MTMR3 and activating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;489:87-99. [51] LI W, ZHANG L, GUO B, et al. Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):22. [52] DENG S, ZHOU X, GE Z, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105564. [53] CAO Q, LIU Y, WU Y, et al. Profilin 2 promotes growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of small cell lung cancer through cancer-derived exosomes. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):25981-25999. [54] YIN Z, MA T, HUANG B, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 2019;38(1):310. [55] SHANG A, GU C, WANG W, et al. Exosomal circPACRGL promotes progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p- TGF-β1 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):117. [56] QU Z, FENG J, PAN H, et al. Exosomes derived from HCC cells with different invasion characteristics mediated EMT through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Oncotargets Ther. 2019;12:6897-6905. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [3] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [5] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [8] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [9] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [10] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [11] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [12] | Lai Han, Wang Jiao, Dong Miaomiao, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Electroacupuncture intervenes with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion due to middle cerebral artery occlusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 225-231. |
| [13] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| [14] | Na Risong, Sun Liang, Zhao Zhenqun, Liang Rong, Wang Xin. Molecular mechanism by which miR-26b regulates fatty acid-binding protein 4-mediated adipocyte differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 260-265. |
| [15] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||