Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 427-434.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0613
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different intensities of endurance training affect serum Irisin level and skeletal muscle protein expression of PGC-1alpha, FNDC5, and PPARdelta in mice with obesity induced by a high-fat diet
Su Kunxia
- (Public Education Department of Xin Lian College, Henan Normal University, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China)
-
Received:2018-07-28 -
About author:Su Kunxia, Master, Lecturer, Public Education Department of Xin Lian College, Henan Normal University, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Kunxia . Different intensities of endurance training affect serum Irisin level and skeletal muscle protein expression of PGC-1alpha, FNDC5, and PPARdelta in mice with obesity induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 427-434.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
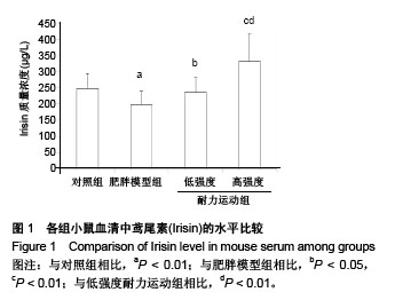
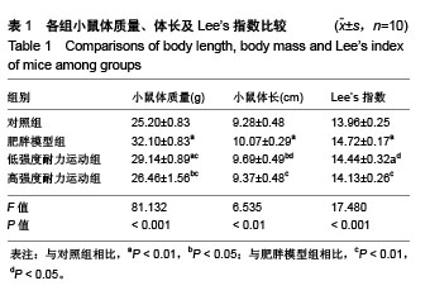
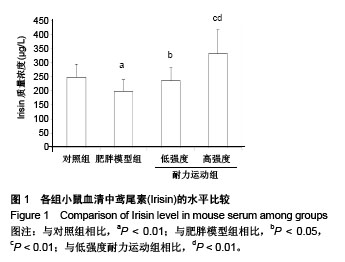
组间比较结果显示,雄性C57BL/6J小鼠经过高脂饲料诱导8周以后,体质量、体长和Lee’s指数与常规饲料喂养的小鼠相比差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),且符合高脂组小鼠体质量≥空白对照组小鼠体质量×120%的要求,表明肥胖小鼠造模成功;肥胖小鼠经过运动以后,高强度耐力运动组与肥胖模型组相比,体质量、体长和Lee’s指数均差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);低强度耐力运动组与肥胖模型组相比,体质量差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),体长和Lee’s指数均差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 同时,发现低强度耐力运动组与对照组相比,体质量、Lee’s指数差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),体长差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);高强度耐力运动组与对照组相比,体质量差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),体长、Lee’s指数差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),结果见表1。 2.3 各组小鼠血清中Irisin质量浓度的差别 经单因素方差分析,结果显示各组小鼠血清中Irisin质量浓度差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.001,F=9.424)。组间比较结果显示,肥胖模型组血清中Irisin水平明显低于对照组(P < 0.01),低强度耐力运动组高于肥胖模型组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),高强度耐力运动组明显高于肥胖模型组,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。同时比较了低强度耐力运动组和高强度耐力运动组,发现之间差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见图1。"
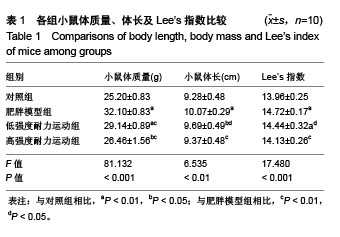
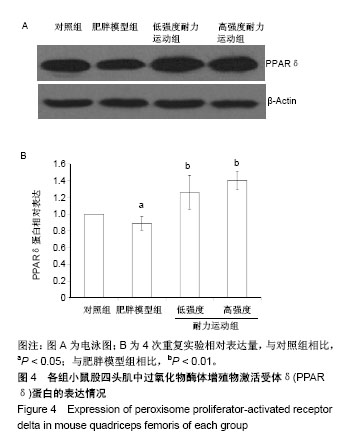
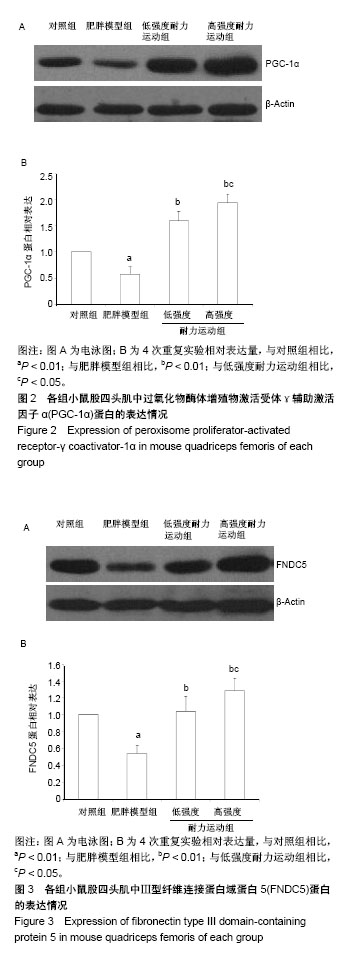
2.4 各组小鼠股四头肌中PGC-1α蛋白表达的差别 经单因素方差分析,结果显示各组小鼠股四头肌中PGC-1α蛋白表达差异性极显著(F=73.680,P < 0.001)。组间比较结果显示,肥胖模型组小鼠PGC-1α蛋白表达与对照组相比差异极显著(P < 0.01);低强度耐力运动组、高强度耐力运动组PGC-1α蛋白表达量与肥胖模型组相比差异均极显著(P < 0.01);高强度耐力运动组PGC-1α蛋白表达量与低强度耐力运动组相比差异显著(P < 0.05),结果见图2。 2.5 各组小鼠股四头肌中FNDC5蛋白表达的差别 经单因素方差分析,结果显示各组小鼠股四头肌中FNDC5蛋白表达差异性极显著(P < 0.001,F=24.155)。组间比较结果显示,肥胖模型组小鼠FNDC5蛋白表达与对照组相比差异极显著(P < 0.01);低强度耐力运动组、高强度耐力运动组FNDC5蛋白表达量与肥胖模型组相比差异均极显著(P < 0.01);高强度耐力运动组FNDC5蛋白表达量与低强度耐力运动组相比差异显著(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.6 各组小鼠股四头肌中PPARδ蛋白表达的差别 经单因素方差分析,结果显示各组小鼠股四头肌中PPARδ蛋白表达差异性极显著(P < 0.001,F=15.345)。组间比较结果显示,肥胖模型组小鼠PPARδ蛋白表达与对照组相比差异极显著(P < 0.01);低强度耐力运动组、高强度耐力运动组PPARδ蛋白表达量与肥胖模型组相比差异均极显著(P < 0.01);高强度耐力运动组PPARδ蛋白表达量与低强度耐力运动组相比无显著差异(P=0.128)。结果见图4。"
| [1] Mitchell NS,Catenacci VA,Wyatt HR,et al.Obesity: overview of an epidemic.Psychiatr Clin North Am.2011;34(4): 717-732.[2] 倪国华,张璟,郑风田.中国肥胖流行的现状与趋势[J].中国食物与营养,2013,19(10):70-74.[3] Strasser B. Physical activity in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1281:141-159.[4] Matsunaga Y,Tamura Y,Sakata Y,et al.Comparison between pre–exercise casein peptide and intact casein supplementation on glucose tolerance in high–fat diet–fed mice. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2017;1. [5] Wang N,Liu Y,Ma Y,et al.High-intensity interval versus moderate-intensity continuous training: Superior metabolic benefits in diet-induced obesity mice.Life Sci. 2017;15(191): 122-131.[6] Bae JY,Woo J,Roh HT,et al.The effects of detraining and training on adipose tissue lipid droplet in obese mice after chronic high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis.2017;16(1):13.[7] Marques CM,Motta VF,Torres TS,et al. Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice.Braz J Med Biol Res.2010;43(5):467-475.[8] Chiu CH,Ko MC,Wu LS,et al.Benefits of different intensity of aerobic exercise in modulating body composition among obese young adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial.Health Qual Life Outcomes.2017;15(1):168.[9] Puigserver P,Wu Z,Park CW,et al.A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis.Cell. 998; 92:829-839.[10] Bostrom P,Wu J,Jedrychowski MP,et al.A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature.2012;481(7382):463-468.[11] Lira VA,Benton CR,Yan Z,et al.PGC-1α regulation by exercise training and its influences on muscle function and insulin sensitivity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2010;299:145-161.[12] Yan Z,Li P,Akimoto T.Transcriptional control of the Pgc-1α gene in skeletal muscle in vivo.Exerc Sport Sci Rev.2007;35(3):97-101.[13] Lopaschuk GD,Belke DD,Gamble J,et al.Regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the mammalian heart in health and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta.1994;1213(4):263-276.[14] Hondares E,Torra IP,Iglesias R,et al.PPARδ, but not PPARα, activates PGC-1α gene transcription in muscle. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;354: 1021-1027.[15] Luquet S,Lopez-Soriano J,Holst D,et al.Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ controls muscle development and oxydative capability.FASEB J.2003;17(15):2299-2301.[16] Wang Y,Lee CH,Tiep S,et al. Peroxisome-proliferator- activated receptor δ activates fat metabolism to prevent obesity.Cell. 2003;113(2):159-170.[17] Dressel U, Allen TL, Pippal JB, et al. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ Agonist, GW501516, Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Catabolism and Energy Uncoupling in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17(12):2477-2493.[18] Roberts MD,Bayless DS,Company JM,et al.Elevated skeletal muscle irisin precursor FNDC5 mRNA in obese OLETF rats. Metabolism. 2013;62(8):1052-1056.[19] Swick AG,Orena S,O'Connor A.Irisin levels correlate with energy expenditure in a subgroup of humans with energy expenditure greater than predicted by fat free mass.Metabolism.2013;62(8): 1070-1073.[20] Handschin C,Chin S,Li P,et al.Skeletal muscle ?ber-type switching, exercise intolerance, and myopathy in PGC-1α muscle-speci?c knock-out animals.J Biol Chem.2007;282:30014-30021.[21] Camargo GL,de Souza RA,da Silva DB,et al.Raman spectral characteristics of neck and head of femur in low-density lipoprotein receptor gene knockout mice submitted to treadmill aerobic training.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;173:92-98.[22] 朱小烽,王茹,杨钦,等.不同强度急性有氧运动对肥胖小鼠PGC-1α及其下游因子的调控影响[J].体育科学, 2017,37(3):44-50.[23] Kus V,Prazak T,Brauner P,et al.Induction of muscle thermogenesis by high-fat diet in mice: association with obesity-resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295(2): E356-E367.[24] Wang B,Sun J,Ma Y,et al.Increased oxidative stress and the apoptosis of regulatory T cells in obese mice but not resistant mice in response to a high-fat diet.Cell Immunol. 2014;288(1-2): 39-46.[25] 王欢,李宛真,汪弋力,等.高脂饮食诱导的肥胖及肥胖抵抗小鼠肠道菌群元基因组的比较研究[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 35(2):240-244.[26] Timmons JA,Baar K,Davidsen PK,et a1.Is irisin a human exercise gene? Nature.2012;488(7413):E9-E10.[27] Chen J,Huang Y,Gusdon AM,et al.Irisin: a new molecular marker and target in metabolic disorder. Lipids Health Dis.2015;14:2.[28] Huh JY,Panagiotou G,Mougios V,et al.FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise.Metabolism.2012;61(12): 1725-1738.[29] Stengel A,Hofmann T,Goebel-Stengel M,et al.Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity-correlation with body mass index.Peptides.2013;39: 125-130.[30] Crujeiras AB,Pardo M,Arturo RR,et al.Longitudinal variation of circulating irisin after an energy restriction-induced weight loss and following weight regain in obese men and women.Am J Hum Biol. 2014;26(2):198-207.[31] Choi YK, Kim MK, Bae KH, et al. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;100(1):96-101.[32] Moreno-Navarrete JM,Ortega F,Serrano M,et al.Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(4):E769-778.[33] Lecker SH,Zavin A,Cao P,et al.Expression of the irisin precursor FNDC5 in skeletal muscle correlates with aerobic exercise performance in patients with heart failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2012; 5(6):812-818.[34] Mahmoodnia L,Sadoughi M,Ahmadi A,et al.Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients.J Renal Inj Prev.2017;6(2):88-92.[35] Rohas LM,St-Pierre J,Uldry M,et al.A Fundamental System of Cellular Energy Homeostasis Regulated by PGC-1α.Proc Natl Acad Sci.U.S.A. 2007;104(19):7933-7938.[36] Arany Z.PGC-1 coactivators and skeletal muscle adaptations in health and disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18(5):426-434.[37] Wenz T,Rossi SG,Rotundo RL,et al.Increased muscle PGC-1α expression protects from sarcopenia and metabolic disease during aging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(48): 20405-20410.[38] Choi CS,Befroy DE,Codella R,et al.Paradoxical effects of increased expression of PGC-1α on muscle mitochondrial function and insulin -stimulated muscle glucose metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(50):19926-19931.[39] Handschin C,Choi CS,Chin S,et al.Abnormal glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle-specific PGC-1α knockout mice reveals skeletal muscle -pancreatic β cell crosstalk.J Clin Invest. 2007;117(11):3463-3474.[40] Mootha VK,Handschin C,Arlow D,et al.Errα and Gabpa/b Specify PGC-1α-Dependent Oxidative Phosphorylation Gene Expression That Is Altered in Diabetic Muscle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(17):6570-6575.[41] de Macêdo SM,Lelis DF,Mendes KL,et a1.Effects of Dietary Macronutrient Composition on FNDC5 and Irisin in Mice Skeletal Muscle.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2017;15(4):161-169.[42] Wang Y,Zhang C,Yu R,et al.Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARδ.PLoS Biol.2004;2:1532-1538.[43] 邹毅,管晓峰,黄淑玉,等.运动对高脂饮食诱导肥胖大鼠过氧化物酶体增长因子活化受体-δ表达和胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2011,3(2):107-111.[44] Nygaard H,Slettaløkken G,Vegge G,et al.Irisin in blood increases transiently after single sessions of intense endurance exercise and heavy strength training.PLoS One.2015;10 (3):e0121367.[45] Lee P,Linderman JD,Smith S,et a1.Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans.Cell Metabolism.2014;19(2):302-309.[46] Saleem A, Safdar A,Haikalis M,et a1.Exercise-Induced Amelioration of Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes is Not Regulated by Irisin.The FASEB Journal.2015;29(1): 992.[47] Hecksteden A,Wegmann M,Steffen A,et al.Irisin and exercise training in humans-Results from a randomized controlled training trial.BMC Med.2013;11(1):235.[48] Ellefsen S,Vikmoen O,Slettalokken G,et al.Irisin and FNDC5: effects of 12-week strength training, and relations to muscle phenotype and body mass composition in untrained women.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(9):1875-1888.[49] Czarkowska-Paczek B,Zendzian-Piotrowska M,Gala K,et al.One session of exercise or endurance training does not influence serum levels of irisin in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol.2014;65(3): 449-454.[50] Seo DY,Kwak HB,Lee SR,et al.Effects of aged garlic extract and endurance exercise on skeletal muscle FNDC-5 and circulating irisin in high-fat-diet rat models.Nutr Res Pract.2014;8(2): 177-182.[51] Kim H,Lee HJ,So B,et a1.Effect of aerobic training and resistance training on circulating irisin level and their association with change of body composition in overweight/obese adults: a pilot study. Physiol Res.2016;65(2):271-279.[52] Tadaishi M,Miura S,Kai Y,et al.Effect of exercise intensity and AICAR on isoform-specific expressions of murine skeletal muscle PGC-1α mRNA: a role of β?-adrenergic receptor activation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2011;300(2):E341-E349.[53] Terada S, Tabata I. Effects of acute bouts of running and swimming exercise on PGC-1α protein expression in rat epitrochlearis and soleus muscle.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(14):208-216.[54] Kannisto K,Chibalin A,Glinghammar B,et al.Differential expression of peroxisomal proliferator activated receptors α and δ in skeletal muscle in response to changes in diet and exercise.Int J Mol Med.2006;17:45-52.[55] 苏丽,姜宁,张玥,等.有氧运动对C57BL/6小鼠骨骼肌PPARδ表达和肌纤维类型的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2008,27(1):27-31. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||