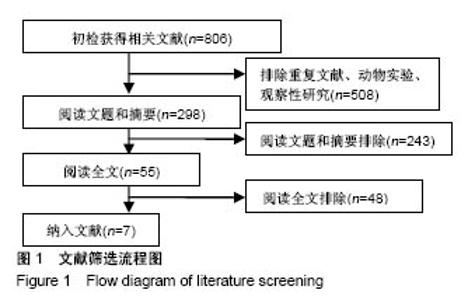
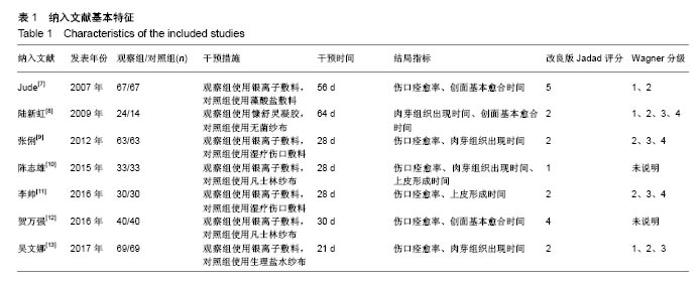
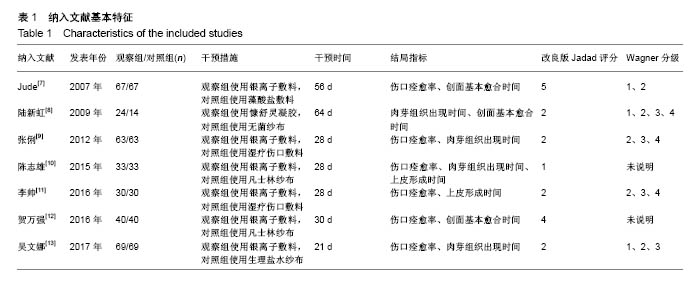
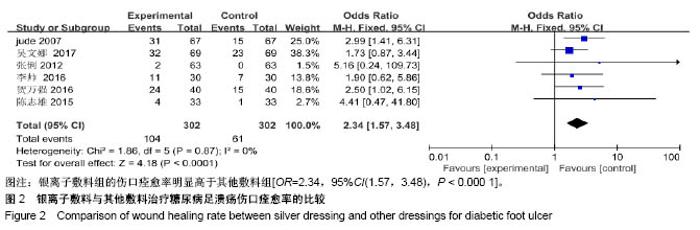
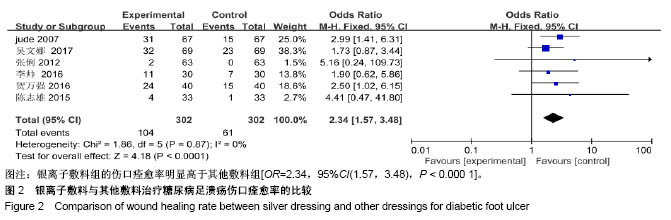
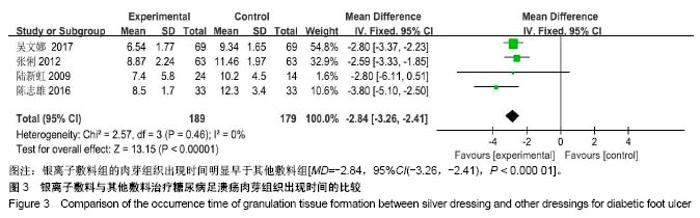
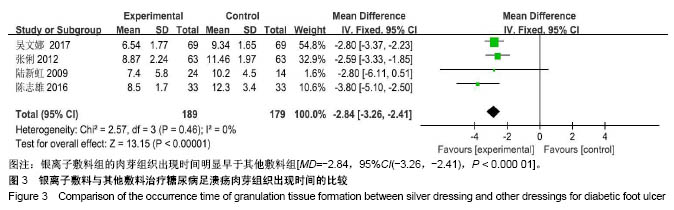
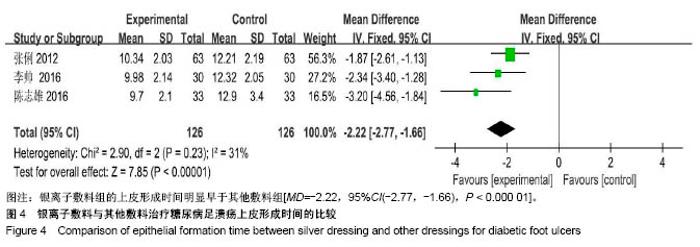
| [1] Martínez-De Jesús FR. A checklist system to score healing progress of diabetic foot ulcers. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2010;9(2):74-83. [2] Woo KY, Botros M, Kuhnke J, etal. Best practices for the management of foot ulcers in people with diabetes. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2013;26(11):512-524; quiz 225-6. [3] International diabetes federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas – 7th Edition. [RB/OL]. http: //www. idd. org, 2015-11-30. [4] 光明日报.《中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2015)》发布[J].食品科技,2015,11(7):13-14.[5] Wanger Jr WJ. The diabetic food. Orthopedics. 1987;10(1):163-172. [6] Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, editors. Cochrane Reviewer, s Handbook 4. 2. 3[updated November 2004]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue1, 2005. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. [7] Jude EB, Apelqvist J, Spraul M, et al. Prospective randomized controlled study of Hydrofiber® dressing containing ionic silver or calcium alginate dressings in non‐ischaemic diabetic foot ulcers. Diabet Med. 2007;24(3):280-288. [8] 陆新虹,温玉洁,胡欣.含银离子敷料慷舒灵治疗糖尿病足疗效观察[J].临床医药实践,2009,18(17):1810-1811.[9] 张俐,马建新,张会峰.银离子敷料联合水凝胶与湿疗伤口敷料治疗糖尿病足感染疗效比较[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2012,22(18):4002-4003.[10] 陈志雄.银离子敷料联合水凝胶治疗糖尿病足的效果观察[J].现代医院,2015,15(3):82-83.[11] 李帅.银离子敷料联合水凝胶治疗糖尿病足的疗效分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2016,10(19):222-223.[12] 贺万强,罗伟华,李磊,等.银离子敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡的疗效观察[J].中国循证医学杂志,2016,16(5):510-512.[13] 吴文娜,陈庚,方亿琼.探究银离子抗菌敷料在糖尿病足溃疡创面护理中的应用疗效[J].中国卫生标准管理,2017,8(24):191-192.[14] Flamm RK, Rhomberg PR, Simpson KM, etal. In vitro spectrum of pexigenan activity when tested against pathogens from diabetic foot infections and with selected resistance machanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(3):1751-1754. [15] Shen Q, Lin D, Zhu H, et al. Clinical distribution and antimicrobial resistance analysis of 754 pathogenic bacteria in diabetic foot infection. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(12):889-894. . [16] 乐忠宏,汤晓姣,崔婷婷,等.糖尿病足感染患者病原学特点及耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(3):590-592,601.[17] 陈美婉,吴红梅,刘长秀,等.不同纳米银制剂抑菌作用的实验研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2009,26(2):132-134.[18] 马宁侠,周琴,吴庆芳,等.美皮康银离子敷料用于拔甲术后伤口的临床体会[J].中国医学创新,2010,7(35):178.[19] Winter GD. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelisation of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. J Wound Care. 1995;4(8):366-371. [20] Hinman CD, Maibach H. Effect of air exposure and occlusion on experimental human skin wounds. Nature. 1963;200(4904):377-378. [21] Rustogi R, Mill J, Frasre JF, Kimble Rm. The use of acticoal inneonatal burns. Burns. 2005;31:878-882. [22] 李东,张杰,牛星焘,等,密闭湿润环境与创面愈合[J].实用美容整形外科杂志,2000,11(3):142-145.[23] 毛庆龙.应用纳米银抗菌敷料治疗烧伤后期残余创面的观察[J].中国误诊学杂志,2009,24(9):848-849.[24] Jørgensen B, Price P, Andersen K E, et al. The silver-releasing foam dressing, Contreet Foam, promotes faster healing of critically colonised venous leg ulcers: a randomised, controlled trial. Int Wound J. 2005;2(1):64-73. [25] Guili Y, Qiuxia L, Junjie L, et al. Synthesis and characteri-zation of dextran-capped silver nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial activity. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;12(5):3766-3774. [26] 何书连,李晓燕.湿性敷料在糖尿病足换药护理中的应用[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(15):4020-4021.[27] Jemec GB, Kerihuel JC, Ousey K, et al. Cost-effective use of silver dressings for the treatment of hard-to-heal chronic venous leg ulcers. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):1-6. [28] Zweiker D, Horn S, Hoell A, et al. Semi-permanent skin staining associated with silver-coated wound dressing Acticoat. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2014;27(4):197-200. [29] Zou SB, Yoon WY, Han SK, et al. Cytotoxicity of silver dressings on diabetic fibroblasts. Int Wound J. 2013;10:306-312. [30] 黄清泉,王蓉蓉,王春仁,等.纳米银医疗产品的体外细胞毒性比较[J].药物分析杂志,2009,29(12):2150-2153.[31] 李旭亚,丁惠萍.糖尿病足感染伤口治疗中使用银离子敷料的临床观察[J].护理实践与研究,2009,6(20):34-35. |