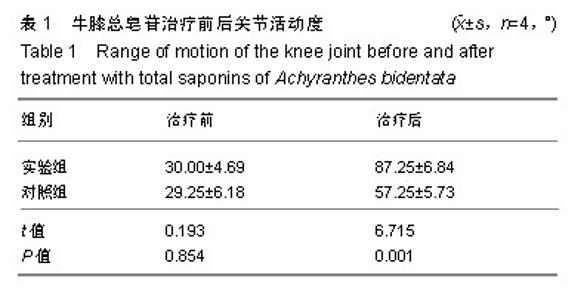
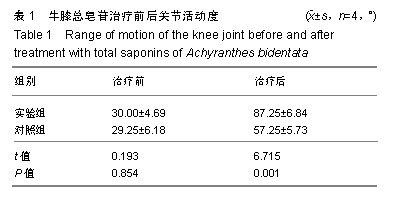
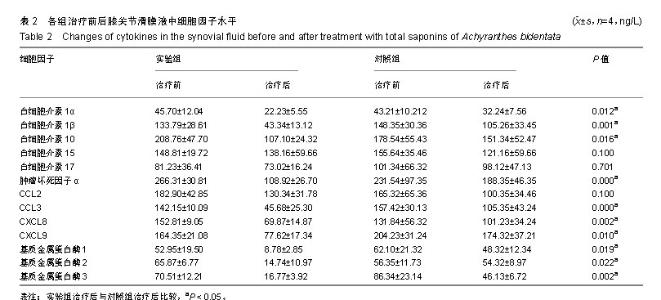
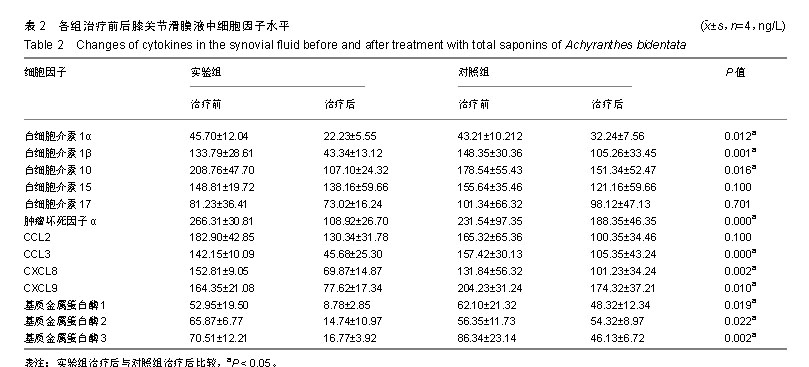
| [1]Berenbaum F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.[2]Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330.[3]Greene MA, Loeser RF. Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11): 1966-1971.[4]Mobasheri A, Bay-Jensen AC, van Spil WE, et al. Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2016: biomarkers (biochemical markers). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):199-208.[5]Huang D, Liu YQ, Liang LS, et al. The Diagnosis and Therapy of Degenerative Knee Joint Disease: Expert Consensus from the Chinese Pain Medicine Panel. Pain Res Manag.2018; 2018:2010129.[6]Scanzello CR, Goldring SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone.2012;51(2):249-257.[7]肖伟,林栋栋,彭力平.牛膝醇提物透入疗法对膝骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(8): 37-40.[8]陈达,廖州伟,马笃军,等.牛膝醇提物对兔骨关节炎模型的疗效比较[J].中国医药导报,2016,13(25):21-24.[9]彭力平,马笃军,裴军宇.牛膝醇提物对急性软骨损伤兔软骨的影响[J].中医杂志,2013,54(17):1504-1506.[10]曾俊华,马笃军,彭力平,等.实验兔膝骨关节炎模型的建立及鉴定[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(5):679-682.[11]孙文才,白玉江,李玉成,等.骨关节炎患者血清及关节滑液中细胞因子的表达水平研究[J].中国全科医学,2012,15(27): 3185-3186.[12]史新立,胡堃,孟祥提.关节软骨修复与相关细胞因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(11): 2047-2050.[13]Vergunst CE, van de Sande MG, Lebre MC, et al. The role of chemokines in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005;34(6):415-425.[14]Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ?A, Szukiewicz D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014: 561459.[15]Hedbom E, Häuselmann HJ. Molecular aspects of pathogenesis in osteoarthritis: the role of inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59(1):45-53.[16]Schulze-Tanzil G, Zreiqat H, Sabat R, et al. Interleukin-10 and articular cartilage: experimental therapeutical approaches in cartilage disorders. Curr Gene Ther. 2009;9(4):306-315.[17]贺占坤,沈杰威.MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9和TIMP-1评价膝关节骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2013,42(32):3872-3874.[18]郭达,张斌山,刘金文.骨关节炎的古代方药规律研究[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(9):2194-2195.[19]姚共和,刘向前,李建斌,等.中医期刊治疗膝关节骨关节炎方剂用药特点分析[J].湖南中医学院学报,2005,25(6):54-56.[20]沈舒,王琼,李友宾.牛膝的化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].海峡药学,2011,23(11):1-6.[21]高晓燕,王大为,李发美,等.牛膝提取物对成骨样细胞增殖的作用[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2000,17(3):210-213.[22]Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. 2012;196(4): 395-406.[23]Konttinen YT, Ainola M, Valleala H, et al. Analysis of 16 different matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1 to MMP-20) in the synovial membrane: different profiles in trauma and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58(11):691-697.[24]Adams SB, Setton LA, Bell RD, et al. Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Synovial Fluid After Intra-articular Ankle Fracture. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36(11): 1264-1271. [25]Jouglin M, Robert C, Valette JP, et al. Metalloproteinases and tumor necrosis factor-alpha activities in synovial fluids of horses: correlation with articular cartilage alterations. Vet Res. 2000;31(5):507-515.[26]Ishizuka S, Sakai T, Hiraiwa H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α induces expression of type X collagen and matrix metalloproteinases 13 in osteoarthritic meniscal cells. Inflamm Res. 2016;65(6):439-448.[27]Yu WG, Shen Y, Wu JZ, et al. Madecassoside impedes invasion of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte from adjuvant arthritis rats via inhibition of NF-κB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16(5): 330-338. [28]van Nieuwenhuijze AE, van de Loo FA, Walgreen B, et al. Complementary action of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-17A induces interleukin-23, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, and matrix metalloproteinases and drives bone and cartilage pathology in experimental arthritis: rationale for combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17: 163.[29]Taraboletti G, D'Ascenzo S, Borsotti P, et al. Shedding of the matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP as membrane vesicle-associated components by endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(2):673-680.[30]Millward-Sadler SJ, Wright MO, Davies LW, et al. Mechanotransduction via integrins and interleukin-4 results in altered aggrecan and matrix metalloproteinase 3 gene expression in normal, but not osteoarthritic, human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(9):2091-2099.[31]Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Coon CI, et al. Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor kappaB: differential regulation of collagenase 1 and collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(4): 801-811.[32]Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. 2002;4(3): 157-164.[33]Hanemaaijer R, Sorsa T, Konttinen YT, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 is expressed in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and doxycycline. J Biol Chem.1997;272(50): 31504-31509.[34]de Lange-Brokaar BJ, Ioan-Facsinay A, van Osch GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12): 1484-1499. |