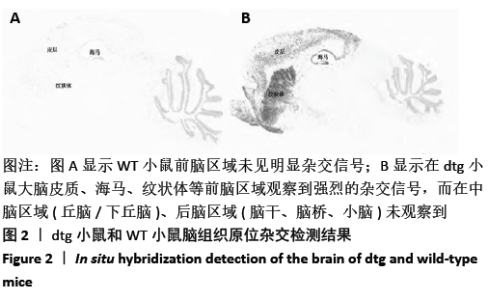
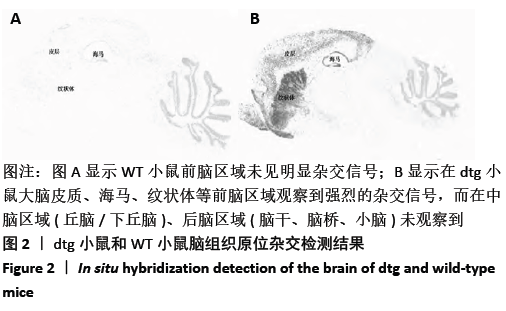
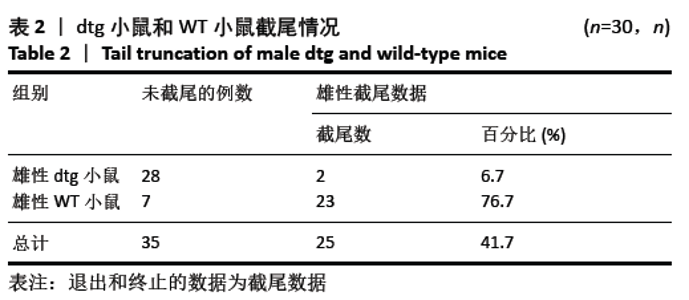
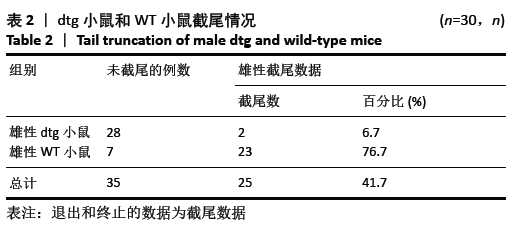
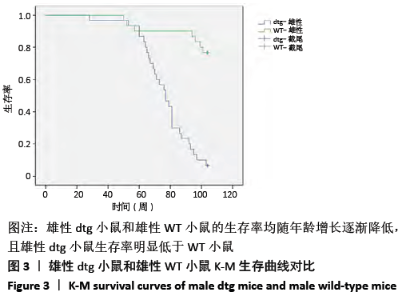
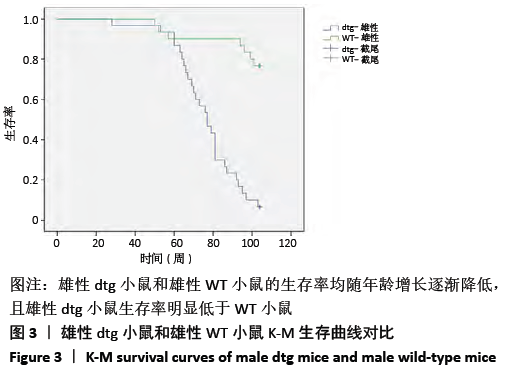
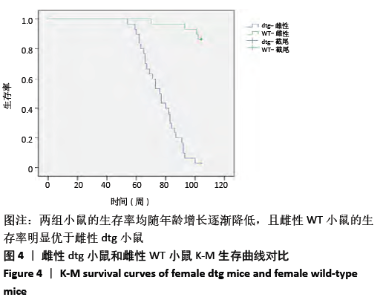
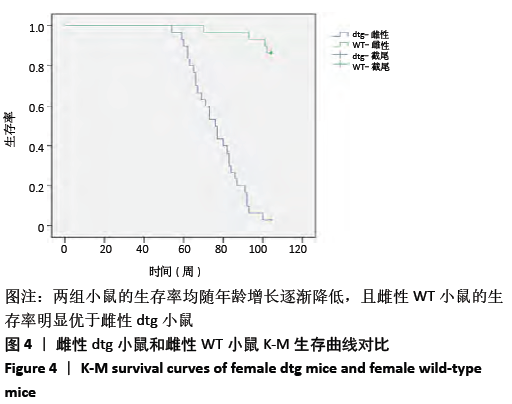
[1] Ma H, Miller C. Trapped in a Double Bind: Chinese Overseas Student Anxiety during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Health Commun. 2020;12:1-8.
[2] Eskander N, Vadukapuram R, Zahid S, et al. Post-traumatic Stress Disorder and Suicidal Behaviors in American Adolescents: Analysis of 159,500 Psychiatric Hospitalizations. Cureus. 2020;12:e8017.
[3] McNeill RV, Ziegler GC, Radtke F, et al. Mental health dished up-the use of iPSC models in neuropsychiatric research. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 May 7. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02197-9.
[4] BALLAZ SJ, BOURIN M, AKIL H, et al. Blockade of the cholecystokinin CCK-2 receptor prevents the normalization of anxiety levels in the rat. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020;96:109761.
[5] ROCA-LAPIROT O, FOSSAT P, MA S, et al. Acquisition of analgesic properties by the cholecystokinin (CCK)/CCK2 receptor system within the amygdala in a persistent inflammatory pain condition. Pain. 2019; 160: 345-357.
[6] 姜云璐,王正文,陈京,等.胆囊收缩素Ⅱ型受体研究进展[J].济宁医学院学报,2018,41(3):199-203.
[7] RATAUD J, DARCHE F, PIOT O, et al. Anxiolytic effect of CCK-antagonists on plus-maze behavior in mice.Brain Res. 1991;48(1-2):315-317.
[8] CHEN Q, NAKAJIMA A, MEACHAM C, et al. Elevated cholecystokininergic tone constitutes an important molecular/neuronal mechanism for the expression of anxiety in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103(10):3881-3886.
[9] CHEN Q, TANG M, MAMIYA T, et al. Bi-Directional effect of cholecystokinin receptor-2 overexpression on Stress-Triggered fear memory and anxiety in the mouse. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15999.
[10] MARIAM H, LAUREN BS. Anxiety and depression in Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Antecedents, consequences, and differential impact on well-being and quality of life. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020;44:102261.
[11] BUNEVICIUS A, DELTUVA VP, TAMASAUSKAS A. Association of pre-operative depressive and anxiety symptoms with five-year survival of glioma and meningioma patients: a prospective cohort study.Oncotarget. 2017;8:57543-57551.
[12] DING T, WANG X, FU A, et al. Anxiety and depression predict unfavorable survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e17314.
[13] AMY M, JANE W, STEPHEN P, et al. Does depression treatment improve the survival of depressed patients with cancer? A long-term follow-up of participants in the SMaRT Oncology-2 and 3 trials.Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5(4):321-326.
[14] 石宏,何伟,王晓宇,等.TRPV1和ASIC3基因敲除小鼠的寿命观察[J].中国比较医学杂志,2014,24(10):79-89.
[15] 唐红,唐晓琴,邓飞,等.presenilin-1/presenilin-2双基因敲除小鼠的寿命观察[J].中国比较医学杂志,2016,26(11):6-10.
[16] ZWANZGER P, DOMSCHKE K, BRADWEJN J, et al. Neuronal network of panic disorder: the role of the neuropeptide cholecystokinin. Depress Anxiety. 2012;29(9):762-774.
[17] ZHANG JF, CHEN L, ZHANG J, et al. Drug Inducible CRISPR/Cas Systems.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;17:1171-1177.
[18] BAI Y, ZHU C, FENG M, et al. Establishment of A Reversibly Inducible Porcine Granulosa Cell Line.Cells.2020; 9:156.
[19] 张文将,易健,贾平,等.载脂蛋白E基因敲除(APOE-/-)小鼠基因的鉴定方法及模型应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7): 1103-1108.
[20] JIANG H, LIU X, LI Q. Application of transgenic animal models in colorectal cancer research.World Chin J Digest. 2015;23(10):1603-1608.
[21] GERBER SD, BEAUCHAMP P, ZHUANG L, et al. Functional domains of the FgfrL1 receptor. Developmental biology. 2020;461(1): 43-54.
[22] MARCHESE M, COWAN D, HEAD E, et al. Autoimmune manifestations in the 3xTg-AD model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014; 39(1):191-210.
[23] RAE EA, BROWN RE. The problem of genotype and sex differences in life expectancy in transgenic AD mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015; 57:238-251.
[24] BOGUE MA, PETERS LL, PAIGEN B, et al. Accessing Data Resources in the Mouse Phenome Database for Genetic Analysis of Murine Life Span and Health Span. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016;71(2):170-177.
[25] PUGH PL, RICHARDSON JC, BATE ST, et al. Non-cognitive behaviours in an APP/PS1 transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease.Behav Brain Res. 2007;178(1):18-28.
|