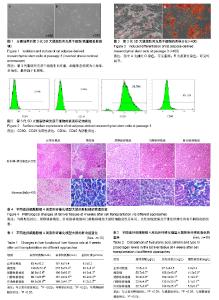
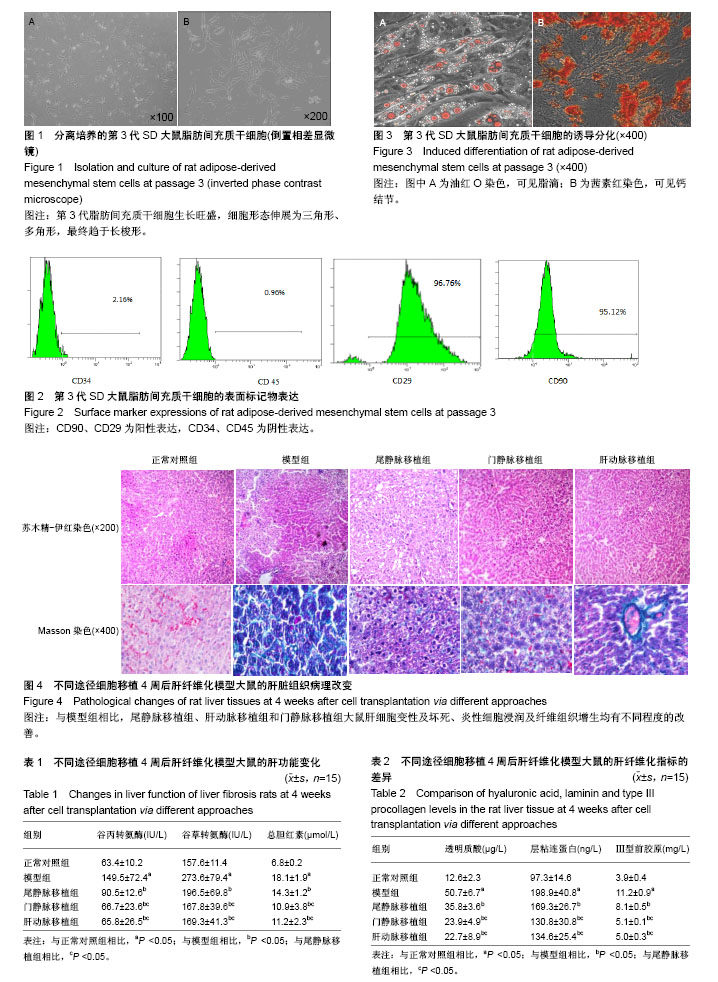
| [1] Pavlov CS, Casazza G, Nikolova D, et al. Transient elastography for diagnosis of stages of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1: CD010542. [2] Friedman SL. Hepatic Fibrosis: Emerging Therapies. Dig Dis. 2015; 33(4):504-507. [3] 李辰,李勇文. 氧化应激致肝纤维化发生机制[J]. 中国保健营养, 2017, 27(5):296.[4] Yamashita T, Takayama K, Sakurai F, et al. Billion-scale production of hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496(4):1269-1275. [5] Takayama K, Akita N, Mimura N, et al. Generation of safe and therapeutically effective human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for regenerative medicine. Hepatol Commun. 2017;1(10):1058-1069.[6] 杜盼,余江南,徐希明. 人源多能干细胞体外定向诱导分化为肝细胞[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版), 2018,28(1):39-46. [7] 王彦会,王志茹,孙岩,等. HBV感染者脂肪间充质干细胞体外诱导为肝样细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(25):3983-3988. [8] 刘卫,余森源,严和中,等. 骨髓间质干细胞移植对肝纤维化模型大鼠治疗效果[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2017,45(9):903-907.[9] 马虎成,王鑫,吴旻娜,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞对急性肝衰竭的治疗作用及机制[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2017,23(10):694-699.[10] 顾世杰,陈云浩,赵辉,等. 不同途径移植人脐带间充质干细胞对大鼠肝脏缺血-再灌注损伤修复研究[J]. 器官移植, 2017,8(3):190-194.[11] 刘志娟,安曦洲,肖莉,等. 人脐带间充质干细胞对类噬血细胞性淋巴组织细胞增多症小鼠模型肝脏损伤的修复作用及机制[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2016,38(17):1929-1936.[12] Abdellatif H, Shiha G, Saleh DM, et al. Effect of human umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation on oval cell response in 2-AAF/CCL4 liver injury model: experimental immunohistochemical study. Inflamm Regen. 2017;37:5. [13] Hong J, Jin H, Han J, et al. Infusion of human umbilical cord?derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively relieves liver cirrhosis in DEN?induced rats. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(4):1103-1111. [14] Teshima T, Matsumoto H, Michishita M, et al. Allogenic Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Acute Hepatic Injury in Dogs. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3892514. [15] Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10): 2491-2502. [16] 张洁利, 靳寸朵. 一例脐带间充质干细胞治疗肝衰竭合并腹水的护理[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2015,21(3):359-360. [17] 薛改,陈则纱,刘建芳, 等. 不同方案移植脐带间充质干细胞对硫代乙酰胺所致大鼠肝纤维化治疗效果的比较[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2016,28(4):12-17, 21.[18] Deng L, Kong X, Liu G, et al. Transplantation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Efficiently Rescues Thioacetamide-Induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2208-2215. [19] Saidi R, Rajeshkumar R, Shariftabrizi A, et al. Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Liver Regeneration. J Invest Surg. 2015;28(6):303-308. [20] 陈霞,胡文君,王英杰. 人眼袋脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞的分离及生物学特性观察[J]. 延安大学学报(医学科学版), 2017,15(2):1-4.[21] 赵刚,刘微微,高伟玮,等. 不同组织来源间充质干细胞体外成骨分化能力的比较研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017,23(5):561-566,584.[22] 周炜,张骏,凡进,等. 过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体2及其磷酸化形式在脂肪干细胞脂向分化过程中的表达[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2017,37(6): 1304-1306.[23] 王三虎,满荣勇,高细强,等. 脂肪干细胞的诱导分化及其来源的研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017,17(24):4606-4609.[24] 兰玲, 于静, 刘冉, 等. 骨髓内皮祖细胞输注后在肝纤维化大鼠肝脏内的示踪研究[J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 2012,33(11):684-688.[25] 李蓉. 脂肪间质干细胞移植对肝硬化大鼠的实验研究[J]. 河北医学, 2016, 22(2):180-184.[26] 曹后康,高雅,黄思茂,等. 杠板归总黄酮抗大鼠肝纤维化作用的机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2017,33(9):1303-1308.[27] 寻权. 人羊膜上皮细胞移植治疗肝硬化大鼠的初步研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013.[28] 范冬梅,张子祥,赵英新,等. 人脐带来源间充质干细胞向HepG2肝癌细胞原位移植瘤的归巢及分化[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2017,24(6):595-600.[29] 杨鹏飞,解景东,颜炳柱,等. Bcl-2基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗急性肝衰竭的初步研究[J]. 肝脏, 2017,22(1):27-31.[30] 李畅. Wip1基因敲除对急性肝损伤的影响及其机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院中国医学科学院;清华大学医学部, 2015.[31] 游佳,焦艳,郑琦,等. 不同途径移植骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠肝纤维化进程的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2015,32(10):2417-2419.[32] 张雯,陈香宇,何巧玉,等. 经不同方式移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肝纤维化的疗效[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2013,29(6):889-891.[33] Wang Y, Lian F, Li J, et al. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation via portal vein improves microcirculation and ameliorates liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rats. J Transl Med. 2012;10:133. |