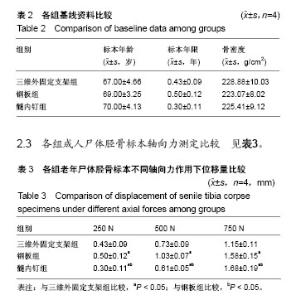
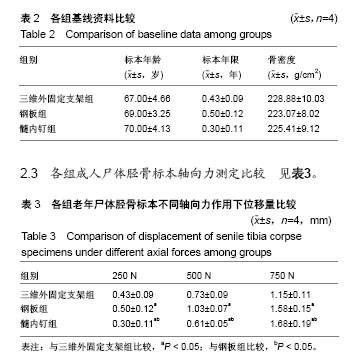
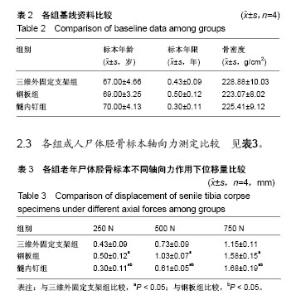
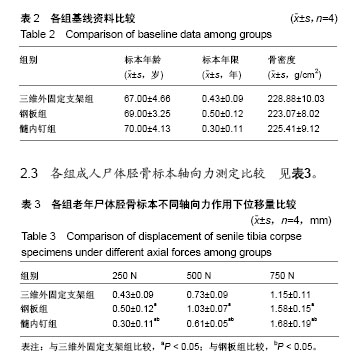
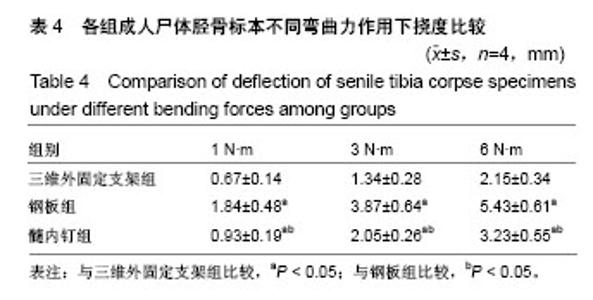
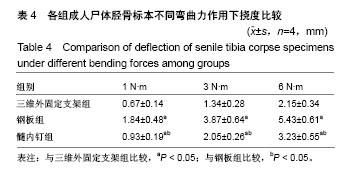
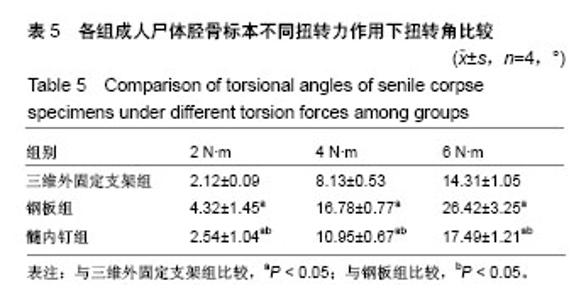
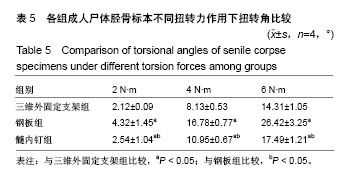
| [1] 毛汉兴,罗轶,沈国平,等. 三种方法固定Schatzker Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的生物力学评价[J]. 中国基层医药,2007,14(8): 1238-1240.[2] 王旭,尹建文,耿翔,等.螺钉与钢板固定骨质疏松患者后踝骨折在模拟正常步态周期中的生物力学研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017, 37(22):1407-1415.[3] Lindsay R. Osteoporosis treatment and fracture outcomes. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(6):921-922.[4] 张晓刚,赵希云,宋敏,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(21):99-204.[5] 李鹏,罗建平,钟家勇,等. 抗旋转股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效分析[J]. 中外医学研究,2015,13(2):19-20.[6] 高壮松.不同手术方案治疗Bennett骨折的近期疗效比较[J]. 山西医药杂志,2017,46(8):953-956.[7] 祝俊雄,宋纯理.骨质疏松及其骨折的局部药物治疗[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(6):806-813.[8] 刘志伟. 椎体后凸成形术治疗脊柱胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的相关有限元研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2012.[9] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2015,8(5): 795-798.[10] 赵俊延,陈柳柳,黄志明,等.脂肪干细胞复合聚乳酸共聚物对大鼠骨折愈合后生物力学的影响[J].中国实用医药, 2018,13(10): 194-195.[11] Choudhry DR,Choudhry DK. To study the clinical and radiological outcomes of closed depressed tibia plateau fracture without the use of a bone graft or a bone substitute. Env Cons. 2016;22(2):127-132.[12] 王春生,苏峰,宗治国,等.骨质疏松模型建立的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(9):1143-1148.[13] 崔轶,李军,郭海,等.骨质疏松模型的评价方法研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(4):416-420.[14] 刘宗超,田泽高,蒋燕,等.三维外固定支架应用于骨质疏松骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(2):145-148.[15] 陈龙,汪国栋,刘曦明,等.3D导航辅助下经皮骶髂螺钉内固定联合逆行前柱螺钉内固定或前环外固定支架治疗Tilt骨盆骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2018,34(2):145-151.[16] 宋长兴.五种外固定方法固定猪胫骨干骨折的生物力学比较[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2011.[17] Giurin I,Bréaud J,Rampal V,et al.A simulation model of nail bed suture and nail fixation: description and preliminary evaluation. J Surg Res. 2018;228(1):142-146.[18] 刘彦士,马信龙,万春友,等.计算机辅助测量在Taylor外固定支架治疗胫腓骨骨折中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(16): 1457-1462.[19] Coughlan T, Dockery F. Osteoporosis and fracture risk in older people. Clin Med (Lond). 2014;14(2):187-191.[20] 章伟,芮碧宇,潘垚,等.新型锁定钢板与AO-PHILOS钢板固定肱骨近端四部分骨折的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2016, 31(6):548-555.[21] 杨萃,陆芸,杨永超.微型外固定支架与掌骨板固定治疗Rolando骨折的三维有限元分析[J].山东医药,2016,56(32):12-14.[22] 丛波,张仲文,韩龙,等.外固定支架与Intertan髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(22): 2058-2061.[23] 莫冰峰,尹东,黄宇,等.手法整复小夹板固定与外固定架固定治疗老年桡骨远端骨折效果对比观察[J].山东医药, 2016,56(44): 89-91.[24] Norris BL, Lang G, Russell TA, et al. Absolute versus relative fracture fixation: impact on fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma. 2018,32 Suppl 1(1):S12-S16.[25] Smith G, Mackenzie SP, Wallace RJ, et al. Biomechanical comparison of intramedullary fibular nail versus plate and screw fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(12):1394-1399.[26] Silverman SL,Kupperman ES,Bukata SV, et al. Fracture healing: a consensus report from the International Osteoporosis Foundation Fracture Working Group. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(7):2197-2206.[27] Maredza M, Petrou S, Dritsaki M, et al. Infographic: Economic justification for intramedullary nail fixation over locking plate fixation for extra-articular distal tibial fractures. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(5):622-623. |