Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (14): 2228-2234.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1661
Previous Articles Next Articles
Choosing appropriate lysis buffers for protein extraction from acidotic mouse skeletal muscles
Luo Xuguang1, Zang Haojing1, Sun Peng1, Cao Ximei2
- 1Department of Microbiology and Immunology, 2Department of Histology and Embryology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-01-10Online:2019-05-18Published:2021-04-28 -
Contact:Cao Ximei, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Histology and Embryology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Luo Xuguang, Master, Experimentalist, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of for the Youth of Shanxi Province, No. 2014021028-1 (to CXM); the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Shanxi Medical University, No. 01201401 (to CXM); the 331 Early Career Researcher Grant of Basic Medical School of Shanxi Medical University, No. 201413 (to CXM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Xuguang, Zang Haojing, Sun Peng, Cao Ximei. Choosing appropriate lysis buffers for protein extraction from acidotic mouse skeletal muscles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2228-2234.
share this article
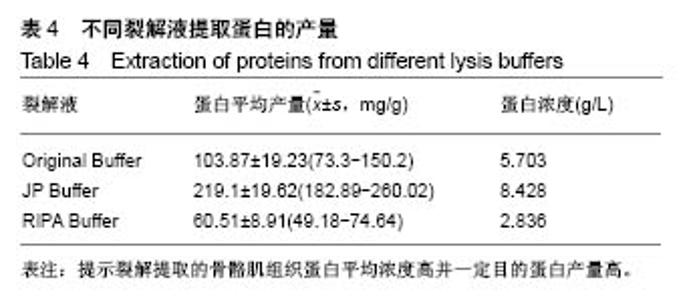
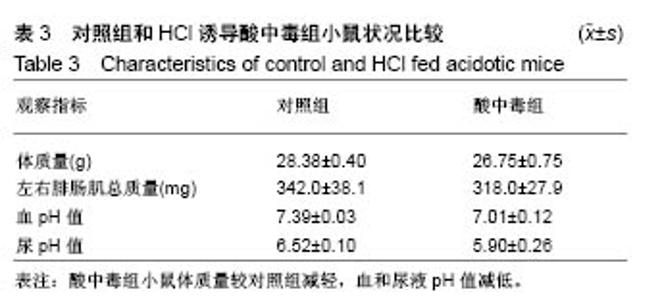
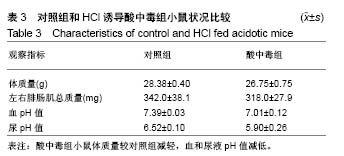
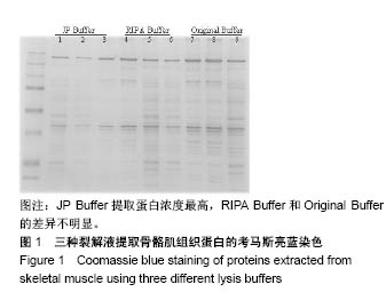
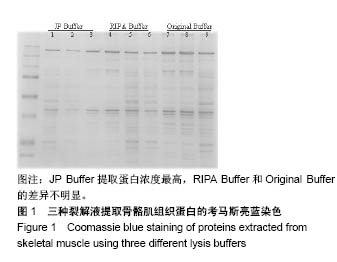
2.2 三种裂解液提取蛋白产量结果评价 按实验设计分组,3种裂解液匀浆处理骨骼肌组织,蛋白产量有显著差异,见表4。骨骼肌组织在JP Buffer中溶解完全,裂解液非常黏稠,离心后无明显沉淀;在Original Buffer和RIPA Buffer中溶解均不完全,离心后肉眼可见沉淀。3种裂解液提取的总蛋白平均浓度见表4,依次为5.703 g/L、8.428 g/L、 2.836 g/L;3种裂解液中JP Buffer提取蛋白平均产量最高、RIPA Buffer最低。虽然JP Buffer提取蛋白浓度最高,但是考马斯亮蓝染色结果显示蛋白条带的数量和强度并不是最强,RIPA Buffer和Original Buffer的差异不明显,见图1。提示裂解提取的骨骼肌组织蛋白平均浓度高并一定目的蛋白产量高。"
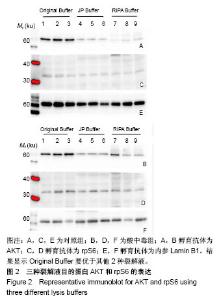
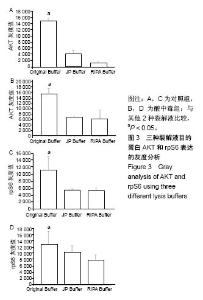
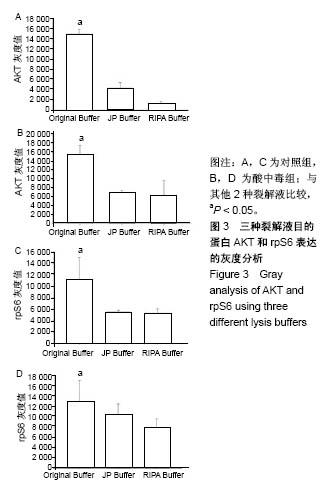
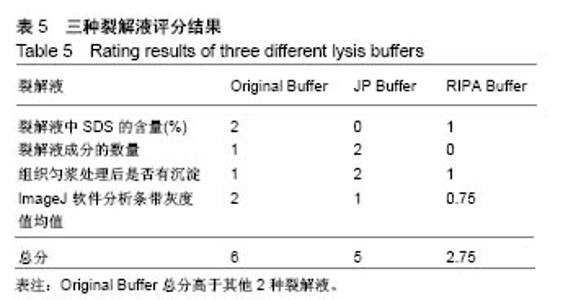
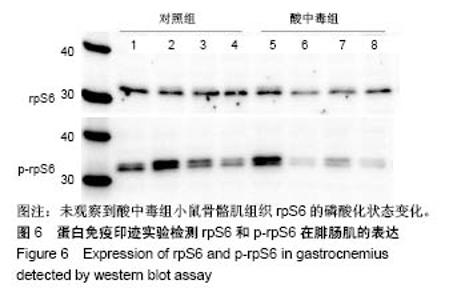
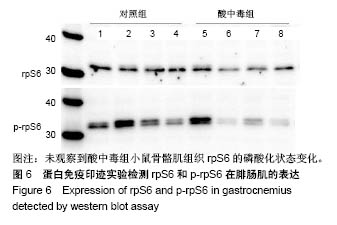
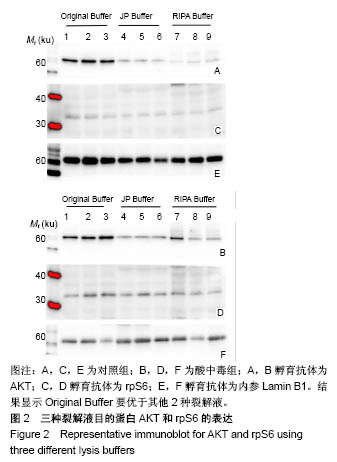
2.3 蛋白免疫印迹实验筛选最佳裂解液 见图2,3。结果显示对照组和酸中毒组Original Buffer提取蛋白的目的蛋白AKT条带最清晰,见图2A、B,蛋白灰度测定值最高,见图3A、B;虽然JP Buffer蛋白平均产量最高,但是目的蛋白条带信号弱,见图2A、B;RIPA Buffer裂解能力温和蛋白平均产量偏低,目的蛋白条带信号较弱,见图2A、B;SigmaPlot分析结果见图3。相同蛋白样本抗S6 Ribosomal Protein单克隆抗体再次评价,见图2C、D,实验结果显示Original Buffer要优于其他2种裂解液,见图2C、D,图3C、D,提示Original Buffer能保证骨骼肌组织目的蛋白的提取质量。 同时根据表2的评分标准,分别对3种裂解液的组成和相应蛋白免疫印迹实验结果评分,结果见表5,Original Buffer总分高于其他2种裂解液,同样提示Original Buffer是适合酸中毒小鼠骨骼肌组织蛋白提取的裂解液。"
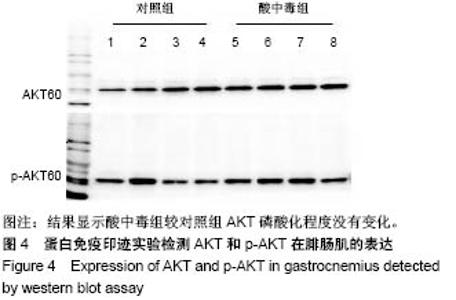
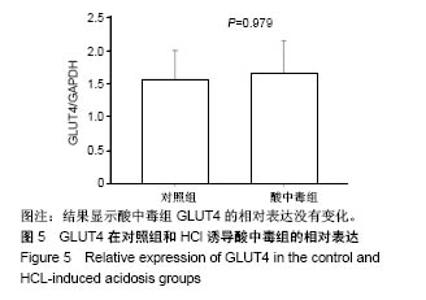
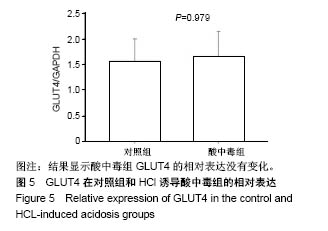
2.4 分析AKT信号通路状态 通过考马斯亮蓝染色、蛋白免疫印迹实验、评分表记分等方法筛选出Original Buffer提取酸中毒小鼠骨骼肌组织蛋白,分析AKT信号通路在酸中毒组的变化。已知AKT信号通路通过磷酸化而活化,参与调节细胞的分化、增殖和凋亡;总AKT相等的情况下磷酸化p-AKT的差异可以反应该信号通路是否活化。AKT有Thr308和Ser473两个磷酸化位点,AKT活化后通过激活或抑制作用调节下游靶蛋白的活性。为了保证实验数据的准确性,对照组和酸中毒组均设重复样本,见图4,结果显示对照组和酸中毒组AKT和p-AKT条带清晰,灰度测定值基本相等,统计分析两组之间P=0.905 > 0.05,提示酸中毒组较对照组AKT磷酸化程度没有变化,AKT信号通路未被"
| [1] Janes KA.An analysis of critical factors for quantitative immunoblotting. Sci Signal.2015;8(371):rs2.[2] Peach M,Marsh N,Miskiewicz EI,et al.Solubilization of proteins: the importance of lysis buffer choice. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1312: 49-60.[3] Ngoka LC.Sample prep for proteomics of breast cancer: proteomics and gene ontology reveal dramatic differences in protein solubilization preferences of radioimmunoprecipitation assay and urea lysis buffers. Proteome Sci.2008;6:30.[4] Gozal YM, Dammer EB, Duong DM,et al. Proteomic analysis of hippocampal dentate granule cells in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: application of laser capture technology. Front Neurol. 2011;2:24.[5] Miskiewicz EI, MacPhee DJ. Lysis buffer choices are key considerations to ensure effective sample solubilization for protein electrophoresis. Methods Mol Biol.2019;1855:61-72.[6] Grabski AC. Advances in preparation of biological extracts for protein purification. Methods Enzymol.2009;463:285-303.[7] Peach M,Marsh N,Macphee DJ.Protein solubilization: attend to the choice of lysis buffer.Methods Mol Biol.2012;869:37-47. [8] Mansour AG,Khalil PA,Bejjani N,et al.An optimized xylene-free protein extraction method adapted to formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue sections for western blot analysis.Histol Histopathol.2017;32(3):307-313.[9] Luís IM,Alexandre BM,Oliveira MM,et al.Selection of an Appropriate Protein Extraction Method to Study the Phosphoproteome of Maize Photosynthetic Tissue. PLoS One.2016;11(10):e0164387. [10] Harfmann BD,Schroder EA,Esser KA.Circadian rhythms, the molecular clock, and skeletal muscle.J Biol Rhythms. 2015;30(2): 84-94. [11] Steidle-Kloc E,Schönfelder M,Müller E,et al.Does exercise training impact clock genes in patients with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus? Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2016;23(13): 1375-1382. [12] Madala SK,Sontake V,Edukulla R,et al.Unique and Redundant Functions of p70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase Isoforms Regulate Mesenchymal Cell Proliferation and Migration in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55(6):792-803.[13] Meng D,Frank AR,Jewell JL.mTOR signaling in stem and progenitor cells. Development.2018;145(1):pii: dev152595.[14] Kopec AM,Rivera PD,Lacagnina MJ,et al.Optimized solubilization of TRIzol-precipitated protein permits Western blotting analysis to maximize data available from brain tissue.J Neurosci Methods. 2017;280:64-76. [15] Gómez-Sánchez R,Pizarro-Estrella E,Yakhine-Diop SM,et al. Routine Western blot to check autophagic flux: cautions and recommendations. Anal Biochem.2015;477:13-20. [16] Ignatoski KM,Verderame MF.Lysis buffer composition dramatically affects extraction of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Biotechniques.1996;20(5):794-796. [17] Hnasko TS,Hnasko RM.The Western Blot. Methods Mol Biol. 2015; 1318:87-96. [18] Vallejo-Illarramendi A,Marciano DK,Reichardt LF.A novel method that improves sensitivity of protein detection in PAGE and Western blot.Electrophoresis.2013;34(8):1148-1150. [19] Krishnaswamy A,Barnes N,Lotlikar NP,et al. An Improved Method for Protein Extraction from Minuscule Quantities of Fungal Biomass.Indian J Microbiol (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s12088-018-0752-y. [20] Santa C,Anjo SI,Manadas B. Protein precipitation of diluted samples in SDS-containing buffer with acetone leads to higher protein recovery and reproducibility in comparison with TCA/acetone approach. Proteomics.2016;16(13):1847-1851. [21] Rodríguez-Rigueiro T,Valladares-Ayerbes M,Haz-Conde M,et al.A novel procedure for protein extraction from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Proteomics. 2011;11(12):2555-2559. [22] Gromov P,Celis JE,Gromova I,et al.A single lysis solution for the analysis of tissue samples by different proteomic technologies.Mol Oncol.2008;2(4):368-379.[23] Yates LD,Greaser ML.Quantitative determination of myosin and actin in rabbit skeletal muscle.J Mol Biol.1983;168(1):123-141.[24] Wang J,Lee YM,Li C,et al.Dramatic improvement of proteomic analysis of zebrafish liver tumor by effective proteinextraction with sodium deoxycholate and heat denaturation.Int J Anal Chem. 2015; 2015:763969. [25] Evans K,Nasim Z,Brown J,et al.Inhibition of SNAT2 by metabolic acidosis enhances proteolysis in skeletal muscle.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(11):2119-2129. [26] Patel S.Stressor-driven extracellular acidosis as tumor inducer via aberrant enzyme activation: A review on the mechanisms and possible prophylaxis. Gene. 2017;626:209-214. [27] Sood S,Chen Y,McIntire K,et al. Acute acidosis attenuates leucine stimulated signal transduction and protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle.Am J Nephrol.2014;40(4):362-370. [28] Aoyama S,Shibata S.The Role of Circadian Rhythms in Muscular and Osseous Physiology and Their Regulation by Nutrition and Exercise. Front Neurosci.2017;11:63. [29] Liu Y,Yuan J,Xiang L,et al.A high sucrose and high fat diet induced the development of insulin resistance in the skeletal muscle of Bama miniature pigs through the Akt/GLUT4 pathway.Exp Anim. 2017;66(4):387-395. [30] Bi Y,Sun WP,Chen X,et al.Effects of early insulin therapy on nuclear factor kappaB pathway in skeletal muscle of diabetes: experiment with rats.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2008;88(46):3287-3292.[31] Wang XH, Mitch WE. Muscle wasting from kidney failure-a model for catabolic conditions.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(10): 2230-2238.[32] Garofalo RS,Orena SJ,Rafidi K,et al.Severe diabetes, age-dependent loss of adipose tissue, and mild growth deficiency in mice lacking Akt2/PKB beta.J Clin Invest.2003;112(2):197-208. [33] Huang S,Czech MP.The GLUT4 glucose transporter.Cell Metab. 2007;5(4):237-252.[34] Carnagarin R,Dharmarajan AM,Dass CR.Molecular aspects of glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle--A focus on the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;417: 52-62.[35] Xiao Y,Sharma N,Arias EB,et al.A persistent increase in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by both fast-twitch and slow-twitchskeletal muscles after a single exercise session by old rats.Age (Dordr).2013;35(3):573-582.[36] Czech MP. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med,2017,23(7):804-814. [37] Mitsuhashi K,Senmaru T,Fukuda T,et al.Testosterone stimulates glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation through LKB1/AMPK signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrine. 2016;51(1):174-184.[38] Meyuhas O.Physiological roles of ribosomal protein S6: one of its kind.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.2008;268:1-37. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||