Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (34): 5501-5509.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0686
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of silk fibroin/polycaprolactone temporary rotator cuff patch by electrospinning technique
Guo Ganggang1, 2, Pang Yabo3, Yang Jianhua1, Liu Shichen1, Gao Shuang4, Xiao Tongguang5, Zhang Weixiang6, Zhai Raosheng1, Guo Quanyi2
- 1Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, PLA Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Trauma, Beijing 100853, China; 3Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; 4Peking University, Beijing 100871, China; 5Haozhou People’s Hospital, Haozhou 236800, Anhui Province, China; 6Lanxi People’s Hospital, Lanxi 321100, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2018-07-24Online:2018-12-08Published:2018-12-08 -
Contact:Guo Quanyi, Professor, Institute of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, PLA Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Trauma, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National Nature Science Foundation of China, No. 81472092, 81772319; the National Key Research and Development Plan of China, No. 2017YFC1104102, 2017YFC1103404; Beijing Natural Science Foundation, No. 7172203; Beijing Science and Technology Special Project, No. Z161100005016059; the Key Science and Technology Project of Jiamusi University, No. 12Z1201507
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Ganggang, Pang Yabo, Yang Jianhua, Liu Shichen, Gao Shuang, Xiao Tongguang, Zhang Weixiang, Zhai Raosheng, Guo Quanyi. Preparation of silk fibroin/polycaprolactone temporary rotator cuff patch by electrospinning technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5501-5509.
share this article
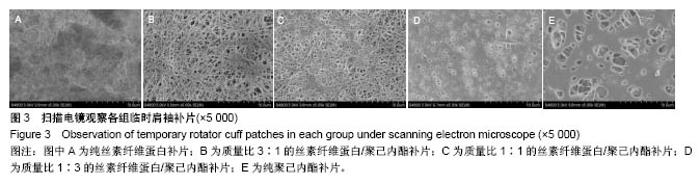
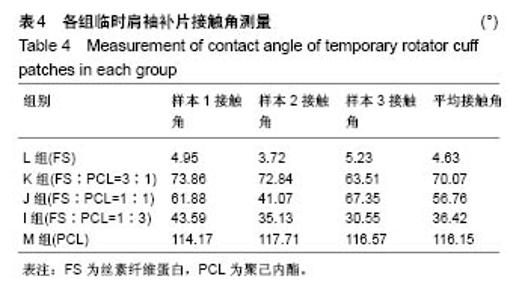
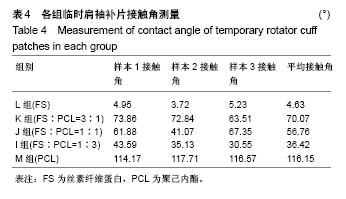
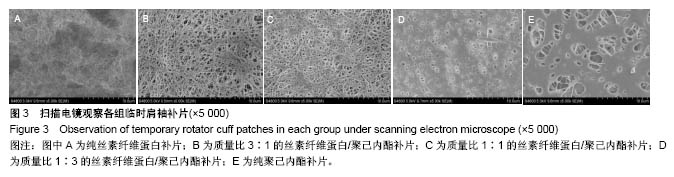
2.2 各组临时肩袖补片的微观结构 见图3。 ①在一定范围内,随着丝素纤维蛋白质量比例的增加,补片的纳米纤维平均直径逐渐减小,孔径数目增多,直径变小;②丝素纤维蛋白本身脆性较高,与聚己内酯混纺后形成的临时肩袖补片表面光滑,无丝珠形成,纤维直径为纳米级,表面可看到明显的孔径。由于电纺丝纤维直径接近纳米级别,虽然扫描电镜下观察的纳米纤维比较紧凑,但电纺丝之间还是会存在很好的空隙[11]。这些空隙有利于局部修复的细胞黏附、迁移,毛细血管重建和细胞间信号的传递及新生组织的长入[12];③宏观状态下发现较于垂直取向方向,在接收轮取向方向上的临时肩袖电纺丝补片有更强的力学强度和抗蠕变潜质相,虽然在扫描电镜下看到的纳米纤维没有明显方向。"
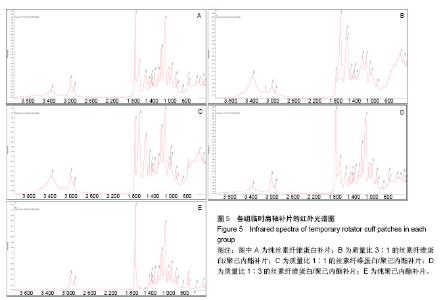
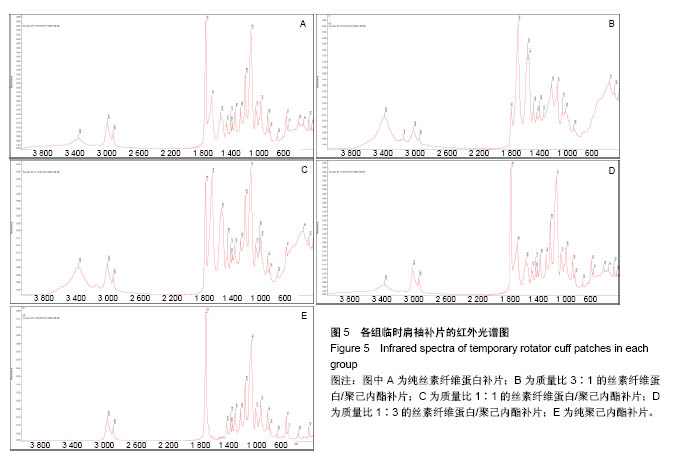
2.4 各组临时肩袖补片的红外光谱 见图5。 ①1 722,2 866 cm-1为聚己内酯的特征性吸收峰; 3 296,3 096,1 651 cm-1为丝素纤维蛋白的特征性吸收峰。在混合电纺丝补片中,随着聚己内酯含量的减少,可发现红外光谱图中1 722 cm-1和2 866 cm-1的峰强逐渐减弱;随着丝素纤维蛋白含量的增加,3 296,3 096, 1 651 cm-1的峰强逐渐增强。其中1 722 cm-1为聚己内酯的双键特征官能团,吸光度比较强,在红外光谱图上比较明显,2 866 cm-1为氢键官能团,吸光强度比较弱;1 651, 3 296 cm-1分别为丝素纤维蛋白的特征性双键和氢键区官能团,吸光度较强,随着混合电纺丝补片中丝素纤维蛋白含量的减少,吸光度迅速下降,在M组完全消失,3 296 cm-1虽然吸光度不强,但峰强也是随混合材料中丝素纤维蛋白含量的降低而逐渐减少。1 500 cm-1 以下的峰强比较多,且各峰强的吸光度都不强,加上干扰较大,分析起来比较复杂;②有文献报道3 328,1 597 cm-1的吸收峰对应N-H拉伸和N-H弯曲,代表β-折叠结构,这种结构的数量和电纺丝膜降解速率呈负相关。丝素纤维蛋白的降解速率直接影响骨髓间充质干细胞的代谢和成骨速率[14]。在各组红外光谱图中并未发现有这两个峰强。丝素纤维蛋白的加工过程和后处理可控制β-折叠的总数量,在后续的研究中可通过增加处理方式来控制电纺丝补片的降解情况;③在混合材料补片中未发现新的吸收峰出现,也没有发现两种材料的特征性吸收峰消失,表明丝素纤维蛋白和聚己内酯这两种物质之间没有发生化学反应,复合的官能团之间互相影响,使复合材料的的亲水性有了较大改观[15]。"
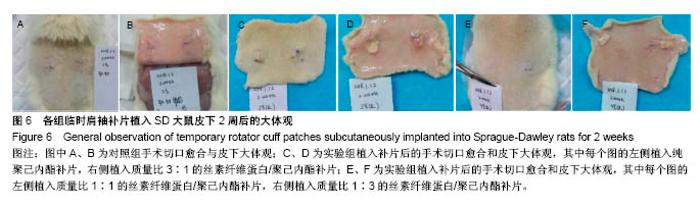
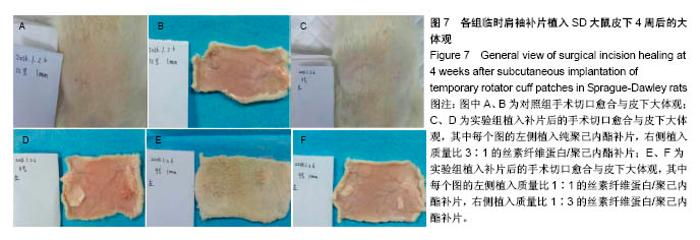
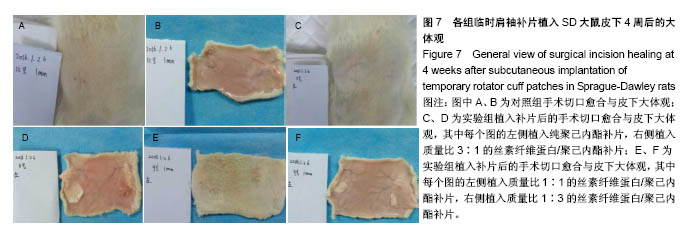
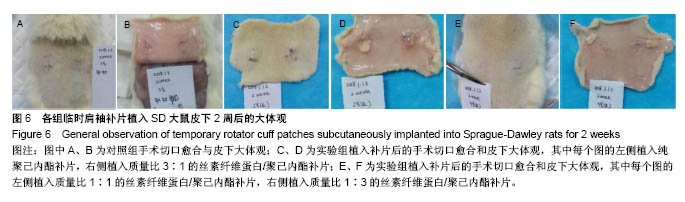
2.6 补片大鼠皮下植入实验 2.6.1 实验动物数量分析 10号和7号大鼠当晚死亡,可能是死于麻醉,毕竟大鼠本身个体存在差异性,也有可能是因为切口原因,加上皮下过多剥离,破损了动静脉,出血导致大鼠耐受能力进一步降低,补片植入实验是在2017年12月28日进行的,加上当时天气比较寒冷,综合作用下,导致2只大鼠死亡,其余大鼠术后很快苏醒,健康状态良好。 2.6.2 术后2周大鼠皮下取材形态分析 见图6。 ①大部分SD大鼠切口愈合良好,手术缝线部分已脱落;②5号大鼠切口内皮下有新生毛细血管网形成,机体局部代偿修复明显,创伤和手术缝合线可能对造模局部有一定的影响;③2号大鼠右侧I组伤口愈合差,仍有较明显的充血瘢痕,皮下充血较明显,血管再生能强,未见皮下植入的补片,可能为手术切口被大鼠自行咬破排出体外所致。根据临床经验,出现这种情况的原因可能是这只大鼠对补片或缝线有强烈的异物排斥反应。4号大鼠仅见血管增生,皮下植入物存在;④实验组共同存在的现象为:皮下植入物形状由最初的平铺四方形转为不规则的皱褶团状,皮下植入补片被机体代偿的黏稠状结缔组织包裹,植入的补片表面有新生血管形成;⑤J组新生血管形成较少,局部充血低,整体手术切口愈合好。"
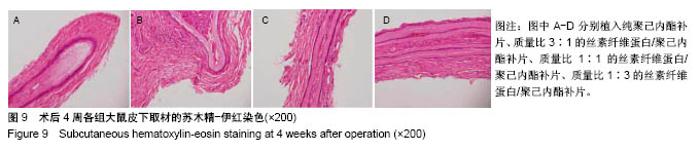
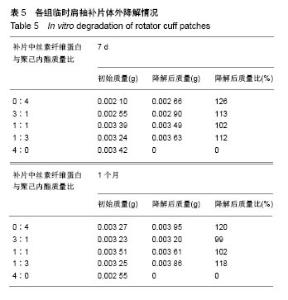
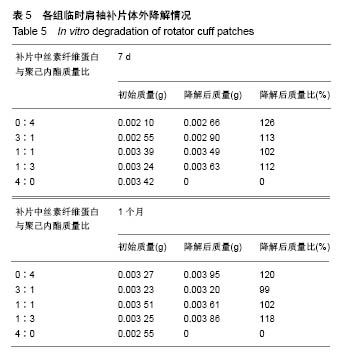
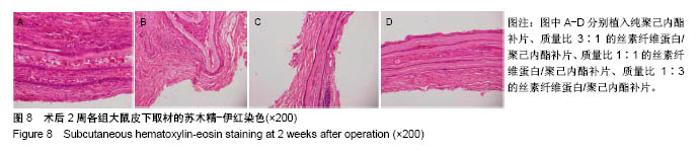
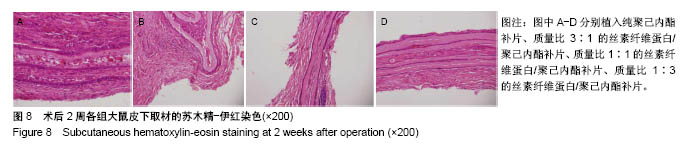
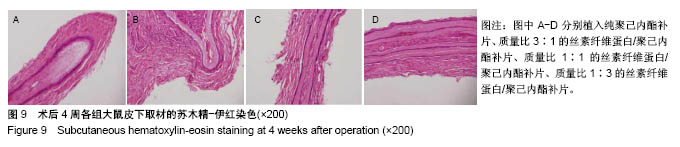
2.6.5 术后4周皮下取材苏木精-伊红染色 见图9。 ①贴附补片新生组织中的细胞数量较2周时明显减少;②补片外新生组织结构类似正常肌腱组织的结构厚度增加,占全层厚度的80%,除最外层的20%;③在新生组织中,各混合补片周围新生组织结构与正常肌腱组织相似度较高,无明显差异性,植入纯聚己内酯补片组较差;④纯聚己内酯补片周围新生组织中的不规则细胞形态比例较大,混合补片各组周围新生组织细胞核形态大部分呈梭形,与补片长轴一致,与肌腱细胞形态一致。最外层20%细胞核形态呈椭圆形,可能是迁移而来的干细胞;⑤各混合补片组中间成分细胞外基质含量明显大于纯聚己内酯补片组,可能与补片的孔隙率和纳米纤维直径相关。"
| [1] Altman GH,Diaz F,Jakuba C,et al.Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials.2003;24(3):401-416.[2] Rockwood DN,Preda RC,Yücel T,et al.Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat Protoc.2011;6(10):1612.[3] Tzur-Balter A,Shatsberg Z,Beckerman M,et al.Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues.Nat Commun.2015;6:6208.[4] Sun H,Luo C,Yang G,et al.Anatomical evaluation of the modified posterolateral approach for posterolateral tibial plateau fracture.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(7):809-818.[5] Sivolella S,Brunello G,Ferrarese N,et al.Nanostructured guidance for peripheral nerve injuries: a review with a perspective in the oral and maxillofacial area.Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):3088-3117.[6] Engelberg I,Kohn J.Physico-mechanical properties of degradable polymers used in medical applications: a comparative study. Biomaterials.1991;12(3):292-304.[7] Sung H,Meredith C,Johnson C,et al.The effect of scaffold degradation rate on three-dimensional cell growth and angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2004;25(26):5735-5742. [8] Font Tellado S,Balmayor ER,Van Griensven M.Strategies to engineer tendon/ligament-to-bone interface: Biomaterials, cells and growth factors.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:126-140.[9] Bedi A,Maak T,Walsh C,et al.Cytokines in rotator cuff degeneration and repair.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):218-227.[10] Zamani F,Amani-Tehran M,Latifi M,et al.The influence of surface nanoroughness of electrospun PLGA nanofibrous scaffold on nerve cell adhesion and proliferation.Journal of materials science. Mater Med. 2013;24(6):1551-1560.[11] Gao S,Yuan Z,Guo W,et al.Comparison of glutaraldehyde and carbodiimides to crosslink tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by decellularized porcine menisci.Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;71:891-900.[12] Agrawal CM,Ray RB.Biodegradable polymeric scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55(2): 141-150.[13] Chou Y,Yeh W,Chao C,et al.Enhancement of tendon-bone healing via the combination of biodegradable collagen-loaded nanofibrous membranes and a three-dimensional printed bone-anchoring bolt.Int J Nanomed.2016;11:4173-4186.[14] Park S,Gil ES,Kim HJ,et al.Relationships between degradability of silk scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2010;31(24):6162-6172.[15] Chandrasekaran AR,Venugopal J,Sundarrajan S,et al.Fabrication of a nanofibrous scaffold with improved bioactivity for culture of human dermal fibroblasts for skin regeneration.Biomedical materials (Bristol, England). 2011;6(1):15001.[16] Ma Z,Kotaki M,Yong T,et al.Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET)nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(15): 2527-2536.[17] 李鹏昊,刘舒云,王亚洁,等.电纺聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/Ⅰ型胶原-聚己内酯双层膜预防腱周粘连的相关研究[J].中国医药生物技术, 2017, 12(4):289-296.[18] Orr SB,Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,et al.Aligned multilayered electrospun scaffolds for rotator cuff tendon tissue engineering.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;24:117-126.[19] Beason DP,Connizzo BK,Dourte LM,et al.Fiber-aligned polymer scaffolds for rotator cuff repair in a rat model.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):245-250. [20] Pham QP,Sharma U,Mikos AG.Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(10):2796-2805.[21] Diseases EI.U.S.Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Recommendations and Reports CONTENTS. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2012;28(11):373-392.[22] Wu XL,Briggs L,Murrell GAC.Intraoperative Determinants of Rotator Cuff Repair Integrity. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2771-2776.[23] Alhakim W,Noorani A,Lambert S.Assessment and treatment strategies for rotator cuff tears. Shoulder Elbow.2015;7(2):76.[24] Lorbach O,Baums MH,Kostuj T,et al.Advances in biology and mechanics of rotator cuff repair.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(2):530-541.[25] 李嘉,戴海峰,刘莎莎,等.骨膜补片加强修复促进肩袖腱骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(30):4847-4751.[26] 刘斌,袁振超,贺聚良,等.肿瘤型肱骨近端假体复合人工补片重建肩关节临床疗效观察[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(1):164-165.[27] Inui A,Kokubu T,Mifune Y,et al.Regeneration of rotator cuff tear using electrospun poly(d,l-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) scaffolds in a rabbit model.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(12):1790-1799.[28] Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,Kishan A,et al.Multilayered electrospun scaffolds for tendon tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(23-24):2594-2604.[29] Zhao S,Zhao J,Dong S,et al.Biological augmentation of rotator cuff repair using bFGF-loaded electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolide) fibrous membranes.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:2373-2385.[30] Zhao S,Xie X,Pan G,et al.Healing improvement after rotator cuff repair using gelatin-grafted poly(L-lactide) electrospun fibrous membranes.J Surg Res.2015;193(1):33-42.[31] Hakimi O,Mouthuy PA,Zargar N,et al.A layered electrospun and woven surgical scaffold to enhance endogenous tendon repair.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;26:124-135.[32] Orr SB,Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,et al.Aligned multilayered electrospun scaffolds for rotator cuff tendon tissue engineering.Acta Biomater2015;24:117-126.[33] Li Z,Song L,Huang X,et al.Tough and VEGF-releasing scaffolds composed of artificial silk fibroin mats and a natural acellular matrix. RSC Adv.2015;5(22):16748-16758.[34] Chou Y,Yeh W,Chao C,et al.Enhancement of tendon–bone healing via the combination of biodegradable collagen-loaded nanofibrous membranes and a three-dimensional printed bone-anchoring bolt.Int J Nanomedicine.2016;11:4173-4186. [35] Li X,Cheng R,Sun Z,et al.Flexible bipolar nanofibrous membranes for improving gradient microstructure in tendon-to-bone healing.Acta Biomaterialia.2017;61:204-216.[36] 任士友,江长青,张文涛.不同肩袖补片特点:应用强度、降解速率及酸性降解物的调控[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(30):4876-4881. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||