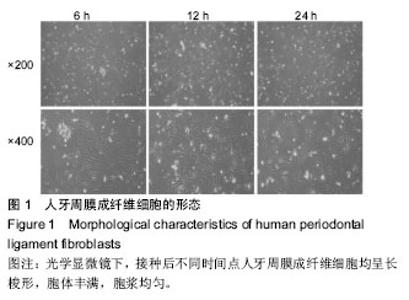
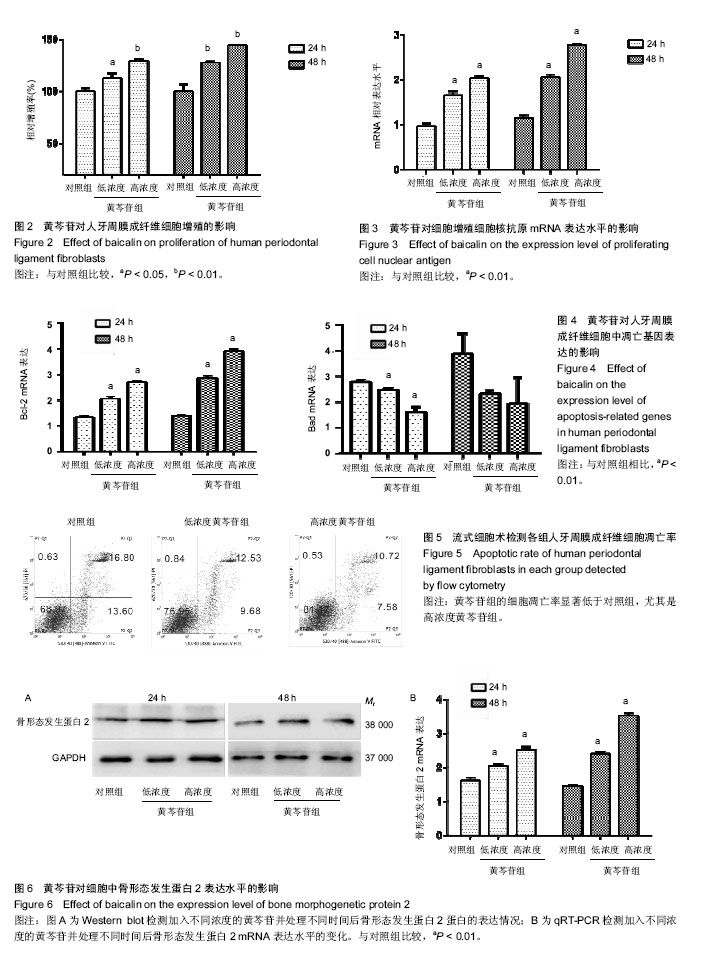
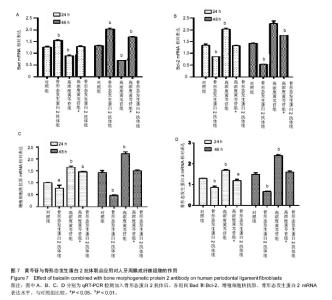
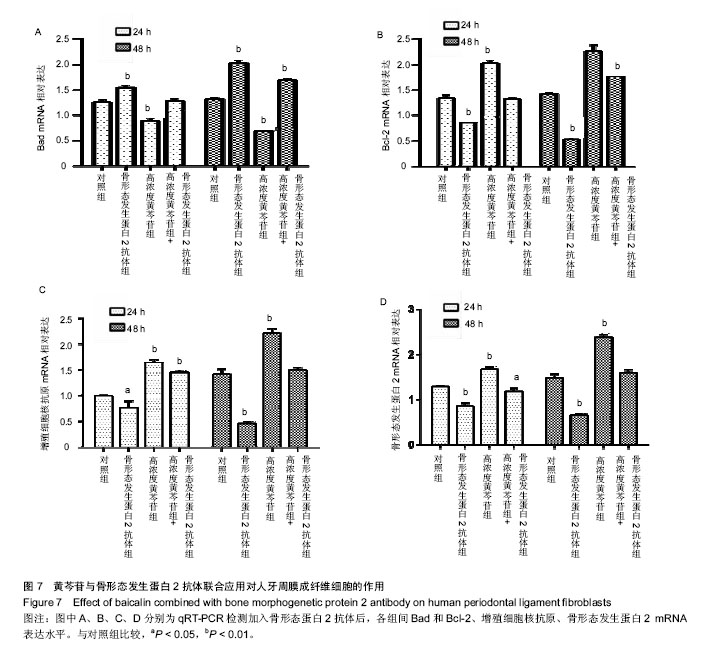
| [1] 李云霞.牙周病的病因及临床治疗研究进展[J].河北医学, 2013,19(3): 466-469.[2] 周志雄,张笋.Er:YAG激光照射对HPLFs增殖的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(3):358-361.[3] Duan X, Ji M, Deng F, et al. Effects of connective tissue growth factor on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol.2017; 84:37-44.[4] 廖海清,曹正国.经典Wnt信号通路在牙周膜细胞成骨分化过程中的调控[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(03):224-227.[5] Wang L, Wu F, Song Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA related to periodontitis interacts with miR-182 to upregulate osteogenic differentiation in periodontal mesenchymal stem cells of periodontitis patients. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(8):e2327.[6] 沈慧娟,李琳娟,康娜.HPLFs培养与鉴定[J].广西医科大学学报, 2015, 32(6):872-875.[7] 郭珲,潘克清,邓婧,等.羧甲基壳聚糖锌多肽复合材料对HPLFs的毒性[J].上海口腔医学,2017,26(02):162-166.[8] 孙卫斌.牙周病松动牙处理的现代观念[J].国外医学.口腔医学分册,1999, 6:331-334.[9] 朱庆勇,陈文君,朱慧,等.抑制Kv1.3表达能够降低HPLFs增殖和分化成骨能力[J].安徽医科大学学报,2017,52(6):819-823.[10] Bhattarai G, Kook SH, Kim JH, et al.COMP-Ang1 prevents periodontitic damages and enhances mandible bone growth in an experimental animal model.Bone. 2016;92:168-179..[11] 李晨睿,孟志远,牛银波,等.黄芩苷通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的促进作用[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2015,31(07):919-924.[12] Chen LJ, Hu BB, Shi XL, et al. Baicalein enhances the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Arch Oral Biol.2017; 78:100-108.[13] 顾青青,邵以诺,安叡,等.葛根芩连汤有效成分对黄芩苷在Caco-2细胞模型中吸收转运的影响[J].中成药, 2015,37(4):694-699.[14] 李会英,赵满琳,尹梓兆,等.中药黄芩苷对HPLFs保护作用的实验研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2006,6:634-637.[15] 桂林源,刘世宇,邱新毓,等.黄芩小分子化合物对雌激素缺乏骨质疏松的预防和治疗作用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016, 26(5):294-300.[16] 张前,杨浩,陈博,等.黄芩苷防治中枢神经系统疾病的研究进展[J].中国药师,2017,20(2):327-331.[17] Liu XM, Feng Y. Nerve protective effect of Baicalin on newborn HIBD rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(10):806-810. [18] Cherng CH, Lee KC, Chien CC, et al. Icalin ameliorates neuropathic pain by suppressing HDAC1 expression in the spinal cord of spinal nerve ligation rats. J Formos Med Assoc.2014;113(8):513-520.[19] 严启新,赵文娟,殷明,等.黄芩总黄酮及黄芩苷对大鼠成骨细胞及破骨细胞活性的研究[J].天然产物研究与开发, 2012,24(10):1367-1370.[20] 葛志华,杨宁,孙立新.野黄芩苷对内毒素抑制人牙周膜细胞碱性磷酸酶活性的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2010,19(04):365-367.[21] Uchida K, Inoue G, Matsushita O, et al.Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor-Anchored Multilayered Mesenchymal Cell Sheets Accelerate Periosteal Bone Formation.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4371460..[22] Hu JG, Zhang YX, Qi Q, et al.Expression of BMP-2 and BMP-4 proteins by type-1 and type-2 astrocytes induced from neural stem cells under different differentiation conditions. ActaNeurobiolExp (Wars). 2012;72(1):95-101.[23] 周心,官堂明,黄韧,等.BMPs在中枢神经系统发育和神经保护中的作用[J].药学研究,2014,33(05):282-285.[24] Ahsan S, Ge Y, Tainsky MA,et al. Combinatorial therapeutic targeting of BMP2 and MEK-ERK pathways in NF1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.Oncotarget. 2016, 7(35):57171-57185.[25] 杨林,徐军美,王亚平,等.骨形态发生蛋白2/4在神经系统中的作用及其研究进展[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2018,43(2):222-228.[26] 田原,邸阳,包翠芬,等.松果菊苷含药血清诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及BMP2表达的研究[J].中药药理与临床, 2015,31(4):60-64.[27] 齐鹏鹏,孟粼,吴梓萁,等.骨形态发生蛋白2在牙槽骨改建中作用的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2015,41(3):671-674.[28] 张勤,郑司鹏,刘红,等.大鼠下颌前导后髁突软骨组织中BMP-2的含量变化研究[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2015,38(12):1489-1491+1495.[29] Park SH, Kwon JS, Lee BS, et al. BMP2-modified injectable hydrogel for osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Sci Rep.2017;7(1):6603.[30] 冯艳红,刁志虹,高毅,等.BMP2基因转染犬牙髓成纤维细胞与异种烧结骨复合组织工程的实验研究[J].河北医科大学学报, 2011,32(8):908-912+921. |