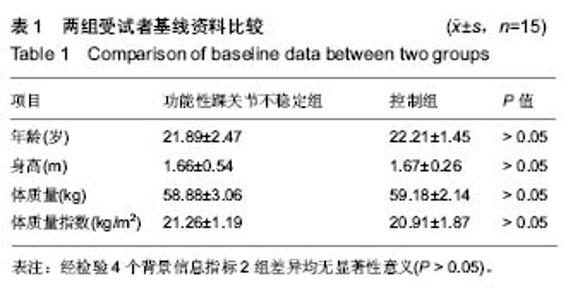
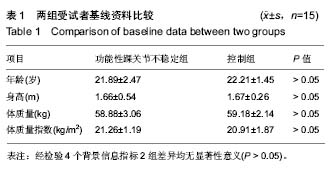
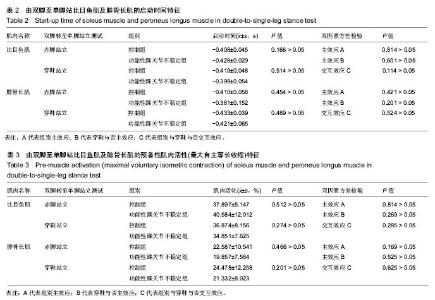
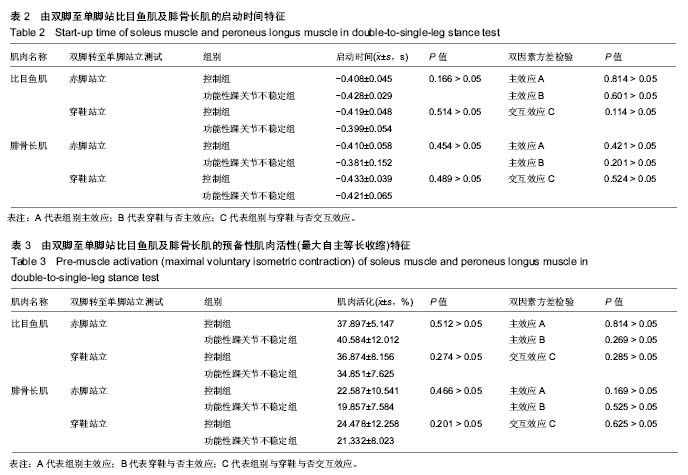
| [1] Freeman MA.Instability of the foot after injuries to the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1965;47(4): 669-677.[2] Doherty C,Delahunt E,Caulfield B, et al.The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: A systemmatic review and meta analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports med.2014;44(1):123-140.[3] 尹彦,罗冬梅,刘卉,于冰. 功能性踝关节不稳者姿势稳定性的研究进展[J].体育科学,2016,36(4):61-67.[4] Santello M, McDonagh MJ. The control of timing and amplitude of EMG activity in landing movements in humans. Exp Physiol. 1998;83(6):857-874.[5] Divya Bhaskaran, Michael Wortley, Qingjian Chen,et al. Effect of a combined inversion and plantarflexion surface on ankle kinematics and EMG activities in landing. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2015;4(4):377-383.[6] Sanam Tavakoli, Saeed Forghany, Christopher Nester. The effect of dual tasking on foot kinematics in people with functional ankle instability . Gait Posture. 2016;49:364-370.[7] Konradsen L, Magnusson P. Increased inversion angle replication error in functional ankle instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2000;8(4):246-251.[8] Yoshida M, Taniguchi K, Katayose M.Analysis of muscle activity and ankle jointmovement during the side-hop test. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(8):2255-2264.[9] Byung-Ki Cho, Ji-Kang Park, Seung-Myung Choi and et al. The peroneal strength deficits in patients with chronic ankle instability compared to ankle sprain copers and normal individuals. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;pii: S1268-7731(17)31330-31339.[10] Munn J, Sullivan SJ, Schneiders AG. Evidence of sensorimotor deficits in functional ankle instability: A systematic review with metaanalysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2010; 13:2-12.[11] Hopkins JT, Brown TN, Christensen L, et al. Deficits in peroneal latency and electromechanical delay in patients with functional ankle instability. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:1541-1546.[12] Lee AJ, Lin WH. Twelve-week biomechanical ankle platform system training on postural stability and ankle proprioception in subjects with unilateral functional ankle instability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2008;23(8):1065-1072.[13] Arnold BL, De La Motte S, Linens S,et al. Ankle instability is associated with balance impairments: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2009;41:1048-1062.[14] Rosen A, Swanik C, Thomas S, et al. Differences in lateral drop jumps from an unknown height among individuals with functional ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2013;48:773-781.[15] Delahunt E, Monaghan K, Caulfield B. Ankle function during hopping in subjects with functional instability of the ankle joint. Scand J Med Sci Sports.2007;17:641-648.[16] Ross SE, Guskiewicz KM, Gross MT, et al. Balance measures for discriminating between functionally unstable and stable ankles. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:399-407.[17] Suda EY, Amorim CF, Sacco Ide C. Influence of ankle functional instability on the ankle electromyography during landing after volleyball blocking. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2009;19:e84-93.[18] Van Deun S, Staes FF, Stappaerts KH, et al. Relationship of chronic ankle instability to muscle activation patterns during the transition from double-leg to singleleg stance. Am J Sports Med.2007;35:274-281.[19] Levin O, Van Nevel A, Malone C, et al. Sway activity and muscle recruitment order during transition from double to single-leg stance in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture.2012;36:546-551.[20] Mitchell A, Dyson R, Hale T, et al. Biomechanics of ankle instability. Part 2: Postural sway-reaction time relationship. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2008;40(15):22-28.[21] Lin CY, Shih YF. The neuromuscular control of the ankle joint in subjects with functional ankle instability. Formos J Phys Ther.2014,39:191-202.[22] Wikstrom EA, Tillman MD, Chmielewski TL, et al. Dynamic postural stability deficits in subjects with self-reported ankl e ins t abi l i ty. Med Sc i Sports Exerc. 2007;39:397-402.[23] Lin CF, Chen CY, Lin CW. Dynamic ankle control in athletes with ankle instability during sports maneuvers. Am J Sports Med.2011;39:2007-2015.[24] Raymond J, Nicholson LL, Hiller CE, et al. The effect of ankle taping or bracing on proprioception in functional ankle instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport.2012;15:386-392. |