Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4184-4190.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0914
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of calcium phosphate coatings on corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of magnesium alloy scaffolds
Ma Fei1, Li Xiang1, Xie Rui-min1, Wang Yong-ping1, He Yao-hua2
- 1兰州大学第一医院骨科,甘肃省兰州市 730000;2上海交通大学第六人民医院骨科,上海市 200233
-
Received:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Wang Yong-ping, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Ma Fei, Master candidate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Program of Gansu Provincial Universities, No. 2018B-013; the Scientific Research Project of the First Hospital of Lanzhou University, No. ldyyyn2017-21, ldyyyn2013-01; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271961, 81572106
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Fei, Li Xiang, Xie Rui-min, Wang Yong-ping, He Yao-hua. Effect of calcium phosphate coatings on corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of magnesium alloy scaffolds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(26): 4184-4190.
share this article
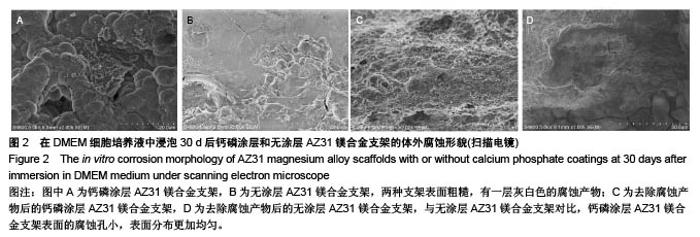
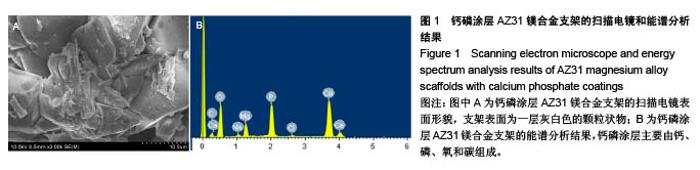
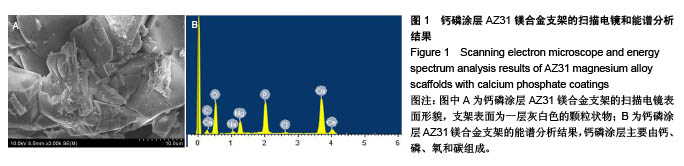
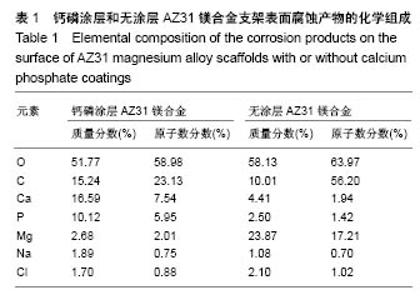
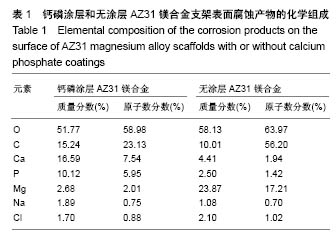
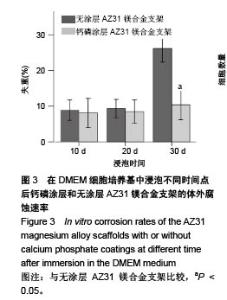
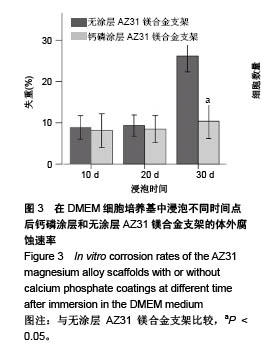
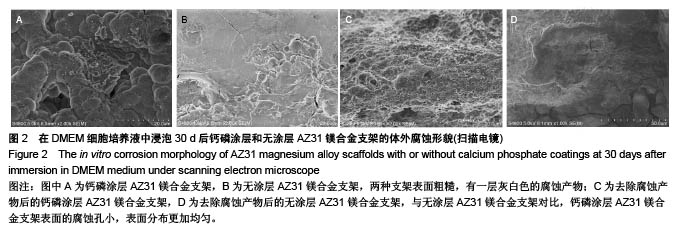
2.2 静态浸泡实验结果 图2显示了在DMEM细胞培养基中浸泡30 d后,钙磷涂层AZ31镁合金支架和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架的表面形貌。在钙磷涂层AZ31镁合金支架和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面有一层腐蚀产物(图2 A,B),能谱分析分析表明腐蚀产物的化学组成主要是氧、碳、钙、磷、镁、钠和氯(表1)。清除腐蚀产物后,钙磷涂层与无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面都能够清晰地看到腐蚀坑,然而,与无涂层AZ31镁合金支架对比,钙磷涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面的腐蚀孔小,表面分布更加均匀,而无涂层AZ31镁合金支架存在严重的凹陷和普遍腐蚀(图2C,D),说明了拥有钙磷涂层的AZ31镁合金支架抗腐蚀性能更好。"
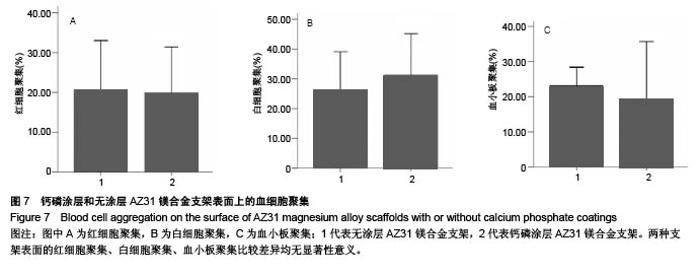
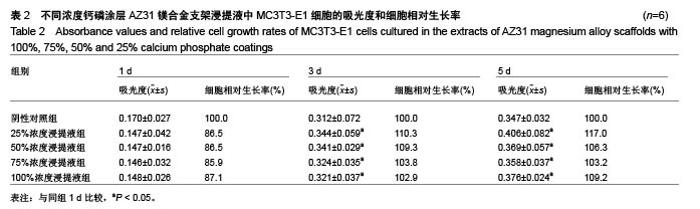
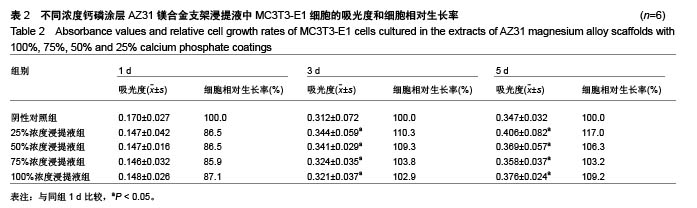
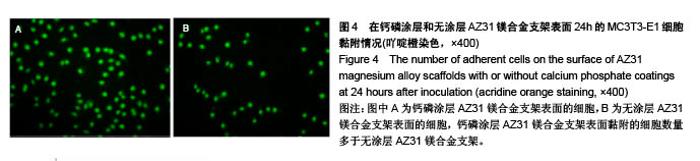
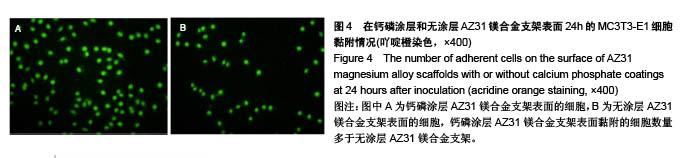
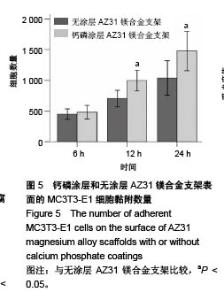
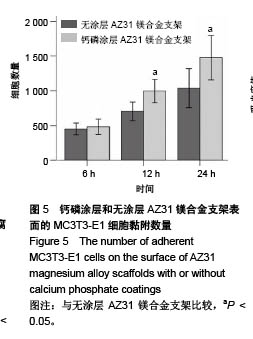
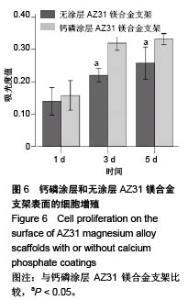
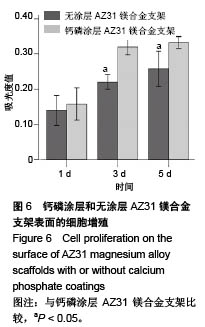
2.6 血细胞聚集实验结果 血细胞聚集实验可用于研究生物材料与血细胞之间的相互作用,血液中的主要有成分是血细胞,包括红细胞、白细胞和血小板,分别在维持营养和氧气供给、炎症和凝血过程中发挥重要作用。生物材料引起的溶血、白细胞活化及血小板黏附和活化情况是血液相容性的主要研究内容。根据ISO标准规定对应用于人体的医用材料,必须进行体外血液相容性的评价[28]。实验主要研究了钙磷涂层和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面血细胞的聚集情况,钙磷涂层和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面的血细胞聚集结果如图7所示。如图7A所示,聚集于钙磷涂层和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面的红细胞分别为19.90%和20.46%,两组红细胞聚聚无明显差异(P > 0.05)。如图7B所示,聚集于钙磷涂层和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面的白细胞分别为31.21%和26.24%,两组白细胞聚集无明显差异(P > 0.05)。如图7C所示,聚集于钙磷涂层和无涂层AZ31镁合金支架表面的血小板分别为19.03%和23.22%,两组血小板聚集无差异(P > 0.05)。这些结果表明,由于优良的血液相容行为,钙磷涂层AZ31镁合金表面没有明显的血细胞聚集。"
| [1] 王勇平,蒋垚.基于SCI数据库收录文献分析镁合金植入物在骨科的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(16):2971-2980. [2] 王勇平,尹自飞,蒋垚,等.镁合金材料在医学临床领域的应用[J].中华临床医师杂志,2011,5(24):7323-7326.[3] Witte F.The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomaterialia.2010;6:1680-1692.[4] Zhang S,Zhang X,Zhao C,et al.Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial.Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(2): 626-640.[5] Staiger MP,Pietak AM,Huadmai J,et al.Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1728-1734.[6] Li Z,Gu X,Lou S,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008;29:1329-1344.[7] Zberg B,Uggowitzer PJ,Löffler JF.MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants.Nat Mater. 2009;8(11):887-891.[8] 王勇平,何耀华,朱兆金,等.Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr镁合金体外降解行为及生物相容性[J].科学通报,2012,57(32):3109-3116.[9] Gu X,Zheng Y,Cheng Y,et al.In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):484-498.[10] 王勇平,蒋垚,毛琳,等.可降解金属Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr镁合金的降解行为[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(47):8189-8195. [11] Witte F,Kaese V,Haferkamp H,et al.In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3557-3563.[12] Walter R,Kannan MB.In vitro degradation behaviour of WE54 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid. Mater Lett. 2011;65: 748-750.[13] Hänzi AC,Gerber I,Schinhammer M,et al.On the in vitro and in vivo degradation performance and biological response of new biodegradable Mg–Y–Zn alloys.Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(5): 1824-1833. [14] Salahshoor M,Guo YB.Surface integrity of biodegradable magnesium- calcium orthopedic implant by burnishing.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(8):1888-1904.[15] Wang Y,Ouyang Y,He Y,et al.Biocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy with rabbit blood. Chin Sci Bull. 2013;58:2903-2908. [16] Wang Y,He Y,Zhu Z,et al.In vitro degradation and biocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy.Chin Sci Bull. 2012; 57(17):2163-2170.[17] Wang Y,Zhu Z,He Y,et al.In vivo degradation behavior and biocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy at early stage.Int J Mol Med. 2012;29(2):178-184.[18] Wang Y,Ouyang Y,Peng X,et al.Effects of degradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy on osteoblastic cell function. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012;25(3):597-606.[19] Zhang S,Li J,Song Y,et al.In vitro degradation, hemolysis and MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion of biodegradable Mg-Zn alloy.Mater Sci Eng C.2009;29:1907-1912.[20] Xu L,Zhang E,Yin D,et al.In vitro corrosion behaviour of Mg alloys in a phosphate buffered solution for bone implant application.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(3):1017-1025.[21] Wei J,Jia J,Wu F,et al.Hierarchically microporous / macroporous scaffold of magnesium-calcium phosphate for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials.2010;31:1260-1269.[22] Yamamoto A,Watanabe A,Sugahara K,et al.Improvement of corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys by vapor deposition. Scr Mater. 2001;44:1039-1042.[23] Gray JE,Luan B.Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys–a critical review. J Alloys Compd.2002;336: 88-113.[24] ASTM-G31-72: Standard practice for laboratory immersion corrosion testing of metals. In: Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Philadelphia,PA: ASTM,2004.[25] ISO 10993.Biological evaluation of medical devices Part 5: Tests for cytotoxicity:In vitro methods.1999. [26] ISO 10993.Biological evaluation of medical devices Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials.2002. [27] Ito Y,Sisido M,Imanishi Y.Adsorption of plasma proteins and adhesion of platelets onto novel polyetherurethaneureas- relationship between denaturation of adsorbed proteins and platelet adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res.1990;24(2):227-242.[28] Persaud-Sharma D,McGoron A.Biodegradable magnesium alloys: A review of material development and applications.J Biomim Biomater Tissue Eng.2012;12:25-39.[29] Kirkland NT,Birbilis N,Walker J,et al.In vitro dissolution of magnesium-calcium binary alloys: Clarifying the unique role of calcium additions in bioresorbable magnesium implant alloys. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;95(1):91-100. [30] Kirkland NT,Lespagnol J,Birbilis N,et al.A survey of bio-corrosion rates of magnesium alloys. Corros Sci.2010;52:287-291.[31] Witte F,Fischer J,Nellesen J,et al.In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys.Biomaterials.2006;27: 1013-1018.[32] Yang J,Cui F,Lee IS.Surface modifications of magnesium alloys for biomedical applications.Ann Biomed Eng.2011;39: 1857-1871.[33] Li GY,Lian JS,Niu LY,et al.Growth of zinc phosphate coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloy.Surf Coat Technol.2006;201: 1814-1820. [34] Zhao M,Wu S,An P,et al.Microstructure and corrosion resistance of a chromium-free multi-ele-ments complex coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy.Mater Chem Phys. 2006; 99:54-60.[35] Wang YQ,Wu K,Zheng MY.Effects of reinforcement phases in magnesium matrix composites on microarc discharge behavior and characteristics of microarc oxidation coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 2006; 201: 353-360.[36] Thorey F,Menzel H,Lorenz C,et al.Osseointegration by bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor beta 2 coated titanium implants in femora of New Zealand white rabbits. Indian J Orthop.2011;45(1):57-62.[37] Aykut S,Ozturk A,Ozkan Y,et al.Evaluation and comparison of the antimicrobial efficacy of teicoplanin- and clindamycin- coated titanium implants: an experimental study.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(1): 159-163. [38] Kazemzadeh-Narbat M,Kindrachuk J,Duan K,et al. Antimicrobial peptides on calcium phosphate-coated titanium for the prevention of implant-associ-ated infections. Biomaterials. 2010;31:9519-9526.[39] Wen C,Guan S,Peng L,et al.Characterization and degradation behavior of AZ31 alloy surface modified by bone-like hydroxyapatite for implant applications.Appl Surf Sci.2009; 255:6433-6438.[40] Witte F,Hort N,Vogt C,et al.Degradable bio-materials based on magnesium corrosion.Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2008;12:63-72.[41] Song GL.Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys.Corros Sci.2007;49:1696-1701.[42] Rude RK,Gruber HE,Wei LY,et al.Magnesium deficiency: Effect on bone and mineral metabolism in the mouse.Calcif Tissue Int. 2003;72(1):32-41.[43] Harry R.Magnesium: The missing element in molecular views of cell proliferation control. Bioassays.2005;27:311-320.[44] Yamaguchi M,Oishi H,Suketa Y.Stimulatory effect of zinc on bone formation in tissue culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987; 36(22): 4007-4012.[45] Villa I,Dal Fiume C,Maestroni A,et al.Human osteoblast-like cell proliferation induced by calcitonin-related peptides involves PKC activity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 284(3):E627-633.[46] Cheng K,Weng W,Wang H,et al.In vitro behavior of osteoblast-like cells on fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials. 2005;26(32): 6288-6295.[47] Lévesque J,Hermawan H,Dubé D,et al.Design of a pseudo-physiological test bench specific to the development of biodegradable metallic biomaterials.Acta Biomater.2008; 4(2):284-295. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [9] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [10] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [14] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||