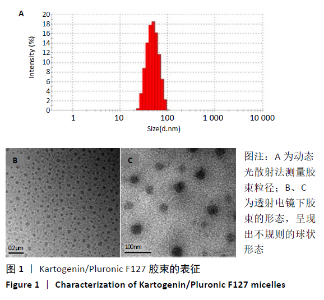
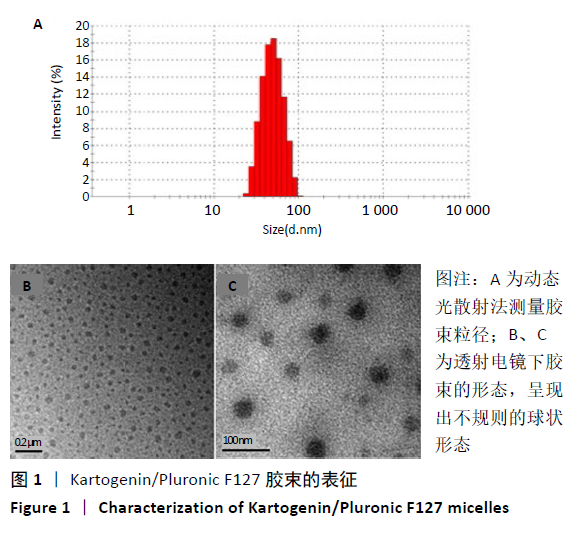
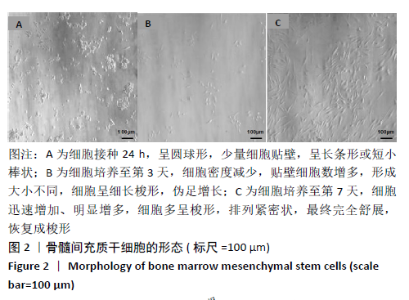
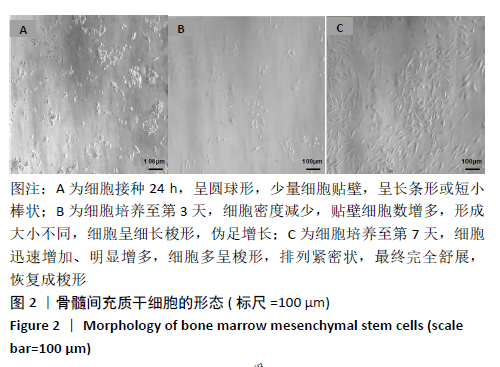
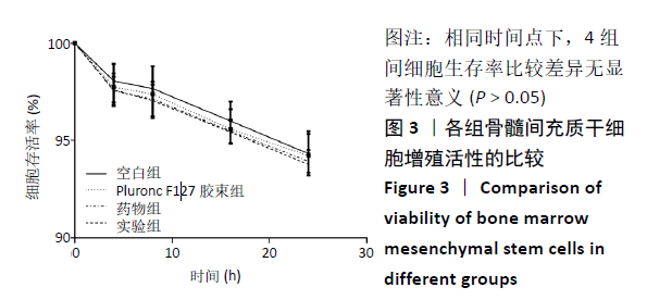
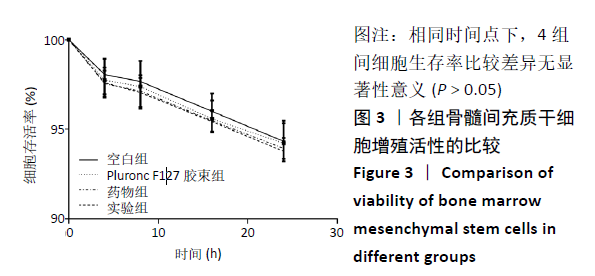
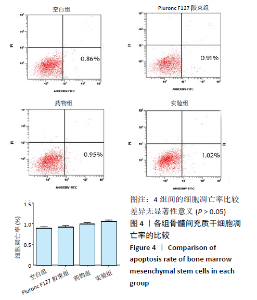
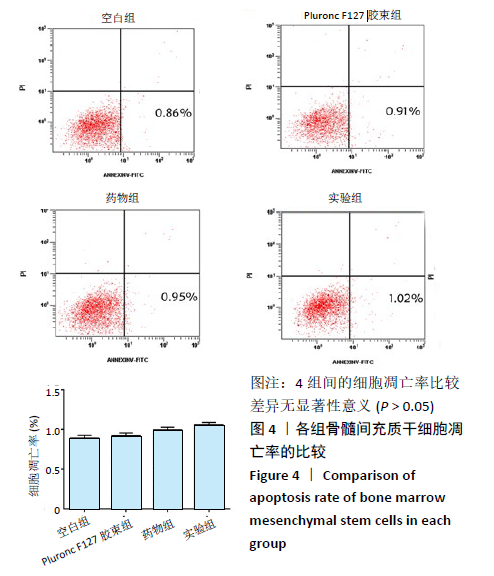
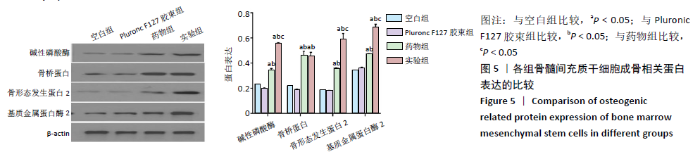
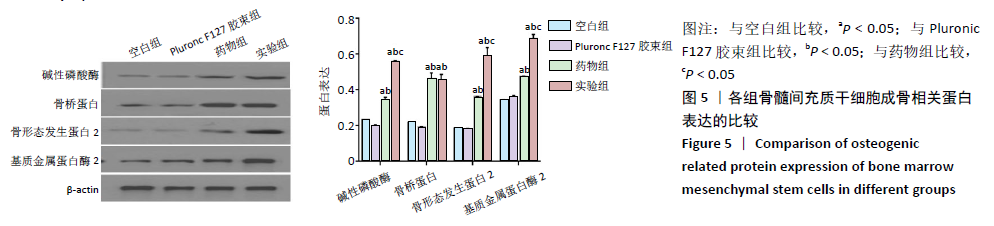
[1] TU KN, LIE JD, WAN CKV, et al. Osteoporosis: A Review of Treatment Options. P T. 2018;43(2):92-104.
[2] YE C, ZHANG W, HANG K, et al. Extracellular IL-37 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(10):753.
[3] PANG XG, CONG Y, BAO NR, et al. Quercetin stimulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation through an estrogen receptor-mediated pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4178021.
[4] 王楠.姜黄素与人参果提取物对间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响与成骨不全模型的作用[D].郑州:郑州大学,2019.
[5] 陈震东,高辉,徐房添.淫羊藿苷促进间充质干细胞成骨分化:为治疗骨缺损提供一个良好的方向[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(50):7594-7600.
[6] 马燕,张华,商建平,等.纯钛表面微米坑复合纳米管形貌对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(29):4614-4619.
[7] 王呈,薄其玉,戴国锋,等.小分子药物Kartogenin诱导骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化中基质金属蛋白酶2的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(50):7475-7480.
[8] ABBAS M, KESSENTINI A, LOUKIL H, et al. A Novel Design of an Intelligent Drug Delivery System Based on Nanoantenna Particles. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019;14(1):289.
[9] ZHANG H, WU Y, HU Y, et al. Targeted Nanoparticle Drug Delivery System for the Enhancement of Cancer Immunotherapy. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(9):1839-1866.
[10] ALLEN TM, CULLIS PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(1):36-48.
[11] Wu B, Takeshita N, Wu Y,et al. Pluronic F127 blended polycaprolactone scaffolds via e-jetting for esophageal tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(9):140.
[12] DUNG TH, HUONG LT, YOO H. Morphological Feature of Pluronic F127 and Its Application in Burn Treatment. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(2):829-832.
[13] WANG Y, CHEN G, YAN J, et al. Upregulation of SIRT1 by Kartogenin Enhances Antioxidant Functions and Promotes Osteogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1368142.
[14] XIN J, WANG S, WANG B, et al. AlPcS4-PDT for gastric cancer therapy using gold nanorod, cationic liposome, and Pluronic®F127 nanomicellar drug carriers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:2017-2036.
[15] FEITOSA VA, ALMEIDA VC, MALHEIROS B, et al. Polymeric micelles of pluronic F127 reduce hemolytic potential of amphiphilic drugs. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;180:177-185.
[16] LIU Y, FU S, LIN L, et al. Redox-sensitive Pluronic F127-tocopherol micelles: synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2635-2644.
[17] ALAVI T, REZVANIAN M, AHMAD N, et al. Pluronic-F127 composite film loaded with erythromycin for wound application: formulation, physicomechanical and in vitro evaluations. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9(2):508-519.
[18] VALIANI A, IZADI MA, BAHRAMIAN H, et al. Comparison between the effect of kartogenin and TGFβ3 on chondrogenesis of human adipose- derived stem cells in fibrin scaffold. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2017;118(10):591-597.
[19] XIA YJ, XIA H, CHEN L, et al. Efficient delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP-2) with dextran sulfate-chitosan microspheres. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 15(4):3265-3272.
[20] JIN Y, CHEN W, YANG H, et al. Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(6):5527-5534.
[21] STANIK J, KRATZSCH J, LANDGRAF K, et al. The Bone Markers Sclerostin, Osteoprotegerin, and Bone-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase Are Related to Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents, Independent of Their Association with Growth and Obesity. Horm Res Paediatr. 2019;91(1):1-8.
[22] ABOUSHADY IM, SALEM ZA, SABRY D, et al. Comparative study of the osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from different sources. J Clin Exp Dent. 2018;10(1):e7-e13.
[23] LIANG J, XU L, ZHOU F, et al. MALAT1/miR-127-5p Regulates Osteopontin (OPN)-Mediated Proliferation of Human Chondrocytes Through PI3K/Akt Pathway. J Clin Exp Dent. 2018;10(1):e7-e13.
[24] MAEDA Y, YONEMOCHI Y, NAKAJYO Y, et al. CXCL12 and osteopontin from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells improve muscle regeneration. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3305. |