Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (21): 3431-3437.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0532
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stem cell therapy for thalassemia: present and future
Hu Jun-jie1, Chen Xin-ping2, Fu Sheng-miao2
- 1Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Forestry, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, Hainan Province, China; 2Medical Examination Center, Hainan Provincial People’s Hospital, Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory for Cell and Molecular Genetic Translational Medicine, Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China
-
Revised:2018-04-12Online:2018-07-28Published:2018-07-28 -
Contact:Fu Sheng-miao, Master, Researcher, Medical Examination Center, Hainan Provincial People’s Hospital, Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory for Cell and Molecular Genetic Translational Medicine, Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Hu Jun-jie, Master candidate, Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Forestry, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical and Health Scientific Support Project in Hainan Province, No. 2010-48; Application Technology Research and Development Special Project in Hainan Province, No. ZDXM2015071
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Jun-jie, Chen Xin-ping, Fu Sheng-miao. Stem cell therapy for thalassemia: present and future[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(21): 3431-3437.
share this article

2.1 输血治疗和除铁治疗方法的不足 输血治疗和除铁治疗自推广以来一直是临床上治疗地贫的主要方法,该治疗方法在一定程度上能够提高患者的生存质量和延长患者的生命周期,但也会带来沉重的经济负担。据统计,一位地贫患者从出生到成年期的治疗费用需要将近20万美元[4-6],由于人力资源和血库设施建设的差距,以及医疗保健制度不够完善,一些资源缺乏的国家无法负担昂贵的地贫治疗费用[7-10]。此外,输血治疗常会造成患者体内铁含量过载,正常成人的体内铁含量大约为4 g,输血过程中每输入4至5个单位的红细胞,体内就会增加1 g的额外铁[11]。当血液中的铁负荷增加并且超过转铁蛋白的结合速率时,就会导致非结合铁蛋白的增加,非结合铁蛋白在体内容易形成活性氧化物质,在细胞水平上介导器官损伤,例如临床上已经证实地贫患者心脏病的发生与非结合铁蛋白增加有关[12-13]。另外铁沉积在肝脏、心脏、中枢神经系统和内分泌系统中也会导致脏器损伤,这就是在输血治疗过程中同时还需要除铁的原因,同时输血治疗还会增加乙型肝炎病毒(Hepatitis B virus,HBV)、巨细胞病毒(Cytomegaoviyns,CMV)和艾滋病病毒(Human Immunodeficiency Virus,HIV)等感染风险[14-15],所以基于地贫输血治疗和除铁治疗存在许多局限性,会造成患者额外的治疗风险。 2.2 干细胞治疗 所谓干细胞治疗就是将具有正常珠蛋白基因功能的干细胞移植到经过预处理的受者体内,并在受者体内成功表达以纠正地贫患者的珠蛋白基因缺陷[16]。目前临床上应用最成功的是采用异体造血干细胞移植(allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation,allo-HSCT)治疗重型β地贫[17-19],患者在接受干细胞移植治疗后能够明显改善贫血症状,同时也能有效地避免输血治疗和除铁治疗所带来的治疗风险。 2.2.1 移植前供者选择、风险评估及预处理方案 见表1。一般情况下地贫患者在进行干细胞治疗前都接受过输血治疗,在反复接受异体抗原的过程中引起机体致敏,导致移植物排斥概率大。临床经验表明人类白细胞抗原(human leukocyte antigen,HLA)完全相合的同胞供者造血干细胞移植是目前治疗重型地贫的首选治疗方法[20],其中供者的选择和患者移植前危险等级评估是干细胞治疗的关键。有研究报道HLA匹配的同胞之间干细胞移植可以使地贫治疗的无病生存率达到90%,但最大限制在于只有不超过30%患者才具有HLA匹配的同胞供者,而非同胞之间移植发生排斥反应的概率较高,其中最大的危险因素是移植物抗宿主病。当前对非同胞之间的移植可以使用抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白(anti-human thymocyte immunoglobulin,ATG)结合多种药物治疗来减少移植物抗宿主病的发生。Li等[21]在52例非同胞之间的重型β 地贫患者造血干细胞移植研究中,采用环孢素、吗替麦考酚酯结合短程甲氨蝶呤和抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白可以预防和减少移植物抗宿主病的发生。"

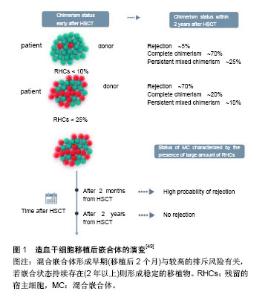
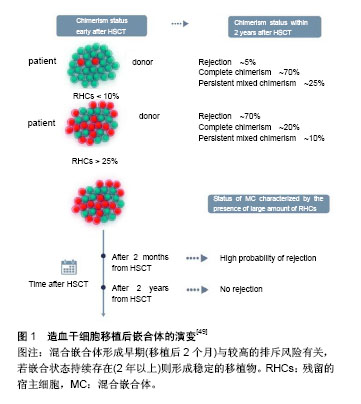
2.2.2 造血干细胞移植 是最早应用于地贫的干细胞治疗方法,据统计目前有超过3 000例重型地贫患者成功接受造血干细胞移植治疗[31]。根据造血干细胞的来源可分为骨髓造血干细胞移植(bone marrow stem cell transplantation,BMSCT)、外周血造血干细胞移植(peripheral blood stem cells transplantation,PBSCT)和脐血造血干细胞移植(cord blood stem cell transplantation,CBSCT)。 (1)骨髓造血干细胞移植:早在1982年美国Thomas等就应用同胞骨髓移植技术成功治愈了1例重型β地贫患者[20]。近期Ramprakash等[32]于2015至2016年完成了具有完全匹配供者(matched sibling donor,MSD)的12例重度地贫患者的骨髓移植,这些患者的肝脏肿大均小于2 cm,被评估为Pesaro 1-2级。移植方案包括:①受者移植前第2-5天使用环磷酰胺50 mg/(kg•d),即4 d总剂量为200 mg/kg;第6-9天口服白消安3.5 mg/kg,每日4次,即总剂量为14 mg/(kg•d);第10-12天使用抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白4 mg/(kg•d);②供者骨髓采集前3 d或5 d内使用非格司亭(Filgrastim)5 μg/kg,每天2次,即总剂量为10 μg(kg•d),以促进供者髓系造血干细胞增殖、分化和成熟,并促使中性粒细胞释放至血流,增加在外周血中的数量和提高其功能;③通过化疗等方式清除受者体内残存的骨髓液,然后将HLA相容骨髓液通过静脉注射输入到受者体内;④使用环孢素联合甲氨蝶呤或霉酚酸酯预防移植物抗宿主病。骨髓造血干细胞移植成功率一般可达80%以上,但在亲缘关系较高的地区,只能找到10%-20%完全匹配的捐赠者[33-34]。由于目前国内骨髓移植治疗缺乏匹配的样本来源,同时手术移植前后患者需要经过长时间的药物预处理治疗和抗免疫治疗,依然使许多地贫患者无法获得及时有效的治疗。 (2)外周血造血干细胞移植:外周血造血干细胞移植相对于骨髓造血干细胞移植的优点在于能够使患者获得更稳定的移植物体系,并且细胞收集相对容易,在移植前通常注射造血细胞生长因子促使骨髓中的干细胞释放到外周血中,并采用血细胞单采技术获取供者外周血造血干细胞。与需要进行手术的骨髓捐献方式相比,捐赠者更愿意选择无创伤性的外周血造血干细胞捐赠方式,所以许多国家的研究主要是以非亲缘捐赠者的外周血造血干细胞为细胞来源进行治疗,由于非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植(unrelated donor,UD-PBSCT)会增加术后移植物抗宿主病风险和移植相关病死率,故目前仅用于儿童地贫治疗[35]。Li等[36]使用一种新型移植方案(通过静脉注射白消安、环磷酰胺、氟达拉滨和噻替派进行药物预处理)治疗82例地贫患者,其中52例HLA配型通过者用非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植治疗,30例进行HLA相合同胞外周血造血干细胞移植治疗,移植对象的年龄范围在0.6-15岁(中位年龄为6岁),男女比例56︰26,随访12-39个月。研究结果表明非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植组3年总生存率和无地贫生存率分别为92.3%和90.4%,HLA相合同胞外周血造血干细胞移植组分别为90.0%和83.3%;非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植组累计移植物排斥发生率和Ⅲ-Ⅳ级急性移植物抗宿主病的发生率分别为1.9%和9.6%,HLA相合同胞外周血造血干细胞移植组分别为6.9%和3.6%;非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植组移植相关病死率为7.7%,HLA相合同胞外周血造血干细胞移植组为10.0%。该研究结果表明经新型方案处理后的非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植与HLA相合同胞外周血造血干细胞移植结果相似,在临床治疗中如果缺乏匹配供者来源,可选择非亲缘外周血造血干细胞移植治疗β地贫,但该治疗方案尚需进一步研究进行验证。 (3)脐血造血干细胞移植:从1988年法国Gluckman等[37]第一次利用脐血造血干细胞移植成功治疗了1例贫血患儿后,目前全球已开展超过4万例的脐血造血干细胞移植,主要用于治疗患有恶性疾病(如白血病)或非恶性疾病(如重型地贫)的患者。与骨髓造血干细胞移植相比其优点主要有:①移植物抗宿主病发生率和严重程度较低;②感染和传播潜伏病毒的风险较低(如巨细胞病毒、EB病毒、肝炎病毒、艾滋病病毒);③受者移植后免疫重建快;④消除了采集造血干细胞过程对供者损伤的风险;⑤在供者选择和配型方面,有研究采用亲缘性和非亲缘性供者的脐血造血干细胞移植,发现患者的无病生存率和总体生存率无显著差别或接近骨髓造血干细胞移植效果[38-39]。在无适合亲缘性骨髓供者和脐血供者的情况下,可以使用非亲缘脐血干细胞进行地贫治疗,但脐血造血干细胞移植也存在移植排斥风险较高和移植后造血恢复延迟等缺点[40]。为了能使移植后重建造血功能,需要一定数量的脐血有核细胞和CD34+细胞,据欧洲多个移植案例分析发现脐血有核细胞数量达2×107/kg时才能保持较高移植成功率,进行异基因移植时这个数值还需提高至3.7×107/kg,CD34+数量需达到1.7×105/kg,患者的地贫严重程度越高所需的细胞数量就越高。Locatelli等[41]对33例地贫患者进行同种异体脐血造血干细胞移植,输注脐血有核细胞数量为(1.2-10)×107/kg,移植后无死亡病例,但有7例患者发生移植排斥(排斥率约21%),26例成功移植后2年无病生存率达79%,该研究指出发生移植排斥与预处理方案的选择有关,联合使用白消安、环磷酰胺或氟达拉滨和抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白的预处理方案,以及在移植后使用环孢霉素进行免疫抑制可以降低排斥风险,提高脐血造血干细胞移植的治疗效果。 2.2.3 诱导多能干细胞移植(induced pluripotent stem cell transplantation,iPSCT) Yamanaka等[42]最早在2006年报道利用病毒载体将4个转录因子(Oct4,Sox2,Klf4 和c-Myc)转入已经分化的体细胞中,经去分化后成功收获一种多能干细胞,并称之为诱导多能干细胞。诱导多能干细胞的优势是细胞来源十分广泛,取自患者的皮肤成纤维细胞、肝细胞、睾丸细胞和神经细胞等经过分化后均可获得,同时还具有无限增殖和多能分化的潜能,进行自体移植时不会发生免疫排斥,也不涉及伦理方面的问题。诱导多能干细胞移植多应用于重型β地贫的治疗,患者突变基因会在去分化为诱导多能干细胞或诱导多能干细胞分化为造血干细胞过程中借助基因编辑技术进行修正,得到正常的造血干细胞后回输到患者体内进行治疗[43-44]。目前常用有3种定向基因编辑技术,即锌指核酸酶(zinc finger nuclease,ZFN)、转录激活因子样效应物核酸酶(transcription activator-like effector nucleases,TALEN)和规律成簇间隔短回文重复CRISPR相关核酸酶(clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic rRepeats/CRISPR- associated systems,CRISPR/Cas)技术能实现地贫致病基因的矫正,其中CRISPR/Cas系统相对于其他基因编辑技术更加精确和高效且操作简单,具有广阔的应用前景[45]。骨髓造血干细胞、外周血造血干细胞和脐血造血干细胞也可以通过基因编辑技术进行基因修正,但成体干细胞在体外难以实现大量的扩增和分化,诱导多能干细胞具有类似于胚胎干细胞的功能,能够在体外经诱导分化为成熟的红细胞,同时诱导多能干细胞能长期保存,将其作为种子细胞可以不断地为重型地贫患者提供血源,为患者建立专属的红细胞血库,保证治疗的安全性。但需要注意的问题是使用动物血清培养液(胎牛血清)和胚胎成纤维细胞作饲养层培养诱导多能干细胞时应避免引入动物病原体,建议用无血清培养基和饲养层的培养方法,此方法已成功用于胚胎干细胞培养,是一种很好的替代培养方法。 目前将体细胞诱导去分化为诱导多能干细胞的最有效方法是使用反转录病毒载体引入转录因子基因,但反转录病毒整合可能干扰基因功能,同时也存在一定诱发癌变的风险,所以无外源基因导入诱导方法和提高诱导效率是目前诱导多能干细胞移植需要解决的主要问题。Ye等[46]利用反转录病毒结合转录因子成功将纯合子β地贫患者皮肤成纤维细胞诱导生成诱导多能干细胞,体外研究表明它可以分化成3个胚层细胞并维持正常核型,且具有类似人类胚胎干细胞功能,能进一步分化为造血干细胞后合成胎儿血红蛋白。该研究还将产前诊断中收集的羊水细胞和绒毛膜滋养细胞诱导生成诱导多能干细胞及成体细胞,并证明其功能与经皮肤成纤维细胞诱导生成的诱导多能干细胞的功能一致。因此,诱导多能干细胞移植已成为地贫和其他遗传性疾病的产前诊断和早期治疗的新方法,且能发挥重要作用。目前已在体外成功建立动物治疗实验模型,但直接应用于临床治疗还需要充足的前期工作准备,各国研究者正在进行理论和技术的完善,相信很快便可转化进入实际临床治疗阶段。 2.2.4 移植后观察与处理 干细胞植入患者体内后需要进行长时间的监护观察,后期工作中对护理人员和医疗条件要求较高[47]。研究证明当移植后2个月的外周血或供者来源细胞的比例小于75%时具有较高的排斥风险,其中重要的影响因素是宿主剩余造血细胞(residual host cells,RHC),RHC < 10%的患者排斥风险仅为13%,而RHC介于10%-25%的患者排斥风险将超过40%[48]。通常危险等级3级患者的排斥风险要高于1级和2级,而移植物与受者造血细胞共存将形成混合嵌合体,在移植后期可能有3种发展趋势:①移植物最终发生免疫排斥,地贫复发;②移植后保持嵌合状态持续2年以上形成稳定混合嵌合体,即称之为“脱地贫状态”,该状态下受者体内一般能产生足够血红蛋白以满足正常需求;③受者原有造血细胞逐渐消失,被移植物完全替代。有研究表明相当比例的混合嵌合体患者可以进入稳定的混合嵌合状态,而没有移植失败的风险,移植失败风险在移植后2年的随访时间判定[49](图1)。混合嵌合体最终发展为免疫排斥的机制可能是免疫介导受同种异型识别调节,外周血单个核细胞和1型调节性T细胞(Tr1)诱导分泌的白细胞介素10在促进和维持混合嵌合状态中发挥重要作用[50]。早期混合嵌合体患者需要进行免疫调节以防止移植物丢失,但免疫抑制的强化并不能改善免疫耐受性,而中断免疫抑制却能很快形成稳定的混合嵌合体或完成完全移植,此后患者不需要输血,体内血红蛋白水平表达正常,并在2年随访中未出现移植物抗宿主病症状,该发现提高了对混合嵌合体进行免疫抑制治疗的认识,避免因过度免疫抑制调节而导致移植失败[51]。对一次移植失败或地贫重新复发的患者,在确认清除原有的移植物和免疫性物质后可以进行二次移植,二次移植可以选择不同类型的干细胞,如骨髓造血干细胞移植失败的患者,二次移植可选择外周血造血干细胞移植等,以增加移植的成功率。"
| [1] Modell B, Darlison M. Global epidemiology of haemoglobin disorders and derived service indicators. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86(6):480-487.[2] Borgna-Pignatti C. The life of patients with thalassemia major. Haematologica. 2010;95(3):345-348.[3] Modell B, Khan M, Darlison M. Survival in beta-thalassaemia major in the UK: data from the UK Thalassaemia Register. Lancet. 2000;355(9220):2051-2052.[4] Seyedifar M, Dorkoosh FA, Hamidieh AA, et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Health Utility Values in Beta Thalassemia Major Patients Receiving Different Types of Iron Chelators in Iran. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2016;10(4):224-231. [5] Esmaeilzadeh F, Azarkeivan A, Emamgholipour S, et al. Economic Burden of Thalassemia Major in Iran, 2015. J Res Health Sci. 2016;16(3):111-115.[6] Weidlich D, Kefalas P, Guest JF. Healthcare costs and outcomes of managing β-thalassemia major over 50 years in the United Kingdom. Transfusion. 2016;56(5):1038-1045.[7] Lee TA, von Riedemann S, Tricta F. Cost-utility of chelators in transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major patients: a review of the pharmacoeconomic literature. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2014;14(5):651-660.[8] Adly AA, Ebeid FS. Cultural preferences and limited public resources influence the spectrum of thalassemia in Egypt. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2015;37(4):281-284.[9] Marwaha N. Whole blood and component use in resource poor settings. Biologicals. 2010;38(1):68-71.[10] Au WY, Li CF, Fang JP, et al. Assessment of iron overload in very young children with limited thalassemia care resources in South China. Hemoglobin. 2014;38(2):119-126. [11] Andrews NC. Disorders of iron metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(26):1986-1995.[12] Brissot P, Ropert M, Le Lan C, et al. Non-transferrin bound iron: a key role in iron overload and iron toxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(3):403-410.[13] Piga A, Longo F, Duca L, et al. High nontransferrin bound iron levels and heart disease in thalassemia major. Am J Hematol. 2009;84(1):29-33.[14] Cappellini MD, Motta I. New therapeutic targets in transfusion-dependent and -independent thalassemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2017;2017(1): 278-283.[15] Vento S, Cainelli F, Cesario F. Infections and thalassaemia. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6(4):226-233.[16] Nienhuis AW, Persons DA. Development of gene therapy for thalassemia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(11): a011833.[17] Bazarbachi A, Labopin M, Ghavamzadeh A, et al. Allogeneic matched-sibling hematopoietic cell transplantation for AML: comparable outcomes between Eastern Mediterranean (EMBMT) and European (EBMT) centers. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(8):1065-1069.[18] Lucarelli G, Gaziev J. Advances in the allogeneic transplantation for thalassemia. Blood Rev. 2008;22(2):53-63.[19] Mathews V, Srivastava A, Chandy M. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for thalassemia major. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014;28(6):1187-1200.[20] 徐宏贵,方建培.造血干细胞移植治疗β地中海贫血[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2014,29(11):818-822.[21] Li C, Wu X, Feng X, et al. A novel conditioning regimen improves outcomes in β-thalassemia major patients using unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(19):3875-3881.[22] Isgrò A, Gaziev J, Sodani P, et al. Progress in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as allogeneic cellular gene therapy in thalassemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1202:149-154.[23] Lucarelli G, Galimberti M, Polchi P, et al. Bone marrow transplantation in patients with thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(7):417-421.[24] Lucarelli G, Clift RA, Galimberti M, et al. Marrow transplantation for patients with thalassemia: results in class 3 patients. Blood. 1996;87(5):2082-2088.[25] Sabloff M, Chandy M, Wang Z, et al. HLA-matched sibling bone marrow transplantation for β-thalassemia major. Blood. 2011;117(5):1745-1750.[26] Sodani P, Gaziev D, Polchi P, et al. New approach for bone marrow transplantation in patients with class 3 thalassemia aged younger than 17 years. Blood. 2004;104(4):1201-1203.[27] Gaziev J, Nguyen L, Puozzo C, et al. Novel pharmacokinetic behavior of intravenous busulfan in children with thalassemia undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective evaluation of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile with therapeutic drug monitoring. Blood. 2010;115(22):4597-4604.[28] Li C, Wu X, Feng X, et al. A novel conditioning regimen improves outcomes in β-thalassemia major patients using unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(19):3875-3881.[29] Mathews V, George B, Viswabandya A, et al. Improved clinical outcomes of high risk β thalassemia major patients undergoing a HLA matched related allogeneic stem cell transplant with a treosulfan based conditioning regimen and peripheral blood stem cell grafts. PLoS One. 2013;8(4): e61637.[30] Hussein AA, Al-Zaben A, Ghatasheh L, et al. Risk adopted allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using a reduced intensity regimen for children with thalassemia major. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60(8):1345-1349.[31] Angelucci E, Matthes-Martin S, Baronciani D, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in thalassemia major and sickle cell disease: indications and management recommendations from an international expert panel. Haematologica. 2014;99(5):811-820.[32] Ramprakash S, Agarwal RK, Dhanya R, et al. Rejection of paternal vs maternal fully matched bone marrow grafts in children with thalassemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017; 52(11):1585-1586.[33] Hamidieh AA, Dehaghi MO, Paragomi P, et al. Efficiency of allogeneic hematopoietic SCT from HLA fully-matched non-sibling relatives: a new prospect of exploiting extended family search. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50(4):545-552.[34] Agarwal RK, Kumari A, Sedai A, et al. The Case for High Resolution Extended 6-Loci HLA Typing for Identifying Related Donors in the Indian Subcontinent. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(9):1592-1596.[35] Lee JW, Kim SK, Jang PS, et al. Impact of CD34+ cell dose in children who receive unrelated PBSCT with in vivo T-cell depletion for hematologic malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50(1):68-73.[36] Li C, Wu X, Feng X, et al. A novel conditioning regimen improves outcomes in β-thalassemia major patients using unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(19):3875-3881.[37] Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HA, Auerbach AD, et al. Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 1989;321(17):1174-1178.[38] Locatelli F, Kabbara N, Ruggeri A, et al. Outcome of patients with hemoglobinopathies given either cord blood or bone marrow transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling. Blood. 2013;122(6):1072-1078.[39] Jaing TH, Hung IJ, Yang CP, et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation for thalassaemia: a single-institution experience of 35 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012; 47(1):33-39.[40] Shahrokhi S, Menaa F, Alimoghaddam K, et al. Insights and hopes in umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantations. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:572821.[41] Locatelli F, Rocha V, Reed W, et al. Related umbilical cord blood transplantation in patients with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Blood. 2003;101(6):2137-2143.[42] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.[43] Liu Y, Yang Y, Kang X, et al. One-Step Biallelic and Scarless Correction of a β-Thalassemia Mutation in Patient-Specific iPSCs without Drug Selection. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;6: 57-67.[44] Xu P, Tong Y, Liu XZ, et al. Both TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 directly target the HBB IVS2-654 (C > T) mutation in β-thalassemia-derived iPSCs. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12065.[45] 李玲丽,张风波,李崎,等.基因修复β-地中海贫血患者诱导多能干细胞可否成为治疗的希望[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(9): 1463-1469.[46] Ye L, Chang JC, Lin C, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells offer new approach to therapy in thalassemia and sickle cell anemia and option in prenatal diagnosis in genetic diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(24):9826-9830.[47] Neumann J. Nursing challenges caring for bone marrow transplantation patients with graft versus host disease. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2017;10(4):192-194.[48] Andreani M, Nesci S, Lucarelli G, et al. Long-term survival of ex-thalassemic patients with persistent mixed chimerism after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000; 25(4):401-404.[49] Srivastava A, Shaji RV. Cure for thalassemia major - from allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to gene therapy. Haematologica. 2017;102(2):214-223.[50] Andreani M, Gianolini ME, Testi M, et al. Mixed chimerism evolution is associated with T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells in a β-thalassemic patient after haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Chimerism. 2014;5(3-4):75-79.[51] Kropshofer G, Sopper S, Steurer M, et al. Successful management of mixed chimerism after bone marrow transplant in beta-thalassemia major. Am J Hematol. 2016; 91(9):E357-358. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||