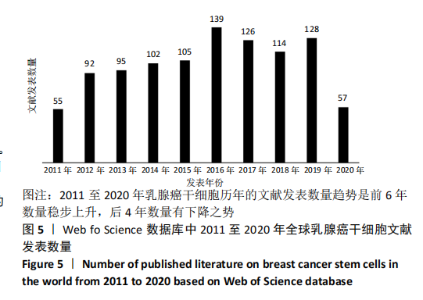
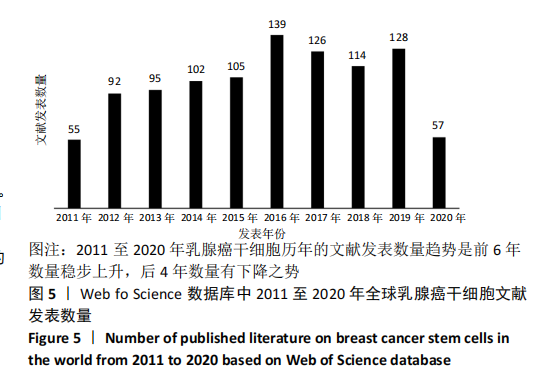
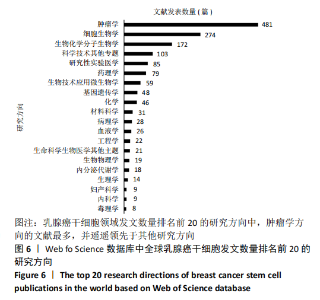
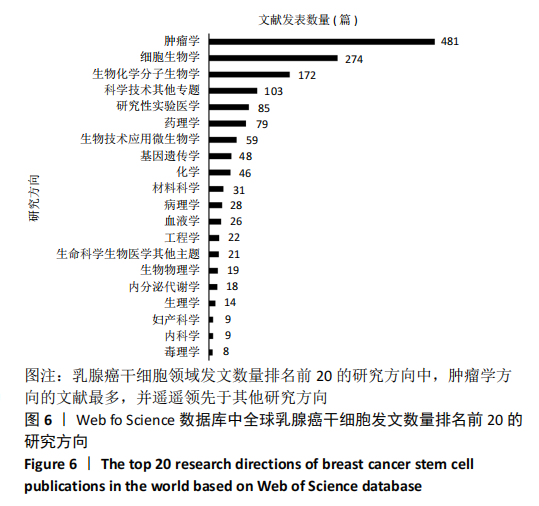
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (25): 4001-4008.doi: 10.12307/2021.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database
Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan
- Department of Mammary Gland, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-09Revised:2020-05-14Accepted:2020-08-07Online:2021-09-08Published:2021-03-26 -
Contact:Lu Yuyun, Department of Mammary Gland, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lu Yuyun, Attending physician, Department of Mammary Gland, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81603653 (to CBY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
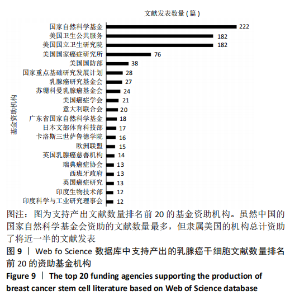
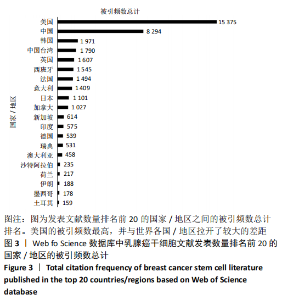
2.2.4 支持乳腺癌干细胞研究的主要资助基金分析 基金分析显示,国家自然科学基金支持产出的文献数量最多,支持了222篇文献的发表,各占全球发表总数的21.915%。其次是NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NIH USA(美国国立卫生研究所)和UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH HUMAN SERVICES(美国卫生公共服务部)都支持产出了182篇文献,占比17.966%,NIH NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE NCI(美国国家癌症研究所)支持产出的文献数量居全国第3,共有76篇文献发表,占比7.502%。见图9。"

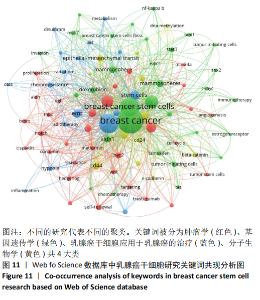
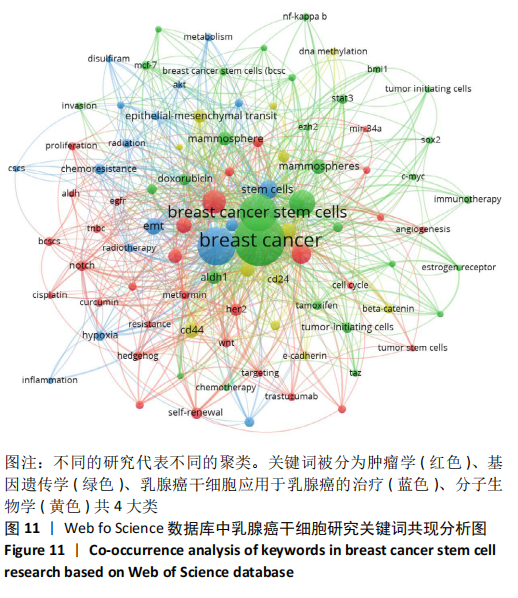
2.3 有关乳腺癌干细胞文献的可视化分析 2.3.1 乳腺癌干细胞的研究方向分析 利用VOSviewer软件的关键词共现分析,文章以共同出现次数大于5次为纳入标准,在1 780个关键词中将91个关键词纳入研究,见图11。根据关键词共现图谱,文章将有关于乳腺癌干细胞的研究分为4大类:肿瘤学(红色)、基因遗传学(绿色)、乳腺癌干细胞应用于乳腺癌的治疗(蓝色)、分子生物学(黄色)。将上述4大研究方向细化,在肿瘤学中,出现次数较多的关键词有:三阴性乳腺癌、扩散、靶标、通路、抵制、药物抵抗、转移、姜黄素、顺铂、细胞凋亡、二甲双胍和细胞周期;在基因遗传学中,c-myc、stat3、bmi1、ezh2、nanog、自我吞噬和sox2为常出现的关键词;在乳腺癌干细胞应用于乳腺癌的治疗中,出现次数较多的关键词有:抗乳腺癌干细胞特性、新陈代谢、生物标志物、放射疗法、双硫仑、辐射及上皮细胞-间充质转化;在分子生物学中,beta-catenin、DNA-甲基化、cd24、e-cadherin和cd44为出现次数较多的关键词。结合表1中被引频次top10文献的相关信息分析,文章发现:有关化疗与二甲双胍的联合治疗、抗血管生成剂的靶向治疗、sox2、ezh2及nanog基因涉及到的调节机制的探索、上皮-间充质干细胞转化及CD44和CD24分子标志物的研究是重点研究方向。 "
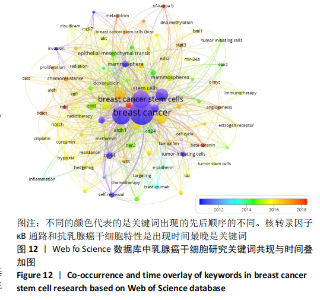
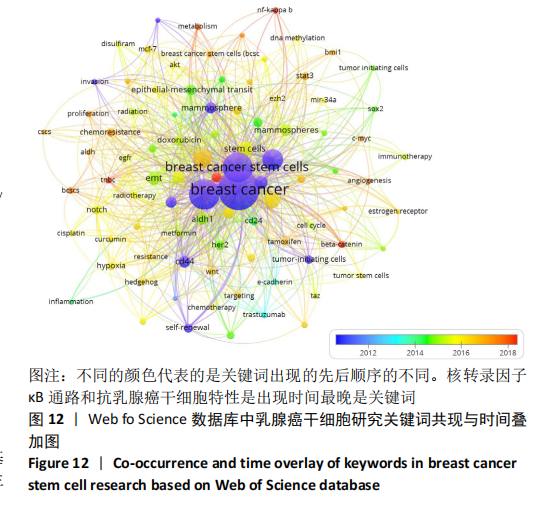
2.3.2 乳腺癌干细胞发展趋势分析 运用VOSviewer的发展趋势分析功能,文章整理出了关键词出现的先后顺序,见图12,图中右下角按颜色从紫-蓝-青-绿-黄-橙-红排列的刻度线代表了时间的先后顺序,圆圈的颜色越接近紫色说明关键词出现在研究早期,越接近红色则说明越接近如今的研究热点。基因遗传学、分子生物学、肿瘤学及乳腺癌干细胞应用于乳腺癌的治疗是该领域发展趋势变化。出现时间最接近当今的关键词是核转录因子κB(NF-κB)通路和抗乳腺癌干细胞特性(stemness)。根据表2,3中的相关文献信息,文章推断:与NF-κB通路相关的HRG/ErbB3信号、紫檀芪和双硫仑是研究热点;与乳腺癌干细胞特性相关的上皮/间充质杂质基因、 miR34a-NOTCH1轴和LINC00511/miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog轴是重点研究内容。"
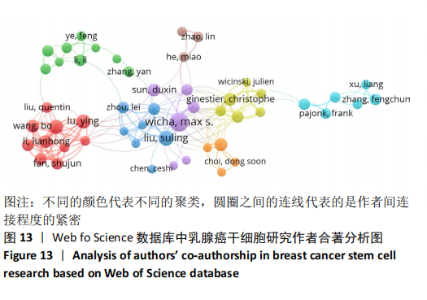
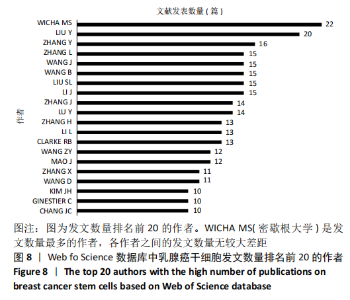
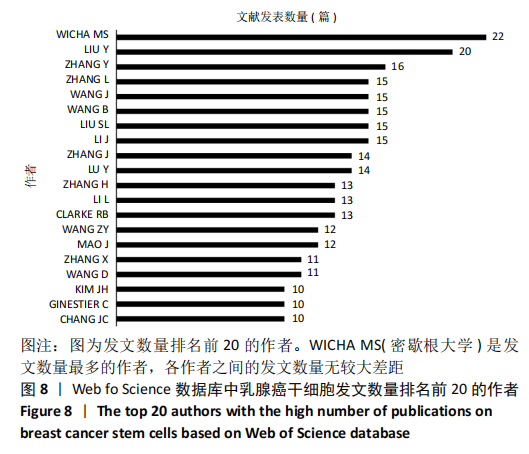
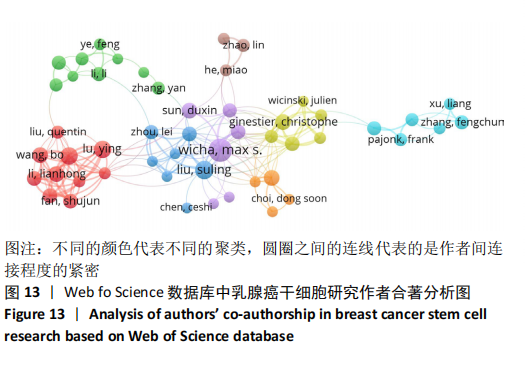
2.4 乳腺癌干细胞的合著分析 2.4.1 作者合著分析 以大于5篇为纳入标准,6 545名作者中共有96名作者被纳入研究范围。链接强度排名前5的作者依次是Mao Jun(大连医科大学)(链接强度=65),Li Lianhong(大连医科大学)和Lu Ying(大连医科大学)(链接强度=56),Fan Shujun(大连医科大学)、Liu Suling(复旦大学)、Song Bo(大连医科大学)、Yu Xiaotang(大连医科大学)(链接强度=55),Wicha Max s(密歇根大学)(链接强度=54),Ginestier Christophe(艾克斯-马赛大学)(链接强度=48),见图13。"
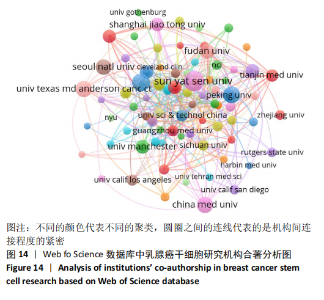
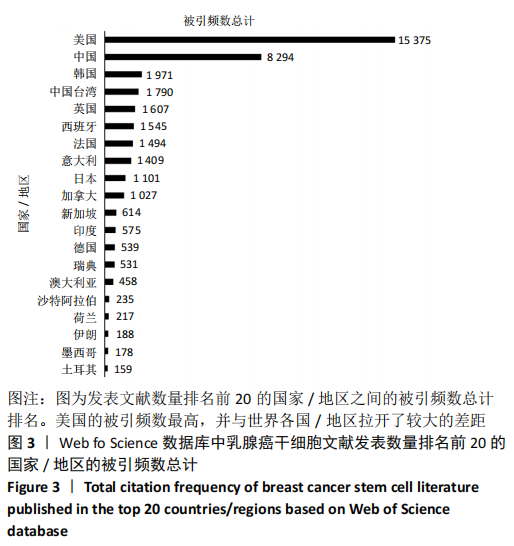
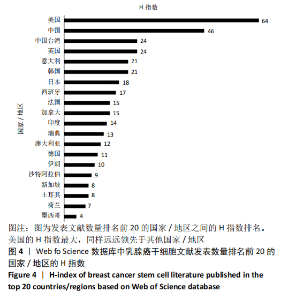
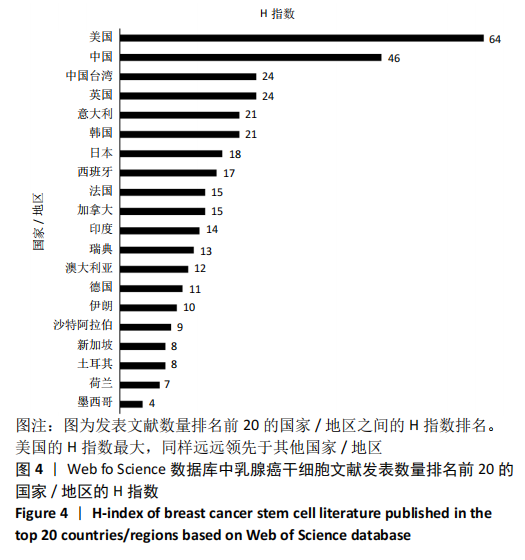
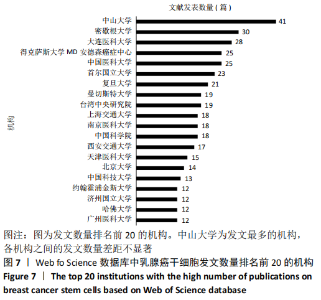
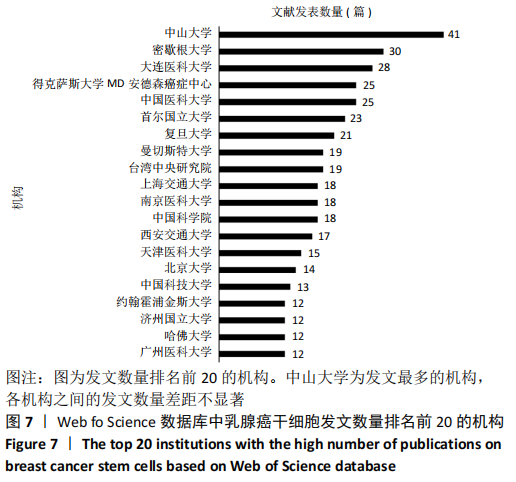
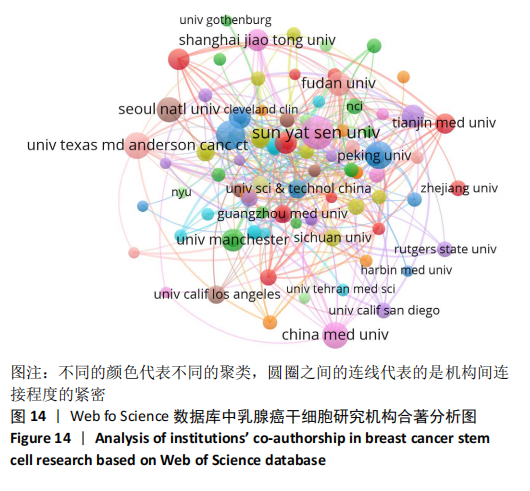
2.4.2 机构合著分析 以大于5篇为纳入标准,在1 302个机构中最终有108个机构符合纳入标准。在乳腺癌干细胞领域合著较多的机构见图14,其中进入前5的依次是中山大学(链接强度= 47)、复旦大学(链接强度=43)、大连医科大学(链接强度=31)、德克萨斯大学德森癌症研究中心(链接强度=30)和密歇根大学(链接强度=29)。 2.4.3 国家/地区合著分析 以大于5篇为纳入标准,在60个国家/地区中有31个国家/地区进入国家/地区合著分析中。链接强度前5名依次为美国(链接强度= 197)、中国(链接强度=109)、英国(链接强度=60)、意大利(链接强度=33)和中国台湾(链接强度=30)。 "
| [1] 王宁,刘硕,杨雷,等.2018全球癌症统计报告解读[J].肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2019,5(1):87-97. [2] CHEN W, ZHENG R, BAADE PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115-132. [3] 尤海生,高乾,陈思颖,等.乳腺癌患者治疗方案指南依从性评价[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2020,39(3):186-190. [4] 刘婷婷,马腾,刘焱,等.乳腺癌干细胞新型多肽标志物的筛选[J].现代肿瘤医学,2020,28(11):1834-1838. [5] 沙新海,邢广琳,黄强.补骨脂素对乳腺癌干细胞的毒性作用及TopoⅡα基因mRNA和蛋白表达水平的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(22):2397-2400. [6] 臧传鑫,刘瑞娟,赵文歌,等.乳腺癌干细胞相关信号通路及其抑制剂的研究进展[J].肿瘤学杂志,2019,25(1):27-31. [7] 周飞,乔娜,马爽,等.乳腺癌肿瘤干细胞及表面标志物的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2019,25(20):4014-4018. [8] 李欣怡,王皓,曾晨欣,等.乳腺癌的分子靶向药物治疗研究进展[J].肿瘤药学, 2020,10(3):257-263. [9] 王鹏,陈晓,任浩.乳腺癌患者TGF-β、SMAD3、SOX2表达特点及临床意义[J].实验与检验医学,2020,38(1):159-161. [10] 吴海歌,高晨慧,刘雨晴,等.乳腺癌干细胞的调控及作用[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2016,43(9):801-805. [11] 黄天霁,杨升东,林豪,等.VOSviewer软件绘制经皮穿刺椎体成形和经皮穿刺球囊扩张椎体后凸成形领域的文献计量学科学知识图谱[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(15):2410-2417. [12] 蔡建平,江子芳.我国乳腺癌患者淋巴水肿的文献计量学分析[J].解放军护理杂志, 2018,35(15):21-24. [13] 沙晓妍,刘竹韵,林细吟.2001-2015年Web of Science数据库中乳腺癌护理研究论文的计量学分析[J].护理学杂志,2017, 32(3):84-87. [14] 姜桐桐,唐沛妍,史铁英.乳腺癌患者积极心理学研究领域文献可视化分析[J].医学与哲学(B),2016,37(12):80-82. [15] HIRSCH JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46): 16569-16572. [16] 何晓铭,龚水帝,郑小龙,等.应用文献计量学与可视化分析探讨骨与关节结核的全球研究现状及发展趋势[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3234-3239. [17] ILIOPOULOS D, HIRSCH HA, WANG G, et al. Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(4):1397-1402. [18] CONLEY SJ, GHEORDUNESCU E, KAKARALA P, et al. Antiangiogenic agents increase breast cancer stem cells via the generation of tumor hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(8):2784-2789. [19] LEIS O, EGUIARA A, LOPEZ-ARRIBILLAGA E, et al. Sox2 expression in breast tumours and activation in breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1354-1365. [20] CHANG CJ, YANG JY, XIA W, et al. EZH2 promotes expansion of breast tumor initiating cells through activation of RAF1-β-catenin signaling. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(1):86-100. [21] ZHANG C, SAMANTA D, LU H, et al. Hypoxia induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated m⁶A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(14):E2047-E2056. [22] LIU S, CONG Y, WANG D, et al. Breast cancer stem cells transition between epithelial and mesenchymal states reflective of their normal counterparts. Stem Cell Reports. 2013;2(1):78-91. [23] RICARDO S, VIEIRA AF, GERHARD R, et al. Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: expression distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64(11):937-946. [24] PARK YH. The nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and response to treatment in breast cancer. Pharmacogenomics. 2017;18(18):1697-1709. [25] BURNETT JP, LIM G, LI Y, et al. Sulforaphane enhances the anticancer activity of taxanes against triple negative breast cancer by killing cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2017; 394:52-64. [26] OJO D, WEI F, LIU Y, et al. Factors Promoting Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer via Stimulating Breast Cancer Stem Cell Expansion. Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(19): 2360-2374. [27] LU H, CLAUSER KR, TAM WL, et al. Addendum: A breast cancer stem cell niche supported by juxtacrine signalling from monocytes Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(12):1607. [28] HINOHARA K, KOBAYASHI S, KANAUCHI H, et al. ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase/NF-κB signaling controls mammosphere formation in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(17):6584-6589. [29] MAK KK, WU AT, LEE WH, et al. Pterostilbene, a bioactive component of blueberries, suppresses the generation of breast cancer stem cells within tumor microenvironment and metastasis via modulating NF-κB/microRNA 448 circuit. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(7):1123-1134. [30] HAN D, WU G, CHANG C, et al. Disulfiram inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like features in breast cancer via ERK/NF-κB/Snail pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(38): 40907-40919. [31] TANG T, GUO C, XIA T, et al. LncCCAT1 Promotes Breast Cancer Stem Cell Function through Activating WNT/β-catenin Signaling. Theranostics. 2019;9(24):7384-7402. [32] ZHENG A, SONG X, ZHANG L, et al. Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1/miR-5582-3p/TCF7L2 axis regulates breast cancer stemness via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):305. [33] DITTMER J. Breast cancer stem cells: Features, key drivers and treatment options. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;53:59-74. [34] ALRAOUJI NN, AL-MOHANNA FH, GHEBEH H, et al. Tocilizumab potentiates cisplatin cytotoxicity and targets cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59(9):1041-1051. [35] TANG W, LI M, QI X, et al. β1,4-Galactosyltransferase V Modulates Breast Cancer Stem Cells through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res Treat. 2020. doi:10.4143/crt.2020.093. [36] PEI J, WANG Y, LI Y. Identification of key genes controlling breast cancer stem cell characteristics via stemness indices analysis. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):74. [37] GROSSE-WILDE A, FOUQUIER D’HÉROUËL A, MCINTOSH E, et al. Stemness of the hybrid Epithelial/Mesenchymal State in Breast Cancer and Its Association with Poor Survival. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0126522. [38] PARK EY, CHANG E, LEE EJ, et al. Targeting of miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2014;74(24):7573-7582. [39] LU G, LI Y, MA Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):289. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||