Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (25): 4095-4100.doi: 10.12307/2021.026
Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived cell transplantation for patients with cerebral palsy
Zhong Liqing, Zhong Shanshan, Han Weichao, Hu Runkai, He Shufen, Ding Shaobo
- Department of Pharmacy, Dongguan People’s Hospital, Dongguan 523000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-08-04Revised:2020-08-05Accepted:2020-08-27Online:2021-09-08Published:2021-03-30 -
Contact:Ding Shaobo, Chief pharmacist, Department of Pharmacy, Dongguan People’s Hospital, Dongguan 523000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhong Liqing, Pharmacist-in-charge, Department of Pharmacy, Dongguan People’s Hospital, Dongguan 523000, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Liqing, Zhong Shanshan, Han Weichao, Hu Runkai, He Shufen, Ding Shaobo. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived cell transplantation for patients with cerebral palsy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4095-4100.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
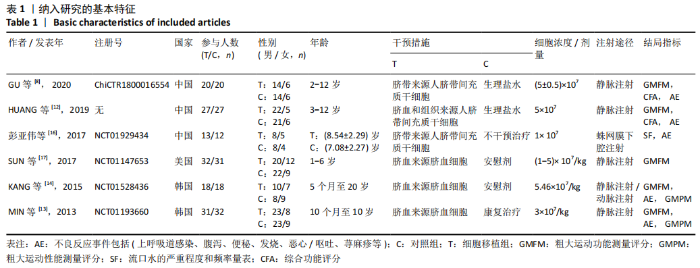
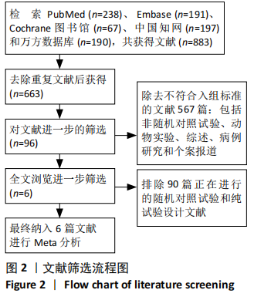
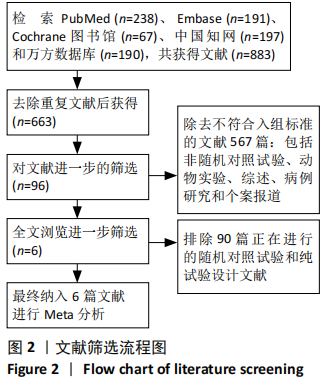
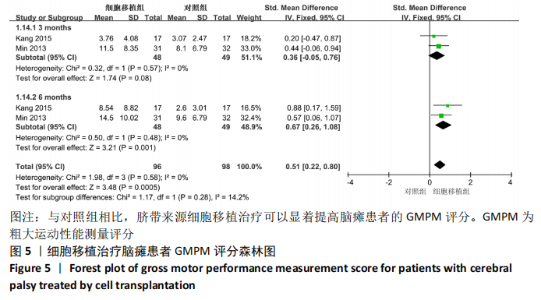
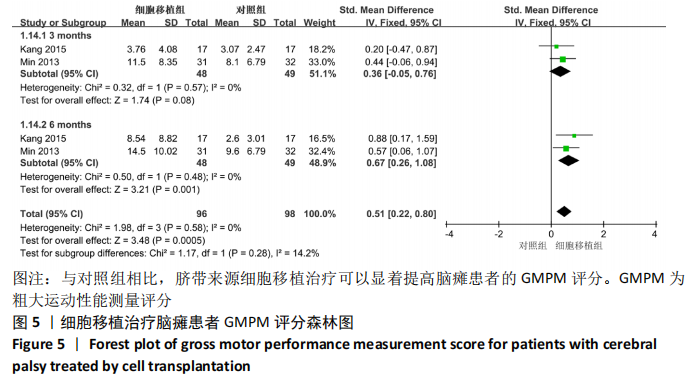
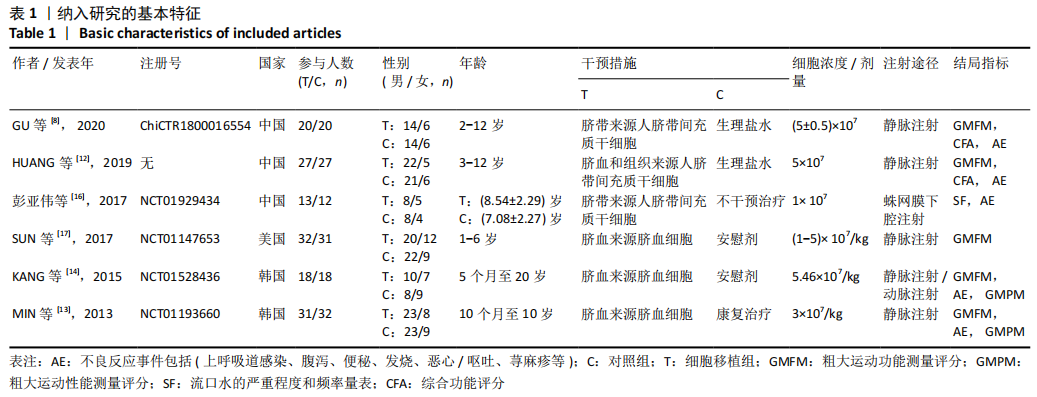
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 文章共纳入了6项随机对照试验。脐带细胞组应用脐带来源细胞移植疗法进行治疗,对照组以正常盐水做安慰剂治疗或康复疗法治疗。有5个研究的临床试验注册号为ChiCTR1800016554,NCT01929434,NCT01147653,NCT01528436和NCT01193660。其中3个随机对照试验中使用的是人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗,另外3个研究中使用脐血细胞移植治疗。主要通过静脉注射的方式进行细胞移植治疗。注射的细胞剂量可以分为107和108数量级。主要的结局指标是粗大运动功能测量评分、粗大运动性能测量评分和不良反应事件,其中不良反应事件包括上呼吸道感染、腹泻、便秘、发烧、恶心呕吐和荨麻疹等,见表1。"

2.3 文献质量评估结果 文章纳入了6项随机对照试验[8,12-14,16-17],其中有3项研究使用了随机数字表进行随机分 配[8,14,17],将其评价为“低风险”的选择性偏倚研究;其他3项未报告随机方法[12-13,16],但提及随机字样,文章评价为“不清楚风险”和“高风险”研究。 随机分组后,共有4项研究为双盲研 究[8,13-14,17],分别对患者组、参与医生、协调员和研究者实施了盲法,在选择偏倚、实施偏倚和测量偏倚方面,文章将其评估为“低风险”。HUANG等[12]研究是一项单盲研究,报告患者和他们的家人被设盲,但是并未提及这项研究是否对研究者和参与医生采用盲法,因此将其评估为“不清楚的风险”,存在选择偏倚、实施偏倚和测量偏倚。另一项研究未报道是否使用盲法[16],文章将其评价为“不清楚风险”或“高风险”,存在选择偏倚、实施偏倚和测量偏倚。文章认为有3项研究具有低损耗偏差的风险[12,14,16],因为在细胞移植治疗组和对照组中,缺失数据的比例很低,且分布均匀,评估为“低风险”研究;同时另外3项研究中有报告患者失去随 访[8,13,17],文章评估其为“不清楚风险”,存在随访偏倚。研究结果显示,患者生活方式和隐私的影响之间的相关性很低,可以认为出现报道偏倚的可能性很低,并将其评估为“不清楚风险”,存在报告偏倚,见图3。 "

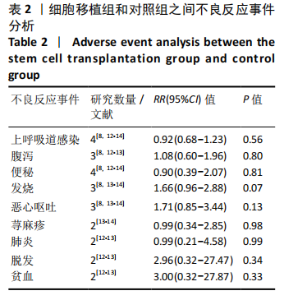
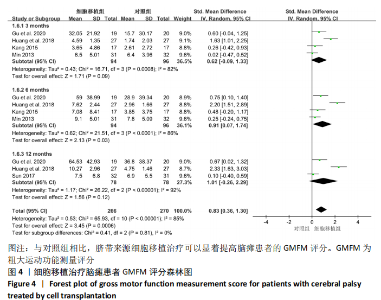
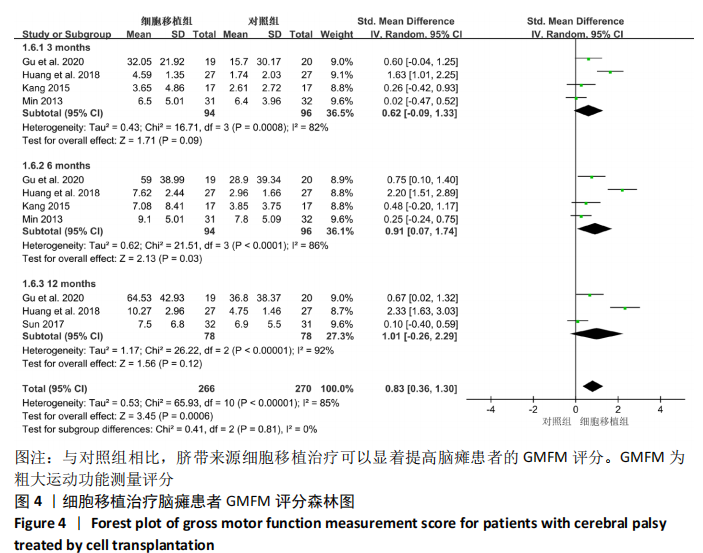
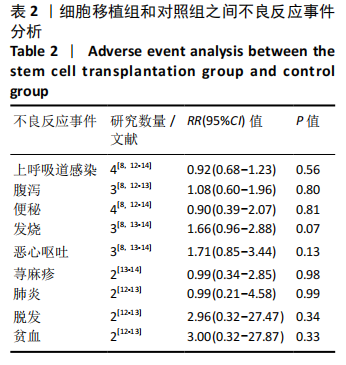
2.4.3 各组其他结局指标结果差异 GU等[8]研究发现,与对照组相比,脐带间充质干细胞移植组在移植治疗后观察到日常生活能力量表评分(ADL),综合功能评分(CFA)评分的显著改善,差异有显著性意义。KANG等[14]研究采用正电子发射断层扫描仪(PET)扫描显示,与对照组相比,接受脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗的患者的脑室周围炎症水平显著降低。MIN等[13]研究发现接受脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗患者的BSID-Ⅱ心理量表原始得分和BSID-Ⅱ运动量表原始分数均在3和6个月内显著提高。彭亚伟等[16]研究发现脐带间充质干细胞移植组流涎频率及严重程度评分和流涎商测定在1,3,6个月均明显低于对照组,差异有显著性意义。 2.4.4 各组不良反应事件差异 为了进一步探究细胞移植治疗脑瘫患者的安全性,文章对纳入研究报道的不良反应事件进行了分析。Meta分析表明,与对照组相比,细胞移植治疗脑瘫患者的不良反应事件包括上呼吸道感染(RR=0.92,95%CI:0.68-1.23,P=0.56)、腹泻(RR=1.08,95%CI:0.60-1.96,P= 0.80)、便秘(RR=0.90,95%CI:0.39-2.07,P=0.81)、发热(RR=1.66,95%CI:0.96-2.88,P=0.07)、呕吐恶心(RR=1.71,95%CI:0.85-3.44,P=0.13)、荨麻疹(RR= 0.99,95%CI:0.34-2.85,P=0.98)、肺炎 (RR=0.99,95%CI:0.21-4.58,P= 0.99),脱发(RR=2.96,95%CI:0.32-27.47,P=0.34)和贫血(RR=3.00,95% CI: 0.32-27.87,P=0.33)差异均无显著性意义,见表2。尽管在1个研究中[16],细胞移植组患者腰椎穿刺术后出现颅内压低的情况,包括轻度头晕头痛、恶心呕吐,但躺在去掉枕头的床上,静脉滴注生理盐水,患者的症状缓解消失。"

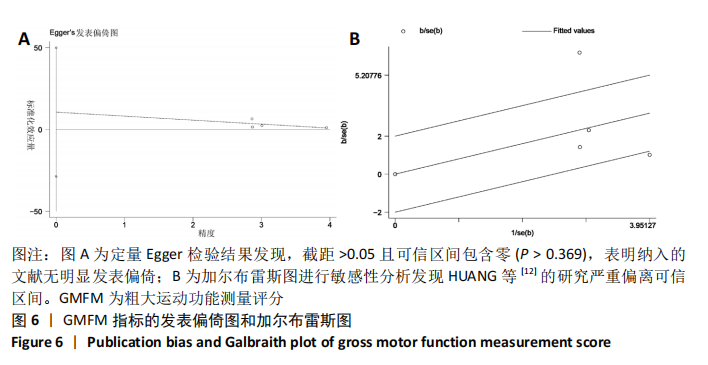
2.5 纳入研究发表偏倚与敏感性分析结果 Meta分析发表偏倚使用漏斗图的方式进行评价,文章采用Stata 12软件对GMFM指标进行Egger发表偏倚检验,从而对本Meta分析的发表偏倚进行更准确定量的评价。定量Egger检验结果发现,截距> 0.05且可信区间包含零(95%CI:-28.76-49.79,P > 0.369),表明纳入的文献无明显发表偏倚,见图6A。 该Meta分析采用考察单项研究对总合并效应量的影响进行敏感性分析,如果敏感性分析前后合并效应量指标没有发生趋势改变,说明Meta分析结果较为可信,若敏感性分析前后结局指标发生趋势改变,提示存在与干预措施有关的潜在的重要因素,影响结果的可信度[18]。文章对异质性高的GMFM指标使用加尔布雷斯图进行敏感性分析,结果发现HUANG等[12]的研究严重偏离可信区间,见图6B,排除该研究后,发现6个月的GMFM指标由(SMD=0.91,95%CI:0.07-1.74,P=0.03)变为(SMD=0.45,95%CI:0.11-0.79,P=0.01),趋势并没有发生改变但异质性I2=86%变为I2=0%,异质性显著降低。敏感性分析结果说明合并的结局指标具有可靠性。"
| [1] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会, 中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑瘫康复专业委员会. 小儿脑性瘫痪的定义、分型和诊断条件[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2007,29(5):309. [2] 中华医学会儿科学分会康复学组.儿童脑性瘫痪运动障碍的康复建议[J].中华儿科杂志, 2020,58(2):91-95. [3] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会,中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑性瘫痪康复专业委员会,编委会中国脑性瘫痪康复指南.中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2015):第一部分[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(7):747-754. [4] TOYOKAWA S, MAEDA E, KOBAYASHI Y. Estimation of the number of children with cerebral palsy using nationwide health insurance claims data in Japan. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017;59(3):317-321. [5] SELLIER E, SURMAN G, HIMMELMANN K, et al. Trends in prevalence of cerebral palsy in children born with a birthweight of 2,500 g or over in Europe from 1980 to 1998. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):635-642. [6] LIU X, FU X, DAI G, et al. Comparative analysis of curative effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell and bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation for spastic cerebral palsy. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):48. [7] RAH W, LEE Y, MOON J, et al. Neuroregenerative potential of intravenous G-CSF and autologous peripheral blood stem cells in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):16. [8] GU J, HUANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Therapeutic evidence of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy: a randomized, controlled trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):43. [9] 刘梦婷,饶巍,韩兵,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的体外免疫调节特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(7):1063-1068. [10] 孙自敏.脐血移植临床应用30年的回顾及展望[J].器官移植,2020,11(2):199-203. [11] JIAO Y, LI X Y, LIU J. A New approach to cerebral palsy treatment: discussion of the effective components of umbilical cord blood and its mechanisms of action. Cell Transplant. 2019; 28(5):497-509. [12] HUANG L, ZHANG C, GU J, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell infusion for children with cerebral palsy. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(2):325-334. [13] MIN K, SONG J, KANG J Y, et al. Umbilical cord blood therapy potentiated with erythropoietin for children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Stem Cells. 2013;31(3):581-591. [14] KANG M, MIN K, JANG J, et al. Involvement of immune responses in the efficacy of cord blood cell therapy for cerebral palsy. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(19):2259-2268. [15] XIE B, CHEN M, HU R, et al. Therapeutic evidence of human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5701920. [16] 彭亚伟,王晓东,徐成娥,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗脑瘫患儿流涎症疗效观察[J].武警医学,2017,28(5):478-482. [17] SUN JM, SONG AW, CASE LE, et al. Effect of autologous cord blood infusion on motor function and brain connectivity in young children with cerebral palsy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2071-2078. [18] 谢保城,王清辉,许周媚,等.自体干细胞移植联合血管成形术治疗糖尿病足或肢体缺血性疾病的系统评价[J].中国普通外科杂志,2017,26(12):1589-1598. [19] EGGENBERGER S, BOUCARD C, SCHOEBERLEIN A, et al. Stem cell treatment and cerebral palsy: Systemic review and meta-analysis. World J Stem Cell. 2019;11(10):891-903. [20] KOMAN LA, SMITH BP, SHILT JS. Cerebral palsy. Lancet. 2004;363(9421):1619-1631. [21] WIMALASUNDERA N, STEVENSON V L. Cerebral palsy. Pract Neurol. 2016;16(3):184-194. [22] SCHIARITI V, SELB M, CIEZA A, et al. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Sets for children and youth with cerebral palsy: a consensus meeting. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57(2): 149-158. [23] ALOTAIBI M, LONG T, KENNEDY E, et al. The efficacy of GMFM-88 and GMFM-66 to detect changes in gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy (CP): a literature review. Disabil Rehabil. 2014;36(8):617-627. [24] WANG X, HU H, HUA R, et al. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells on motor functions of identical twins with cerebral palsy: pilot study on the correlation of efficacy and hereditary factors. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(2): 224-231. [25] ZHANG C, HUANG L, GU J, et al. Therapy for cerebral palsy by human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation combined with basic rehabilitation treatment: a case report. Glob Pediatr Health. 2015.doi:10.11177/2333794X-15574091X. [26] KO J, KIM M. Inter-rater Reliability of the K-GMFM-88 and the GMPM for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012;36(2): 233-239. [27] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞制剂的质量管理及有效性和安全性[J].转化医学杂志,2020, 9(2):65-69. [28] LIU M, LEI H, DONG P, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Elderly Exhibit Decreased Migration and Differentiation Abilities with Senescent Properties. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(9):1505-1519. [29] PACHóN-PEñA G, SERENA C, EJARQUE M, et al. Obesity Determines the Immunophenotypic Profile and Functional Characteristics of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4):464-475. [30] XIE B, LUO H, ZHANG Y, et al. Autologous stem cell therapy in critical limb ischemia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:7528464. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [8] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [9] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [10] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [11] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [12] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [13] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [14] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [15] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||