Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 2961-2967.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0192
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy and safety of artificial total disc replacement in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases
Chen Jun1, 2, Wu Guang-hui1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Emergency, Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Wu Guang-hui, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Chen Jun, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Emergency, Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jun, Wu Guang-hui. Efficacy and safety of artificial total disc replacement in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 2961-2967.
share this article
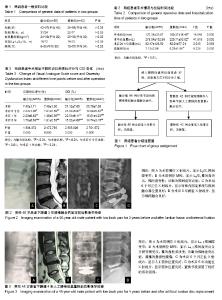
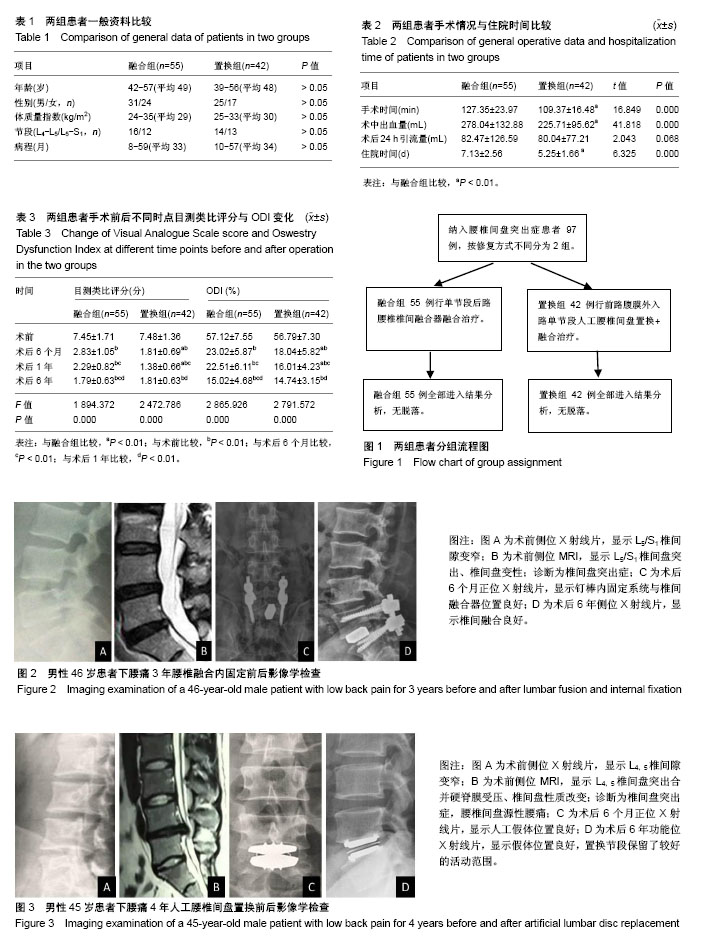
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理分析,入选患者97例,均完成6年随访,所有患者随访数据均计入结果进行分析。试验流程图见图1。 2.2 两组患者一般资料分析 2组患者一般资料比较差异无显著性意义,具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 两组患者手术情况与住院时间分析 置换组手术时间、术后住院时间明显短于融合组,术中出血量明显少于融合组(P < 0.01),见表2。 2.4 两组患者目测类比评分与ODI变化 2组患者术后各随访时点目测类比评分与ODI较术前有明显改善(P < 0.01);2组间术后6个月、1年目测类比评分与ODI差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);2组间术前、术后6年目测类比评分与ODI差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);融合组内各随访点间目测类比评分与ODI差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);置换组术后1年与术后6个月、6年目测类比评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);置换组内各随访点间ODI差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。 2.5 典型病例 病例1:融合组男性患者,46岁,下腰痛3年,诊断为腰椎间盘退行性变、腰椎间盘突出症、椎间盘源性腰痛。采取腰椎后路单椎间融合器融合与双侧钉棒内固定系统内固定治疗,术后随访6年,X射线片可见融合器与钉棒位置良好,骨桥形成,融合效果良好(图2)。 病例2:置换组男性患者,45岁,下腰痛4年,诊断为腰椎间盘突出症与椎间盘源性腰痛。采取Link SB CharitéⅢ型人工椎间盘假体置换病变椎间盘并进行生物固定治疗,术后随访6年,X射线片可见椎间盘假体位置良好,椎间盘置换节段具有良好ROM,置换效果满意(图3)。 2.6 并发症分析 融合组55例患者术后随访6年,融合内固定手术过程中有1例患者因牵拉引起神经根损伤导致下肢疼痛,对症治疗10 d后疼痛消失;术后手术切口无感染、钉棒内固定系统无松动或断裂、椎间融合器无移位或脱出;末次随访发现2例患者出现关节突关节轻度增生;并发症发生率为5%。 置换组42例患者术后随访6年,人工腰椎间盘置换过程中未出现神经、血管损伤和腹膜撕裂;术后出现1例患者发生摔伤后椎体骨折行再次手术治疗不计入手术原因引起的并发症,1例患者出现小关节轻度退变;术后未出现切口感染、人工椎间盘假体位置不良、异位骨化引起的椎间隙融合、植入物机械故障、小关节退变、切口疝和犁状肌综合征等并发症;末次随访手术节段活动度良好;并发症发生率为2%。 "
| [1] Suh SP,Jo YH, Jeong HW, et al. Outcomes of revision surgery following instrumented posterolateral fusion in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparative analysis between pseudarthrosis and adjacent segment disease. Asian Spine J.2017;11(3):463-471.[2] 严冬雪,黄永吉,马广斌,等. 侧路与后路单椎间融合器联合单侧钉棒置入治疗腰椎退行性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(4):541-546. [3] Baranowska A,Baranowska J,Baranowski P. Analysis of reasons for failure of surgery for degenerative disease of lumbar spine. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil.2016;18(2):117-129.[4] Hsieh CT,Chang CJ,Su IC, et al. Clinical experiences of dynamic stabilizers: Dynesys and Dynesys top loading system for lumbar spine degenerative disease. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016;32(4):207-215.[5] Chen XL,Guan L,Liu YZ, et al. Interspinous dynamic stabilization adjacent to fusion versus double-segment fusion for treatment of lumbar degenerative disease with a minimum follow-up of three years. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1275-1283.[6] Ebata S,Takahashi J,Hasegawa T, et al. Role of weekly teriparatide administration in osseous union enhancement within six months after posterior or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for osteoporosis-associated lumbar degenerative disorders: a multicenter, prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(5):365-372.[7] Bielecki M,Kunert P,Prokopienko M, et al. Midline lumbar fusion using cortical bone trajectory screws. Preliminary report . Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2016,11(3):156-163.[8] Xu BS,Liu Y,Xu HW, et al. Intervertebral fusion with mobile microendoscopic discectomy for lumbar degenerative disc disease. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(2):241-245.[9] Ding F,Jia Z,Zhao Z, et al. Total disc replacement versus fusion for lumbar degenerative disc disease: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Eur Spine J. 2017; 26(3):806-815.[10] 刘付仟,梁伟国,叶冬平. 髓核置换、全椎间盘置换及腰椎后路动态稳定系统治疗腰椎退行性疾病的应用与思考[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3): 440-444.[11] 白文媛,顾洪生,廖振华, 等.人工腰椎间盘置换的临床应用:现状与未来[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35): 6321-6326.[12] 吴亮,孙晓亮,张雷,等. 人工腰椎间盘置换治疗退行性腰椎间盘疾病16例分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4):638-641.[13] 陈小龙,海涌,张强,等. 腰椎 Active-L人工椎间盘置换术与腰椎融合术的临床比较研究[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2012,5 (1):3-10.[14] 孙文志,鲁世保,孔超. 人工腰椎椎间盘置换术并发症的研究进展[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2015,13(2):121-125.[15] Gautschi OP,Corniola MV,Smoll NR, et al. Sex differences in subjective and objective measures of pain, functional impairment, and health-related quality of life in patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease. Pain. 2016;157(5):1065-1071.[16] Gautschi OP,Corniola MV,Joswig H, et al. The timed up and go test for lumbar degenerative disc disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(12):1943-1948.[17] Lee RK,Griffith JF,Lau YY, et al. Diagnostic capability of low- versus high-field magnetic resonance imaging for lumbar degenerative disease. Spine. 2015;40(6):382-391.[18] Greiner-Perth R,Sellhast N,Perler G, et al. Dynamic posterior stabilization for degenerative lumbar spine disease: a large consecutive case series with long-term follow-up by additional postal survey. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(8):2563-2570.[19] Moriguchi Y,Alimi M,Khair T, et al. Biological treatment approaches for degenerative disk disease: a literature review of in vivo animal and clinical data. Global Spine J. 2016;6(5): 497-518.[20] Villavicencio AT,Nelson EL,Rajpal S, et al. The timing of surgery and symptom resolution in patients undergoing transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disk disease and radiculopathy. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(6):E765-E769.[21] Madera M,Brady J,Deily S, et al. The role of physical therapy and rehabilitation after lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative disease: a systematic review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;26(6): 694-704.[22] Phan K,Rao PJ,Kam AC, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(5):1017-1030.[23] Deukmedjian AJ,Cianciabella AJ,Cutright J, et al. Combined transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with posterolateral instrumented fusion for degenerative disc disease can be a safe and effective treatment for lower back pain. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2015; 6(4):183-189.[24] Lee YC,Zotti MG,Osti OL. Operative management of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(4): 801-819.[25] Noshchenko A,Hoffecker L,Lindley EM, et al. Perioperative and long-term clinical outcomes for bone morphogenetic protein versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion in degenerative disk disease: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(3):117-135.[26] Ghogawala Z,Whitmore RG,Watters WC, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 3: assessment of economic outcome . J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(1):14-22.[27] Rao MJ,Cao SS. Artificial total disc replacement versus fusion for lumbar degenerative disc disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134(2):149-158.[28] Nunley PD,Jawahar A,Cavanaugh DA, et al. Symptomatic adjacent segment disease after cervical total disc replacement: re-examining the clinical and radiological evidence with established criteria. Spine J. 2013;13(1):5-12.[29] Saavedra-Pozo FM,Deusdara RA,Benzel EC. Adjacent segment disease perspective and review of the literature . Ochsner J. 2014;14(1):78-83.[30] Alahmadi H,Deutsch H. Outcome of salvage lumbar fusion after lumbar arthroplasty. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(1):13-18.[31] Thavaneswaran P,Vandepeer M. Lumbar artificial intervertebral disc replacement: a systematic review. ANZ J Surg. 2014;84(3):121-127.[32] Son S,Lee SG,Park CW, et al. Minimally invasive multilevel percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for lumbar spinal diseases. Korean J Spine. 2012;9(4):352-327.[33] 卓祥龙,胡建中,王文军,等. 人工腰椎间盘(Charité Ⅲ)置换治疗腰椎间盘病长期疗效[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(1):5-9.[34] Mattei TA,Beer J,Teles AR, et al. Clinical outcomes of total disc replacement versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion for surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Global Spine J. 2017;7(5):452-459.[35] Phan K,Xu J,Maharaj MM, et al. Intraoperative navigation for accurate midline placement of anterior lumbar interbody fusion and total disc replacement prosthesis. J Spine Surg. 2017;3(2):228-232.[36] Clavel P,Ungureanu G,Catalá I, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients undergoing lumbar total disc replacement: A comparison with the general population. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;160:119-124.[37] Telfeian AE,Oyelese AA,Gokaslan ZL. Rhode Island Hospital's Contribution to the Field of Endoscopic Spine Surgery. R I Med J (2013). 2017;100(6):34-38.[38] Lanman TH,Burkus JK,Dryer RG, et al. Long-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of the Prestige LP artificial cervical disc replacement at 2 levels: results from a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017; 27(1):7-19.[39] 康南,鲁世保,海涌,等. 腰椎人工椎间盘置换术治疗腰椎间盘退变性疾病的中长期疗效分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(4): 296-301. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||