Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3647-3653.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0226
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lumbar interbody fusion with interspinous dynamic fixation: a finite element analysis
Ma Liang, Xu Yong-tao, She Yuan-ju
- Department of Orthopedics, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434020, Hubei Province, China
-
Online:2018-08-18Published:2018-08-18 -
Contact:Xu Yong-tao, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434020, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ma Liang, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434020, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Program of Jingzhou City of Hubei Province, No. 2015036
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Liang, Xu Yong-tao, She Yuan-ju . Lumbar interbody fusion with interspinous dynamic fixation: a finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(23): 3647-3653.
share this article
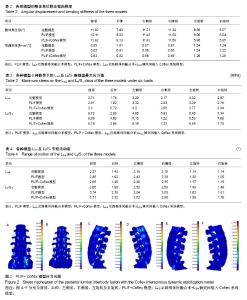
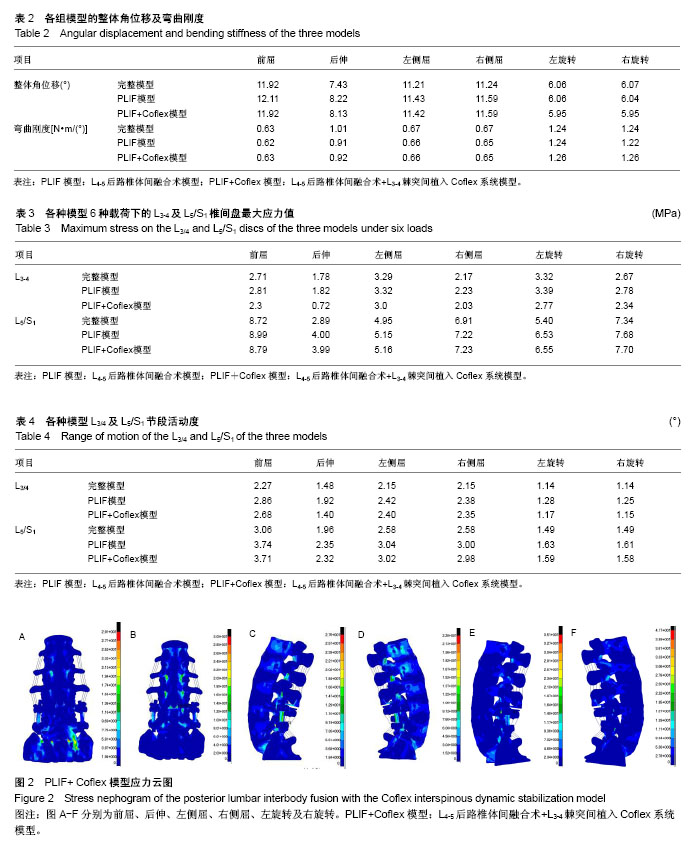
2.1 加载前屈、后伸、左右侧屈及左右旋转载荷时模型的受力情况分析 在加载400 N的轴向载荷,并附加7.5 N•m的前屈,后伸,左右侧屈,左右旋转载荷时,计算完整模型,PLIF模型及PLIF+L3/4 Coflex模型的整体角位移,弯曲刚度见表2。 PLIF模型和PLIF+Coflex模型的6个方向的弯曲刚度与完整模型接近。说明这两种手术方式都能有效的恢复脊柱屈伸、左右侧屈、左右旋转时的稳定性。 2.2 邻近节段椎间盘应力比较 此3种模型在前屈,后伸,左右侧弯,左右旋转6种状态下的邻近L3/4及L5/S1椎间盘最大应力值如表3。 PLIF模型L3-4椎间盘最大应力值比完整模型增大。PLIF+Coflex模型的L3-4椎间盘应力值明显减小,在屈伸及旋转时降幅较明显,后伸时减小最明显,左右侧屈时降幅稍低。PLIF模型及PLIF+Coflex模型的L5/S1椎间盘最大应力都比完整模型增加,在后伸及左旋转时增加稍大。 从上述邻近节段椎间盘最大应力值对比变化可见Coflex动态稳定能有效的降低屈伸及旋转时L3-4椎间盘内的应力,预防其退变,其作用在屈伸及旋转活动时较明显,在左右侧屈时影响较小,这与Coflex假体的特殊形态有关,它的固定翼设计,使得对屈伸及旋转时的过度应力起到分散保护作用,但对左右侧屈时的异常应力集中保护能力稍差。从L5/S1椎间盘最大应力值变化可以看到L4-5融合后L5/S1椎间盘应力明显增加,造成其退变风险增加,在L3-4棘突间添加稳定装置对L5/S1椎间盘应力变化影响不大。 2.3 邻近节段活动度比较 各种模型在前屈,后伸,左右侧弯,左右旋转6种状态下的L3-4及L5/S1节段的活动度如表4。 PLIF+Coflex模型在前屈,左右侧屈L3-4节段活动度比完整模型增加,比PLIF模型减小。后伸时活动度比完整模型减小。左右旋转时L3-4节段活动度比PLIF模型减小,与完整模型接近。PLIF模型及PLIF+Coflex模型的L5/S1节段活动度比完整模型都明显增加,两者间相比在6种状态下变化不明显。 在行L4-5 PLIF术后邻近的L3-4及L5/S1节段活动度均代偿性增加,退变风险增加。在联合行L3-4棘突间动态固定后在前屈,后伸及左右旋转时L3-4节段活动度比L4-5融合时稍减小。对于L5/S1节段活动度,L4-5 PLIF和L4-5 PLIF+L3-4 Coflex模型比完整模型都明显增加,两者间相比在6种状态下变化不明显。说明行L3-4棘突间动态固定对L5/S1节段活动度影响不大。 2.4 PLIF联合Coflex动态固定后的应力分布特点 通过应力云图来观察L4-5 PLIF+L3-4 Coflex后的应力情况,见图2。 从应力云图来看在屈伸,侧屈,旋转状态下,邻近的L2-3,L3-4,L5/S1关节突处都有明显的应力集中,屈伸时关节突处的应力集中最明显。内固定钉棒系统的连接棒上在各种活动状态下都有明显的应力集中。Coflex假体的U形装置最凹面处有明显的应力集中,在屈伸时最大。Coflex假体的固定翼与棘突连接处也有明显的应力集中,在左右侧屈时最明显。 "
| [1] Mobbs RJ, Phan K, Malham G et al.Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J Spine Surg. 2015;1(1):2-18. [2] Fleege C, Rickert M, Rauschmann M.The PLIF and TLIF techniques. Indication, technique, advantages, and disadvantages. Orthopade. 2015;44(2):114-123.[3] Pan A, Hai Y, Yang J, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal fusion compared with motion-preservation procedures: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(5): 1522-1532.[4] Virk SS, Niedermeier S, Yu E, et al. Adjacent segment disease. Orthopedics. 2014;37(8):547-555. [5] Pintauro M, Duffy A, Vahedi P, et al. Interspinous implants: are the new implants better than the last generation? A review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(2):189-198.[6] Ravindra VM, Ghogawala Z. Is there still a role for interspinous spacers in the management of neurogenic claudication? Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2017;28(3):321-330. [7] Zhu Z, Liu C, Wang K, et al. Topping-off technique prevents aggravation of degeneration of adjacent segment fusion revealed by retrospective and finite element biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:10. [8] Nguyen NL, Kong CY, Hart RA. Proximal junctional kyphosis and failure-diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9(3):299-308. [9] Reichl M, Kueny RA, Danyali R, et al. Biomechanical effects of a dynamic topping off instrumentation in a long rigid pedicle screw construct. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(4):E440-E447.[10] Lo CC, Tsai KJ, Zhong ZC, et al. Biomechanical differences of Coflex-F and pedicle screw fixation combined with TLIF or ALIF-a finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(11):947-956. [11] Heth JA, Hitchon PW, Goel VK, et al. A biomechanical comparison between anterior and transverse interbody fusion cages. Spine. 2001;26(12):261-267.[12] Ghasemi AA. Adjacent segment degeneration after posterior lumbar fusion: An analysis of possible risk factors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;143:15-18. [13] Liu X, Liu Y, Lian X, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging on disc degeneration changes after implantation of an interspinous spacer and fusion of the adjacent segment. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(4):6097-6102. [14] Okuda S, Oda T, Yamasaki R, et al. Repeated adjacent-segment degeneration after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(5):538-541. [15] Abode-Iyamah K, Kim SB, Grosland N, et al. Spinal motion and intradiscal pressure measurements before and after lumbar spine instrumentation with titanium or PEEK rods. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(4):651-655.[16] Kashkoush A, Agarwal N, Paschel E, et al. Evaluation of a hybrid dynamic stabilization and fusion system in the lumbar spine: a 10 year experience. Cureus. 2016;8(6):e637. [17] Nachanakian A, El Helou A, Alaywan M. Posterior dynamic stabilization: The interspinous spacer from treatment to prevention. Asian J Neurosurg. 2016;11(2):87-93. [18] Lee SE, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Facet joint changes after application of lumbar nonfusion dynamic stabilization. Neurosurg Focus. 2016;40(1):E6. [19] Fleege C, Rickert M, Werner I, et al. Hybrid stabilization technique with spinal fusion and interlaminar device to reduce the length of fusion and to protect symptomatic adjacent segments: clinical long-term follow-up.Orthopade. 2016;45(9): 770-779. [20] Nomura H.A novel strategy of non-fusion instrumentation with coflex interlaminar stabilization after decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(2):149-153. [21] Chen XL, Guan L, Liu YZ, et al. Interspinous dynamic stabilization adjacent to fusion versus double-segment fusion for treatment of lumbar degenerative disease with a minimum follow-up of three years. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1275-1283. [22] Liu HY, Zhou J,Wang B,et al. Comparison of topping-off and posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery in lumbar degenerative disease: a retrospective study. Chin Med J. 2012;125(22):3942-3946. [23] 李冬月,海涌,孟祥龙,等.Topping-off与融合固定治疗退行性腰椎疾病的临床疗效及邻近节段退变的对比研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(11):967-973.[24] Chou PH, Lin HH, An HS, et al. Could the topping-off technique be the preventive strategy against adjacent segment disease after pedicle screw-based fusion in lumbar degenerative diseases? A systematic review. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4385620. [25] Siewe J, Otto C, Knoell P et al. Comparison of standard fusion with a "topping off" system in lumbar spine surgery: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:239. [26] Che W, Chen Q, Ma YQ, et al. Single-level rigid fixation combined with coflex: a biomechanical study. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:1022-1027. [27] 刘海鹰,王捷夫,朱震奇.融合与Topping-off术对腰椎影响的有限元分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2013,45(5):723-727.[28] Zhu Z, Liu C, Wang K, et al. Topping-off technique prevents aggravation of degeneration of adjacent segment fusion revealed by retrospective and finite element biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:10. [29] Fu L, Ma J, Lu B, et al. Biomechanical effect of interspinous process distraction height after lumbar fixation surgery: an in vitro model. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(7):663-672.[30] Yue ZJ, Liu RY, Lu Y, et al. Middle-period curative effect of posterior lumbar intervertebral fusion (PLIF) and interspinous dynamic fixation (Wallis) for treatment of L4/5 degenerative disease and its influence on adjacent segment degeneration. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(23):4481-4487. [31] Kuang MJ, Ma JX, Ma XL. Decompression and coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with conventional surgical procedures for lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2017;45:164-165. [32] Yuan W, Su QJ, Liu T, et al. Evaluation of Coflex interspinous stabilization following decompression compared with decompression and posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative disease: a minimum 5-year follow-up study. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;35:24-29. [33] Lee SH, Seol A, Cho TY, et al. Systematic review of interspinous dynamic stabilization. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015; 7(3):323-329. [34] Landi A. Interspinous posterior devices: What is the real surgical indication? World J Clin Cases. 2014;2(9):402-408. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [5] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [6] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||