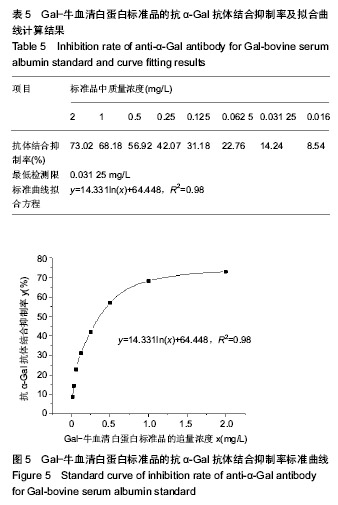
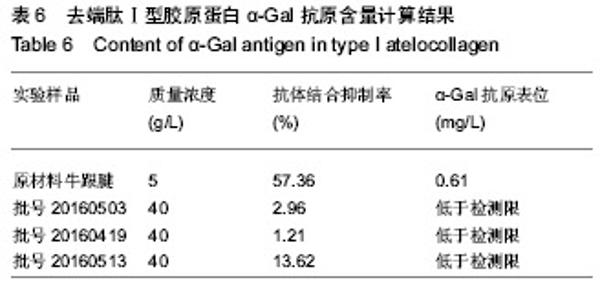
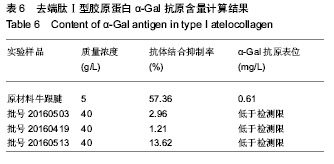
| [1]梁健华.超声波辅助提取罗非鱼皮胶原蛋白及其功能结构性质的研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2016.[2]张达江,王亮.Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的结构、功能及其应用研究的现状与前景[J].生物技术通讯,2006, 17(2):265-269.[3]Tokunaga T,Yamamoto H,Shimada S,et al.Antitumor activity of deoxyribonucleic acid fraction from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. I. Isolation, physicochemical characterization, and antitumor activity. J Natl Cancer Inst.1984;72(4):955-962.[4]Ansaloni L,Cambrini P,Catena F,et al.Immune response to small intestinal submucosa (surgisis) implant in humans: preliminary observations.J Invest Surg.2007;20(4):237-241.[5]Patino MG,Neiders ME,Andreana S,et al.Cellular inflammatory response to porcine collagen membranes. J Periodontal Res. 2003;38(5):458-464.[6]史新立,刘传玉,医用胶原材料免疫原性的研究进展[J].中国医药, 2010,5(10):962-964.[7]雷静,李奕恒,刘旭昭,等.动物源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白可引起BALB/c小鼠细胞免疫反应和组织免疫毒性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(34):5506-5512.[8]许和平.保持胶原特有三螺旋结构的I 型医用胶原材料及其产品和应用:CN,101569765[P].2009.[9]刘(龙天).胶原蛋白三螺旋结构及热稳定性的研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院中国医学科学院清华大学医学部, 2009.[10]张自强.去端肽胶原蛋白生物材料结构设计、制备及应用[D].北京:中国地质大学,2018.[11]崔凤霞.海参胶原蛋白生化性质及胶原肽活性研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2007.[12]曹慧,许时婴.酶解工艺对Ⅱ型胶原蛋白分子结构及提取率的影响[J].食品与发酵工业,2010,36(1):52-55.[13]陆艳,单永强,邵安良,等.ELISA抑制法检测动物组织中α1,3-Gal抗原[J].药物分析杂志,2015, 35(10):1729-1735.[14]张自强,张以河,安琪,等.胶原蛋白海绵对大鼠股主静脉创伤止血效果及组织相容性观察[J].转化医学杂志, 2017,6(6):350-354[15]张自强,张以河,祖耀先,等.胶原蛋白海绵对肝脏创伤止血的效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(30):4874-4879.[16]张静怡,吴文惠,王南平,等.罗非鱼皮Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的抗原反应特性分析[J].食品科学,2015,36(7):79-83.[17]杜晓丹,方玉,奚廷斐,等.动物源性胶原的生产、应用及其免疫原性[J].中国组织工程研究,2008,12(23):4511-4514.[18]Naso F,Gandaglia A,Iop L,et al.Alpha-Gal detectors in xenotransplantation research: a word of caution. Xenotransplantation.2012;19(4):215-220.[19]Galili U.The alpha-gal epitope and the anti-Gal antibody in xenotransplantation and in cancer immunotherapy.Immunol Cell Biol.2005;83(6):674-686.[20]单永强,徐丽明,柯林楠,等.动物源性生物材料中残留α-Gal抗原检测方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015,32(3):662-668,679.[21]Moore MA,Samsell B,Wallis G,et al.Decellularization of human dermis using non-denaturing anionic detergent and endonuclease: a review.Cell Tissue Bank. 2015;16(2):249-259.[22]徐丽明,邵安良,赵艳红.动物源性生物材料残留DNA的定量检测法[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2012,29(3):479-485.[23]何创龙,王远亮,杨立华,等.牛骨胶原基质的制备和性能研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2005, 22(4):698-703.[24]王秋卓,王彩虹,张文博,等.可吸收性胶原止血海绵的制作工艺研究[J].中国医药导报,2010,7(17):47-48.[25]贠志敏,李素波,张雪,等.酶解法清除猪皮α-Gal抗原的研究[J].军事医学,2015,39(12):938-940.[26]吴世福,刘成虎,侯丽,等.胶原蛋白海绵浸提液对小鼠体外脾脏淋巴细胞转化作用的研究[J].中国医疗器械杂志, 2014,38(4): 308-311. |