Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3640-3646.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0232
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of strengthened transvertebral pedicle screw internal fixation and internal fixation plus percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral fractures
Zhang Cai-yi1, Zuo Cai-hong1, Tao Zhong-liang1, Zhang Qing1, Wang Shao-gang1, Wang Sheng1, Dai Lian-sheng2
- 1The People’s Hospital of Xuancheng City, Xuancheng 242000, Anhui Province, China; 2Wuxi Third People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2018-08-18Published:2018-08-18 -
About author:Zhang Cai-yi, Master, Associate chief physician, The People’s Hospital of Xuancheng City, Xuancheng 242000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81240011
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Cai-yi, Zuo Cai-hong, Tao Zhong-liang, Zhang Qing, Wang Shao-gang, Wang Sheng, Dai Lian-sheng. Comparison of strengthened transvertebral pedicle screw internal fixation and internal fixation plus percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(23): 3640-3646.
share this article
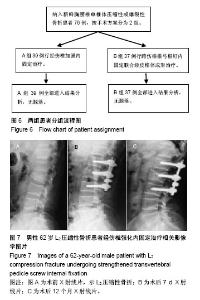
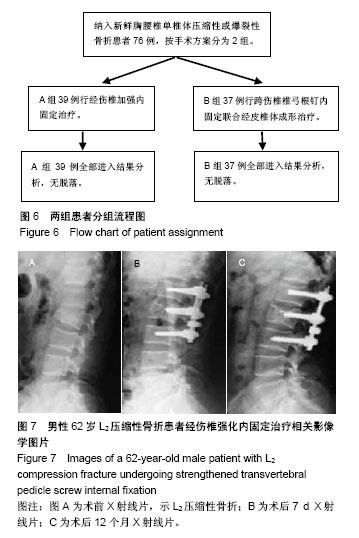
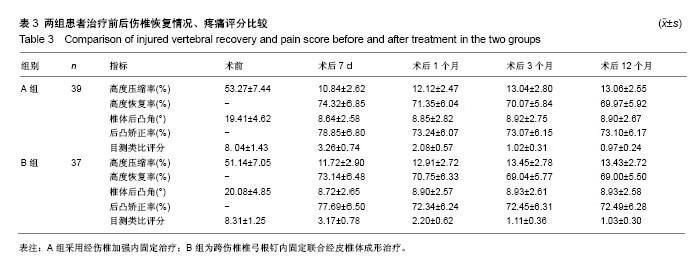
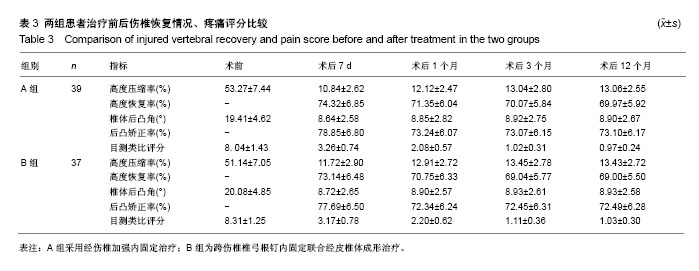
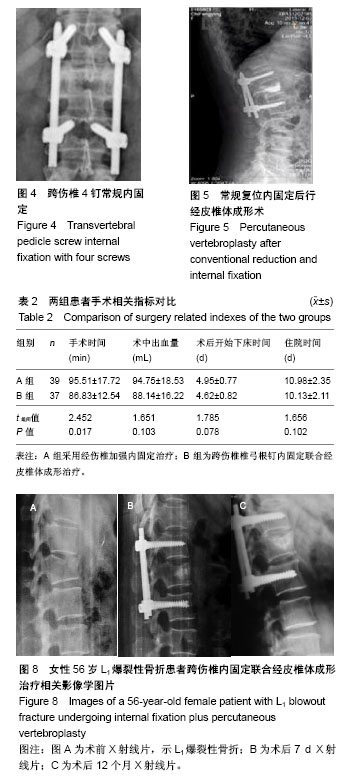
2.2 手术相关指标比较 2组术中出血量、术后开始下床活动时间及住院时间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),A组手术时间显著长于B组(P < 0.05),见表2。 2.3 术后疗效比较 2组患者椎体高度、脊柱生理弯曲、疼痛程度均不同程度恢复或减轻;自术后3个月始,2组伤椎椎体高度无明显丢失;2组术后7 d、1个月、3个月、12个月伤椎高度压缩率、高度恢复率、椎体后凸角、后凸矫正率、目测类比评分差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。 2.4 典型病例 典型病例1:男,62岁,L2椎体压缩性骨折,术前目测类比评分9分,椎体高度压缩率58.4%,椎体后凸角22°;术后7 d目测类比评分3分,高度压缩率11.1%,高度恢复率73.7%,后凸角14°,后凸矫正率80.6%;术后3个月目测类比评分2分,高度恢复率71.9%,后凸矫正率78.8%;术后12个月目测类比评分1分,高度恢复率71.3%,后凸矫正率78.1%,见图7。 典型病例2:女,56岁,L1椎体爆裂性骨折,术前目测类比评分8分,椎体高度压缩率41.3%,椎体后凸角20°;术后7 d目测类比评分2分,高度压缩率8.5%,高度恢复率78.5%,后凸角11°,后凸矫正率83.3%;术后3个月目测类比评分1分,高度恢复率75.3%,后凸矫正率81.0%;术后12个月目测类比评分0分,高度恢复率74.5%,后凸矫正率81.0%,见图8。 2.5 并发症比较 术后2组切口均一期愈合。B组术后CT检查有2例(5%)出现少量骨水泥漏至椎体外缘,1例漏向椎体左前方,1例漏入椎间盘,未发现漏入椎管病例。随访期间2组均未出现钉棒松动、断裂及脱落现象,也未出现神经根损伤及迟发性神经功能障碍病例。B组术后有1例(3%)发生邻近椎体骨折,后经PVP治疗,疼痛解除,A组未出现临近椎体骨折病例。 "
| [1] 崔冠宇,田伟,刘波.椎体强化后椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(6):502-505.[2] Nakamae T, Fujimoto Y, Yamada K,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture with intravertebral cleftassociated with delayed neurologic deficit. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(7):1624-1632.[3] 陈兆军,朱建华,邹辉,等.经椎弓根钉内固定系统结合椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折48例分析[J].江苏医药, 2015,41(6): 723-724.[4] 高浩然,赵海恩,钱澍,等.经皮螺钉置入固定结合关节突植骨修复胸腰椎骨折:建立伤椎长久稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(17): 2688-2693.[5] 张振云,丁江平,李宗健,等.经皮微创经伤椎置钉术与跨伤椎置钉术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效对比研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015, 25(1):68-70.[6] 肖侃侃,赵劲民,殷国前,等.Sextant系统下微创与开放手术方式经伤椎治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效对照研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2015, 32(1):90-92.[7] 朱卉敏,张锴,王衡,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉固定同时经伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2015,20(6):515-518.[8] 伍红桦,施建国,屈波,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉加强内固定+植骨治疗胸腰段椎体骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(12):1190-1194.[9] 刘岩,吴立君,宋正鑫,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定技术治疗胸腰段椎体骨折[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2015,14(1):17-19.[10] 葛建忠,王凯红,戈朝晖,等. 改良经皮椎体成形术在老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中的临床应用[J].中国骨伤, 2013,26(6): 464-466.[11] Li C,Pan J,Gu Y, et al. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for thetreatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture.Int J Surg. 2016;36(Pt A):255-260. [12] 杨炯,周武平,何纯青,等.经伤椎与跨伤椎短节段内固定术在胸腰椎骨折中的应用价值比较[J].中国医药导报,2015,12(3):42-44.[13] Li K, Zhang W, Liu D,et al.Pedicle screw fixation combined with intermediate screw at the fracture level for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(33):e4574.[14] 闫石,苏峰,张志敏,等.经伤椎置钉对椎弓根皮质劈裂合并椎体骨折的生物力学稳定性的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报, 2014,36(4): 416-421.[15] 刘上楼,徐军,倪卓民,等.经胸腰段伤椎单节段椎弓根螺钉固定后的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(39):3608-6910.[16] Wang H, Ma L, Yang D,et al. Incidence and risk factors of adjacent segment disease following posterior decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative lumbar disorders. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(5):e6032.[17] Wang L, Wang Y, Yu B,et al.Comparison of cranial facet joint violation rate between percutaneous and open pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(5):e504. [18] 袁强,田伟,张贵林,等.骨折椎垂直应力螺钉在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):217-222.[19] 张正平,昌震,赵勤鹏,等.经皮骨水泥强化复位内固定联合椎体成形术治疗Genant Ⅲ型骨质疏松性胸腰段骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(6):497-500.[20] Gu Y,Zhang F,Jiang X, et al. Minimally invasive pediclescrew fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty in the surgical treatment ofthoracolumbar osteoporosis fracture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(6):634-640.[21] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092. [22] Gu YT, Zhu DH, Liu HF,et al.Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for preventing secondaryfracture after vertebroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015; 10:31.[23] Lin Y, Chen W, Chen A, et al. Comparison between minimally invasive and open transfora-minal lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis of clinical results and safety outcomes. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2016;77(1):2-10. [24] 顾宇彤,张键,姜晓幸,等.微创椎弓根钉内固定加经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(12):1057-1061.[25] Buchbinder R, Golmohammadi K, Johnston RV,et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteo-porotic vertebral compression fracture. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(4): CD006349. [26] Shen X,Wang L, Zhang H,et al.Radiographic analysis of one-level minimally invasive trans-foraminal lumbar interbody fusion (MI-TLIF) with unilateral pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(1):E1-8. [27] Liu X, Li G, Wang J,et al.Minimally invasive unilateral vs. bilateral pedicle screw fixation and lumbar interbody fusion in treatment of multi-segment lumbar degenerative disorders. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:3652-3657.[28] 刘华,赵胡瑞,邓万祥,等.经椎弓根及伤椎内固定治疗胸腰段椎体骨折体会[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(11):1011-1023.[29] Stevenson M, Gomersall T, Lloyd Jones M,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014; 18(17):1-290. [30] 顾宇彤,梁朝革,张亮,等.微创椎弓根钉内固定联合磷酸钙骨水泥椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国临床医学, 2015,22(2): 181-184.[31] Lau D, Terman SW, Patel R,et al.Incidence of and risk factors for superior facet violation in minimally invasive versus open pedicle screwplacement duringtransforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comparative analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(4): 356-361. [32] 陈家麟.个体优化经椎弓根置钉复位内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22):4046-4048.[33] Joseph JR, Smith BW, La Marca F,et al.Comparison of complication rates of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusionand lateral lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39(4):E4. [34] Sakaura H, Miwa T, Yamashita T,et al.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posteriorlumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbarspondylolisthesis: a comparative study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(5):591-595.[35] Choi UY, Park JY, Kim KH,et al.Unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbarinterbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 2013; 35(2):E11. [36] Ren C, Qin R, Sun P,et al.Effectiveness and safety of unilateral pedicle screw fixation in trans-foraminal lumbar interbodyfusion (TLIF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(4):441-450.[37] Zeng ZL, Jia L, Xu W,et al. Analysis of risk factors for adjacent superior vertebral pedicle-induced facet joint violationduring the minimally invasive surgery transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a retrospective study. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:80. [38] Goldstein CL, Macwan K, Sundararajan K,et al.Perioperative outcomes and adverse events of minimally invasive versus open posterior lumbarfusion: meta-analysis and systematic review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):416-427. [39] Liu H, Xu Y, Yang SD,et al.Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation with posterior lumbar interbody fusion forlumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(21):e6882. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||