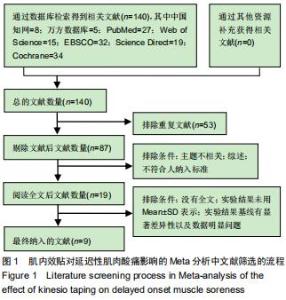
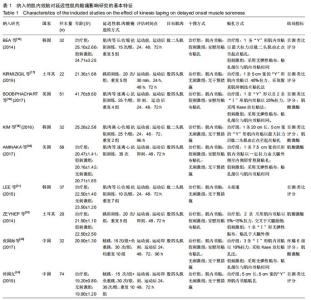
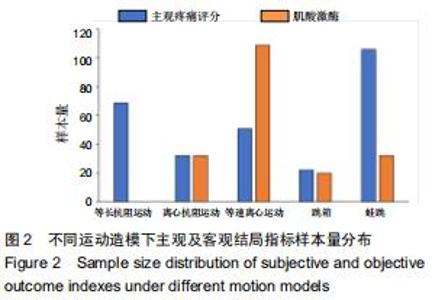
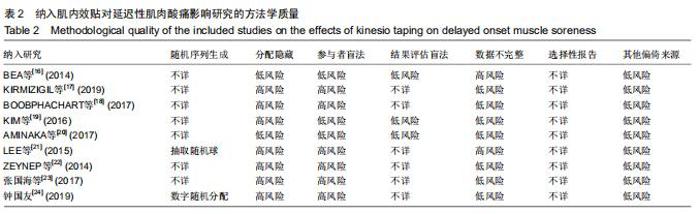
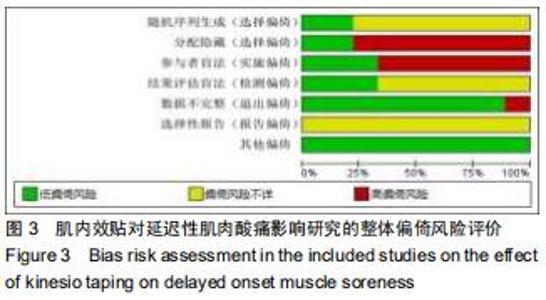
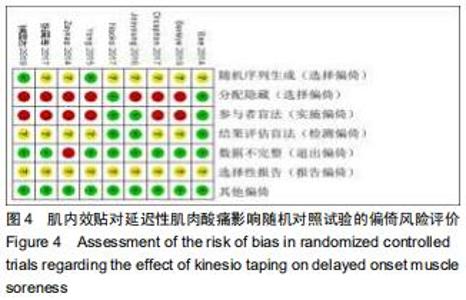
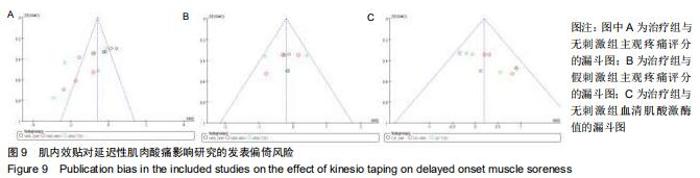
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (35): 5733-5740.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2351
A meta-analysis of kinesio taping in the treatment of delayed onset muscle soreness
Geng Zhizhong1, Pei Ziwen2, Yan Gongli1, Chen Jian3
1Graduate School, 3School of Health Science, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, the First Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-07Revised:2020-01-15Accepted:2020-03-04Online:2020-12-18Published:2020-10-19 -
Contact:Chen Jian, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Health Science, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Geng Zhizhong, Master candidate, Graduate School, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Zhizhong, Pei Ziwen, Yan Gongli, Chen Jian. A meta-analysis of kinesio taping in the treatment of delayed onset muscle soreness[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5733-5740.
share this article
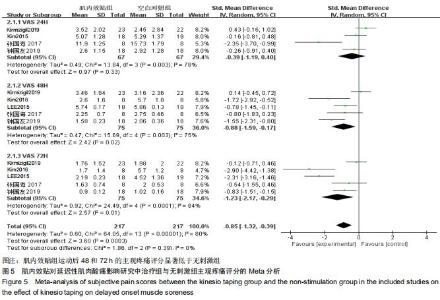
2.4.1 主观疼痛评分 共纳入5篇随机对照试验,研究对象共150例。其中4篇以目测类比评分评价[17,19,21,24],1篇以疼痛6级评分法评价患者主观疼痛程度[19]。研究间异质性高(I2≥50%,P ≤ 0.01),故采用随机效应模型分析;由于测量单位不同,故采用SMD进行合并,结果显示肌内效贴组主观疼痛评分显著低于无刺激组[SMD=-0.85,95%CI(-1.32, -0.39),P=0.000 3]。亚组分析中发现,2组运动后24 h主观疼痛评分差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.39,95%CI(-1.19,0.40),P=0.33],肌内效贴组运动后48h主观疼痛评分显著低于无刺激组[SMD=-0.88,95%CI(-1.59,-0.17),P=0.02],肌内效贴组运动后72 h主观疼痛评分亦显著低于无刺激组[SMD=-1.23,95%CI(-2.17,-0.29),P=0.01],见图5。 "

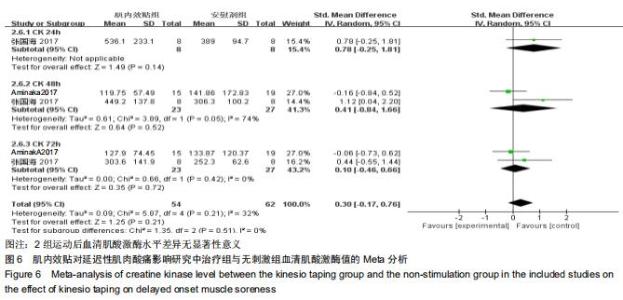
2.4.2 血清肌酸激酶水平 共纳入2篇随机对照试验,研究对象共50例。2篇均以血清肌酸激酶评价患者延迟性肌肉酸痛的恢复情况[20,23]。研究间异质性高(I2 ≥ 50%,P ≤0.01),故采用随机效应模型分析;由于测量单位不同,故采用SMD进行合并,结果显示相较于无刺激组,治疗组血清肌酸激酶差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.30,95%CI(-0.17,0.76),P=0.21]。亚组分析中发现,2组运动后48 h血清肌酸激酶差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.41,95%CI(-0.84,1.66),P=0.52],肌内效贴组运动后72 h血清肌酸激酶差异亦无显著性意义[SMD=0.10,95%CI(-0.46,0.66),P=0.72] 其中仅1篇文章显示治疗组与无刺激组在运动后24 h肌酸激酶水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)[19],见图6。 "

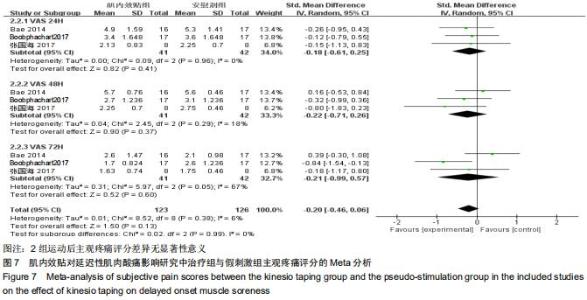
2.5.1 主观疼痛评分 共纳入3篇随机对照试验,研究对象共83例。2篇以目测类比评分评价[16,18],1篇以疼痛6级评分法评价患者主观疼痛程度[23]。研究间异质性高(I2 ≥ 50%, P ≤ 0.01),故采用随机效应模型分析;由于测量单位不同,故采用SMD进行合并,结果显示治疗组主观疼痛评分差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.20,95%CI(-0.46,0.06),P=0.13]。亚组分析中发现,2组运动后24 h主观疼痛评分差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.18,95%CI(-0.61,0.25),P=0.41],肌内效贴组运动后48 h主观疼痛评分差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.22,95%CI(-0.71,0.26),P=0.37],肌内效贴组运动后72 h主观疼痛评分差异亦无显著性意义[SMD=-0.21,95%CI(-0.99,0.57),P=0.60],见图7。 "

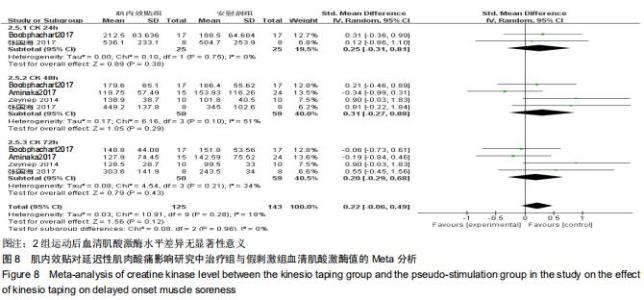
2.5.2 血清肌酸激酶水平 共纳入4篇随机对照试验,研究对象共109例。4篇均以血清肌酸激酶评价患者延迟性肌肉酸痛的恢复情况[18,20,22-23]。研究间异质性高(I2 ≥ 50%, P ≤ 0.01),故采用随机效应模型分析;由于测量单位不同,故采用SMD进行合并,结果发现结果显示肌内效贴组血清肌酸激酶较安慰剂对照组差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.22,95%CI(-0.06,0.49),P=0.12]。亚组分析中发现,两组运动后24h血清肌酸激酶差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.25,95%CI(-0.31,0.81),P=0.38],肌内效贴组运动后48h血清肌酸激酶较假刺激组差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.31,95%CI(-0.27,0.88),P=0.29] 肌内效贴组运动后72 h血清肌酸激酶差异亦无显著性意义[SMD=0.20,95%CI(-0.29,0.68),P=0.43],见图8。 "

|
[1] AGTEN CA, BUCK FM, DYER L, et al. Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness: Temporal Assessment With Quantitative MRI and Shear-Wave Ultrasound Elastography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017; 208(2):402-412.
[2] MESZAROS AJ, IGUCHI M, CHANG SH, et al. Repetitive eccentric muscle contractions increase torque unsteadiness in the human triceps brachii. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2010;20(4):619-626.
[3] CHEUNG K, HUME P, MAXWELL L. Delayed onset muscle soreness : treatment strategies and performance factors. Sports Med. 2003;33(2): 145-164.
[4] AGOSTINI V, VISCONTI L, TRUCCO M, et al. Knee proprioception may be altered by treatment in athletes suffering from delayed onset muscle soreness. J Mech Med Biol. 2018;19:1950011.
[5] HOULE M, DANEAU C, LESSARD A, et al. Short-term effect of delayed-onset muscle soreness on trunk proprioception during force reproduction tasks in a healthy adult population: a crossover study. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(1):181-190.
[6] VISCONTI L, FORNI C, COSER R, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness of manual massage, long-wave diathermy, and sham long-wave diathermy for the management of delayed-onset muscle soreness: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Physiother. 2020;10:1.
[7] 瞿超艺,徐金成,赵杰修.超低温冷疗对延迟性肌肉酸痛的作用——系统综述[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,11(8):754-769.
[8] XIE Y, FENG B, CHEN K, et al. The Efficacy of Dynamic Contract-Relax Stretching on Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness Among Healthy Individuals: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin J Sport Med. 2018;28(1):28-36.
[9] GUO J, LI L, GONG Y, et al. Massage Alleviates Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness after Strenuous Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Physiol. 2017;8:747.
[10] 张国海,王人卫.肌内效贴对人体运动能力影响与相关机理的研究进展与展望[J].中国体育科技,2015,10(1):73-80.
[11] FARHADIAN M, MOROVATI Z, SHAMSODDINI A. Effect of Kinesio Taping on Pain, Range of Motion, Hand Strength, and Functional Abilities in Patients with Hand Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2019;7(6):551-560.
[12] GÜLENÇ B, KUYUCU E, BIÇER H, et al. Kinesiotaping Reduces Knee Diameter but Has No Effect on Differences Pain and Edema Following Knee Artroscopy. Kinesiotaping kolena následující po artroskopii zmenšuje obvod kloubu, ale nemá efekt na rozdíly v bolesti a otoku. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2018;85(4):285-290.
[13] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照研究Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148.
[14] 曾宪涛,包翠萍,曹世义,等.Meta分析系列之三:随机对照试验的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(3):183-185.
[15] FRAGKOS KC, TSAGRIS M, FRANGOS CC. Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis: Confidence Intervals for Rosenthal's Fail-Safe Number. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014;2014:825383.
[16] BAE SH, LEE YS, KIM GD, et al. The Effects of Kinesio-taping Applied to Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness on Changes in Pain. Int J Bio Sci Bio Tech. 2014;3(6):133-142.
[17] KIRMIZIGIL B, CHAUCHAT JR, YALCINER O, et al. The Effectiveness of Kinesio Taping in Recovering from Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness: A Cross-Over Study. J Sport Rehabil. 2019. doi:10.1123/jsr.2018-0389
[18] BOOBPHACHART D, MANIMMANAKORN N, MANIMMANAKORN A, et al. Effects of elastic taping, non-elastic taping and static stretching on recovery after intensive eccentric exercise. Res Sports Med. 2017; 25(2):181-190.
[19] KIM J, KIM S, LEE J. Longer application of kinesio taping would be beneficial for exercise-induced muscle damage. J Exerc Rehabil. 2016; 12(5):456-462.
[20] AMINAKA N, FOHEY T, KOVACS A, et al. Kinesiology Tape does not Affect Serum Creatine Kinase Level and Quadriceps Activity during Recovery from Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness. Inter J Kinesiol Sports Sci. 2017;5(1):17-25.
[21] LEE YS, BAE SH, HWANG JA, et al. The effects of kinesio taping on architecture, strength and pain of muscles in delayed onset muscle soreness of biceps brachii. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(2):457-459.
[22] ZEYNEP HK, SEYIT C. Effects of kinesiology taping on delayed onset muscle soreness: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Exerc Ther Rehabil. 2014;1(2):49-54.
[23] 张国海,王人卫.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛和肌肉功能恢复的影响[J].体育科学,2017,37(12):46-51.
[24] 钟国友.振动刺激附加肌内效贴治疗运动性膝关节延迟性肌肉酸痛[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27):4305-4309.
[25] DE MARTINO E, PETRINI L, SCHABRUN S, et al. Cortical Somatosensory Excitability Is Modulated in Response to Several Days of Muscle Soreness. J Pain. 2018;19(11):1296-1307.
[26] HOTFIEL T, FREIWALD J, HOPPE MW, et al. Advances in Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS): Part I: Pathogenesis and Diagnostics. Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness – Teil I: Pathogenese und Diagnostik. Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2018;32(4):243-250.
[27] DOUGLAS J, PEARSON S, ROSS A, et al. Eccentric Exercise: Physiological Characteristics and Acute Responses. Sports Med. 2017;47(4):663-675.
[28] YANAGISAWA O, SAKUMA J, KAWAKAMI Y, et al. Effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on muscle hardness evaluated by ultrasound real-time tissue elastography. Springerplus. 2015;4:308.
[29] SICARI BM, DEARTH CL, BADYLAK SF. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches to enhance the functional response to skeletal muscle injury. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014;297(1):51-64.
[30] PIRES LG, PADULA RS, JUNIOR MADL, et al. Can Kinesio Taping® influence the electromyographic signal intensity of trunk extensor muscles in patients with chronic low back pain? A randomized controlled trial [published online ahead of print, 2019 Dec 15]. Braz J Phys Ther. 2019. doi:10.1016/j.bjpt.2019.12.001.
[31] OZMEN T, AYDOGMUS M, DOGAN H, et al. The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Muscle Pain, Sprint Performance, and Flexibility in Recovery From Squat Exercise in Young Adult Women. J Sport Rehabil. 2016; 25(1):7-12.
[32] TOZZI U, SANTAGATA M, SELLITTO A, et al. Influence of Kinesiologic Tape on Post-operative Swelling After Orthognathic Surgery. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2016;15(1):52-58.
[33] LIETZ-KIJAK D, KIJAK E, KRAJCZY M, et al. The Impact of the Use of Kinesio Taping Method on the Reduction of Swelling in Patients After Orthognathic Surgery: A Pilot Study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24: 3736-3743. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||