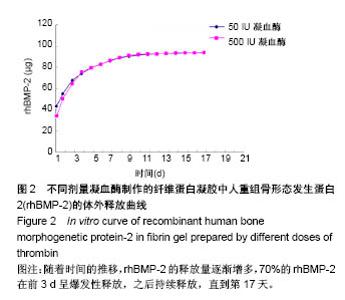
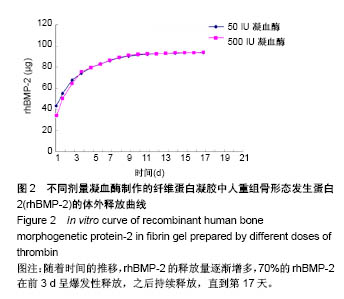
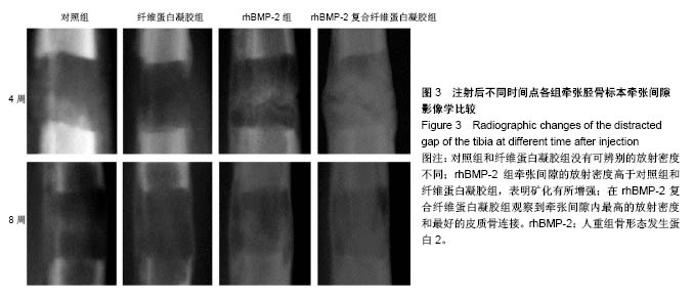
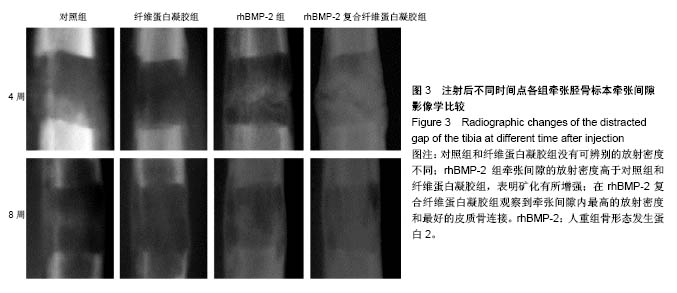
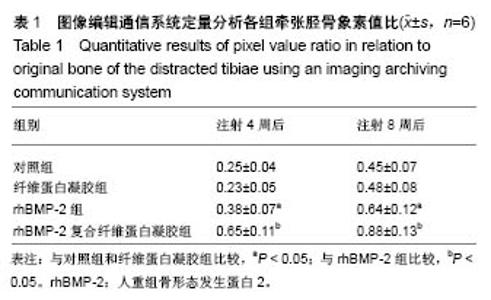
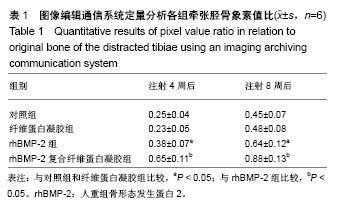
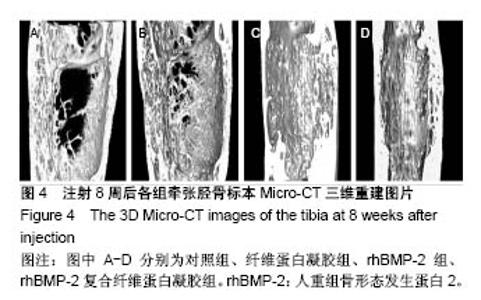
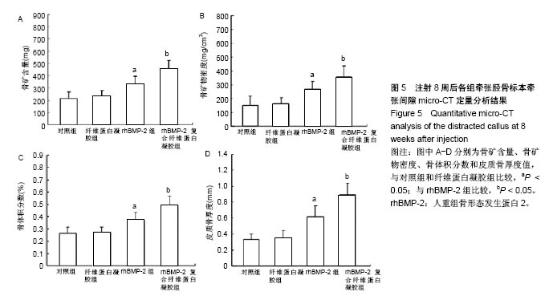
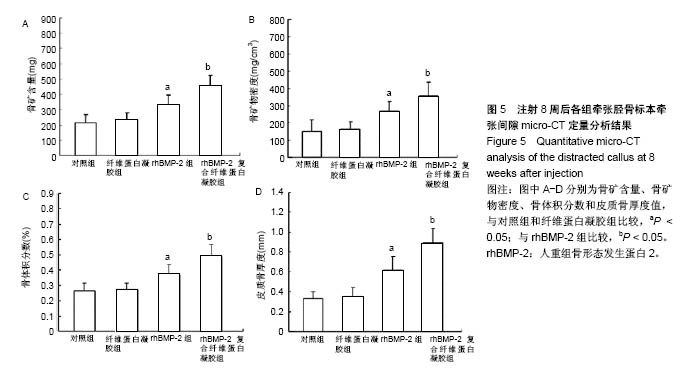
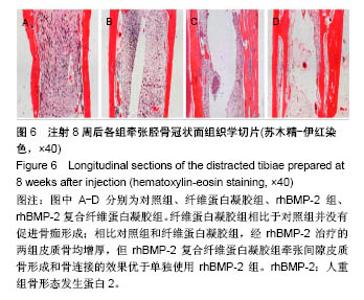
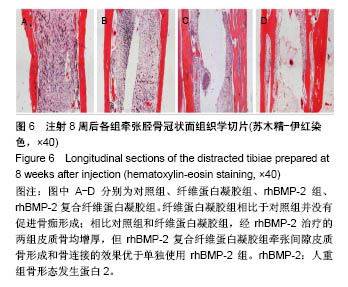
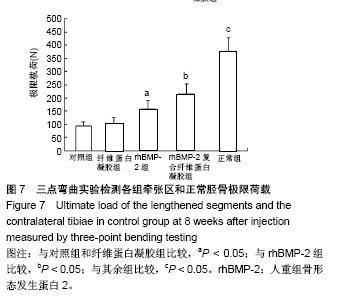
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4763-4768.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0976
Previous Articles Next Articles
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/fibrin gel enhances bone formation in a rabbit model of tibial distraction osteogenesis
Guo Jiao-yang, Xu Lu-chen, Li Yun-feng
- Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2018-04-28Online:2018-10-28Published:2018-10-28 -
Contact:Li Yun-feng, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Guo Jiao-yang, Master candidate, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81300858
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Jiao-yang, Xu Lu-chen, Li Yun-feng. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/fibrin gel enhances bone formation in a rabbit model of tibial distraction osteogenesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4763-4768.
share this article
| [1] McCarthy JG,Katzen JT,Hopper R,et al.The first decade of mandibular distraction: lessons we have learned.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110: 1704-1713.[2] 李永頔,朱鹏娜,王冬香,等.骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体在甲状旁腺激素调控下颌骨牵张成骨中的表达效应[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2016, 34(3):234-238.[3] Saleh M,Royston S.Management of nonunion of fractures by distraction with correction of angulation and shortening.J Bone Joint Surg B. 1996; 78:105-109.[4] Aronson J.Limb-lengthening, skeletal reconstruction, and bone transport with the Ilizarov method.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1997;79:1243-1258.[5] 谢红军,王银龙,周健.低强度脉冲超声对牵张成骨新骨形成的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2008,35(2):186-188.[6] El-Hakim IE,Azim AM,El-Hassan MF,et al.Preliminary investigation into the effects of electrical stimulation on mandibular distraction osteogenesis in goats.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2004;33:42-47.[7] Aronson J.Modulation of distraction osteogenesis in the aged rat by fibroblast growth factor. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;(425):264-283.[8] Li G,Ryaby JT,Carney DH,et al.Bone formation is enhanced by thrombin-related peptide TP508 during distraction osteogenesis.J Orthop Res.2005;23:196-202.[9] Haque T,Hamade F,Alam N,et al.Characterizing the BMP pathway in a wild type mouse model of distraction osteogenesis.Bone. 2008;42: 1144-1153.[10] Yang X,Gong P,Lin Y,et al.Cyclic tensile stretch modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells via the BMP-2 pathway. Arch Med Sci.2010;6:152-159.[11] Rakian A,Yang WC,Gluhak-Heinrich J,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene controls tooth root development in coordination with formation of the periodontium.Int J Oral Sci.2013; 5:75-84.[12] Issa JP,do Nascimento C,Lamano T,et al.Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bone formation in the acute distraction osteogenesis of rat mandibles.Clin Oral Implants Res.2009;20:1286-92.[13] Ashinoff RL,Cetrulo CL Jr,Galiano RD,et al.Bone morphogenic protein-2 gene therapy for mandibular distraction osteogenesis.Ann Plast Surg. 2004;52:585-590;discussion 591.[14] Li G,Bouxsein ML,Luppen C,et al.Bone consolidation is enhanced by rhBMP-2 in a rabbit model of distraction osteogenesis.J Orthop Res. 2002;20:779-788.[15] 黄鑫,孟国林,刘建,等.rhBMP-2壳聚糖微球的制备及体外检测[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(15):1172-1174.[16] Chung YI,Ahn KM,Jeon SH,et al.Enhanced bone regeneration with BMP-2 loaded functional nanoparticle-hydrogel complex.J Control Release.2007;121:91-99.[17] Hosseinkhani H,Hosseinkhani M,Khademhosseini A,et al. Bone regeneration through controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from 3-D tissue engineered nano-scaffold.J Control Release. 2007;117: 380-386.[18] Wildemann B,Kandziora F,Krummrey G,et al.Local and controlled release of growth factors (combination of IGF-I and TGF-beta I, and BMP-2 alone) from a polylactide coating of titanium implants does not lead to ectopic bone formation in sheep muscle.J Control Release.2004; 95:249-256.[19] 黄琳琳,曾奕明,施丽泳.多种生长因子纤维蛋白凝胶释放系统的建立[J].国际呼吸杂志, 2015,35(10):766-770.[20] Chudek J,Kowalczyk A,Kowalczyk AK,et al.Quality of life (QOL) evaluation after acute coronary syndrome with simultaneous clopidogrel treatment.Arch Med Sci. 2014;10:33-38. [21] Pandit AS,Wilson DJ,Feldman DS.Fibrin scaffold as an effective vehicle for the delivery of acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-1).J Biomater Appl. 2000;14:229-242.[22] Taylor SJ,Sakiyama-Elbert SE.Effect of controlled delivery of neurotrophin-3 from fibrin on spinal cord injury in a long term model.J Control Release.2006;116:204-210.[23] Gorodetsky R,Peylan-Ramu N,Reshef A,et al.Interactions of carboplatin with fibrin(ogen), implications for local slow release chemotherapy.J Control Release.2005;102:235-245.[24] Wang EA,Rosen V,D'Alessandro JS,et al.Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(6):2220-2224.[25] Singh S,Song HR,Venkatesh KP,et al.Analysis of callus pattern of tibia lengthening in achondroplasia and a novel method of regeneration assessment using pixel values. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39:261-266.[26] Song SH,Sinha S,Kim TY,et al.Analysis of corticalization using the pixel value ratio for fixator removal in tibial lengthening.J Orthop Sci. 2011; 16:177-183.[27] Zheng LW,Wong MC,Rabie AB,et al.Evaluation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in mandibular distraction osteogenesis in rabbits: Effect of dosage and number of doses on formation of bone.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2006;44:487-494.[28] Abbaspour A,Takata S,Sairyo K,et al.Continuous local infusion of fibroblast growth factor-2 enhances consolidation of the bone segment lengthened by distraction osteogenesis in rabbit experiment.Bone. 2008; 42:98-106.[29] Kona? E,Emin Mavili M,Korkusuz P,et al.Acceleration of distraction osteogenesis with drug-releasing distractor.J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20: 2041-2048.[30] Foley RL,Nixon AJ.Insulin-like growth factor I peptide elution profiles from fibrin polymers determined by use of high-performance liquid chromatography.Am J Vet Res. 1997;58:1431-1435.[31] Brittberg M,Sjögren-Jansson E,Lindahl A,et al.Influence of fibrin sealant (Tisseel) on osteochondral defect repair in the rabbit knee.Biomaterials. 1997;18:235-242.[32] Fakhry A,Ratisoontorn C,Vedhachalam C,et al.Effects of FGF-2/-9 in calvarial bone cell cultures: differentiation stage-dependent mitogenic effect, inverse regulation of BMP-2 and noggin, and enhancement of osteogenic potential.Bone.2005;36:254-266.[33] Otto F,Thornell AP,Crompton T,et al.Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development.Cell. 1997;89:765-771.[34] 杨绍安,靳安民.富含酸性成纤维细胞生长因子纤维蛋白凝胶预防失神经支配运动终板退行性变的免疫组织化学研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(16):3089-3092. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [5] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [8] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [9] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [15] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||