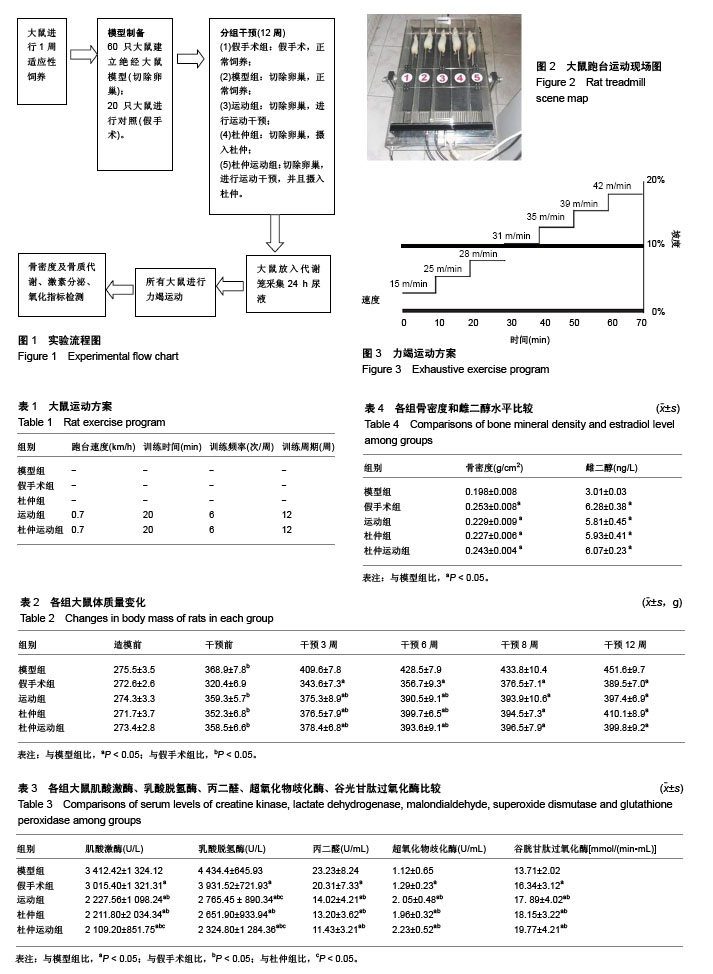
| [1] 张玲莉,闫晓,邹军.运动训练与骨生长代谢的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(7):761-765[2] 黄相杰,毕晓英,姜红江,等.绝经后骨质疏松症治疗的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(8): 602-605.[3] Cooper CE, Vollaard NB, Choueiri T,et al.Exercise, free radicals and oxidative stress.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30(2):280-285. [4] Johnson P.Antioxidant enzyme expression in health and disease: effects of exercise and hypertension.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2002;133(4):493-505.[5] Ma KJ, Zhu ZZ, Yu CH, et al.Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic activities of the ethanol extract from Desmodium caudatum. Pharm Biol. 2011;49(4):403-407.[6] Yoon SJ, Yu MA, Pyun YR,et al.The nontoxic mushroom Auricularia auricula contains a polysaccharide with anticoagulant activity mediated by antithrombin.Thromb Res. 2003;112(3):151-158.[7] Yuan Z, He P, Cui J, et al.Hypoglycemic effect of water-soluble polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula-judae Quel. on genetically diabetic KK-Ay mice.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62(10): 1898-1903.[8] 骆瑶,陈兰英,官紫祎,等.杜仲提取物对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢、骨密度及骨微结构的影响[J].中药材, 2016,39(11):2624-2627.[9] 高照,杨杏萍,张援,等.. 运动后氧化应激水平及合理补充抗氧化剂的科学评价方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28):4577-4584.[10] Jackson MJ, McArdle A.Age-related changes in skeletal muscle reactive oxygen species generation and adaptive responses to reactive oxygen species.J Physiol. 2011;589(Pt 9):2139-2145.[11] Ma SC, Du J, But PP,et al.Antiviral Chinese medicinal herbs against respiratory syncytial virus.J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;79(2):205-211.[12] Alessio HM, Goldfarb AH.Lipid peroxidation and scavenger enzymes during exercise: adaptive response to training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1988;64(4):1333-1336.[13] Yang SJ, Hwang SY, Baik SH,et al.Serum magnesium level is associated with type 2 diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus: the Korea National Diabetes Program study.J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29(1):84-89.[14] Lokanatha V,Subramanyam D,Rajendra W.Role of free radicals and antioxidants in gynecological cancers: currentstatus and future prospects. Oxidants Antioxidants Med Sci.2014;3(1):15-26.[15] Slattery K, Bentley D, Coutts AJ.The role of oxidative, inflammatory and neuroendocrinological systems during exercise stress in athletes: implications of antioxidant supplementation on physiological adaptation during intensified physical training.Sports Med. 2015;45(4): 453-471.[16] 冯晗,周宏灏,欧阳冬生.杜仲的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2015,20(6):713-720.[17] Yen GC, Hsieh CL.Reactive oxygen species scavenging activity of Du-zhong (Eucommia ulmoides oliv.) and its active compounds.J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48(8):3431-3436.[18] Park SA, Choi MS, Jung UJ,et al.Eucommia ulmoides Oliver leaf extract increases endogenous antioxidant activity in type 2 diabetic mice.J Med Food. 2006;9(4):474-479..[19] Ho JN, Lee YH, Lee YD,et al.Inhibitory effect of Aucubin isolated from Eucommia ulmoides against UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in human skin fibroblasts.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2005; 69(11):2227-2231. |