Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (13): 2011-2019.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0510
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway on the differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells
Peng Qin1, 2, Yin Yan-feng2, Guan Zheng2, Lv Sha2, Su Wen-jun2, Shan Hai-yan1, 2, Zhang Lei2
- 1Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Af?liated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University (First Hospital of Kunming), Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Revised:2018-01-07Online:2018-05-08Published:2018-05-08 -
Contact:Zhang Lei, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Researcher, Af?liated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University (First Hospital of Kunming), Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Peng Qin, Master, Physician, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; Af?liated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University (First Hospital of Kunming), Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660303; the Yunnan Province-Kunming Medical University Joint Scientific Projects
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Peng Qin, Yin Yan-feng, Guan Zheng, Lv Sha, Su Wen-jun, Shan Hai-yan, Zhang Lei. Influence of Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway on the differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(13): 2011-2019.
share this article
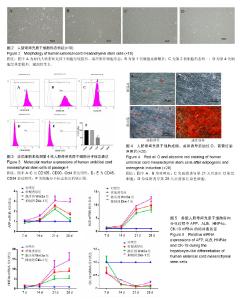
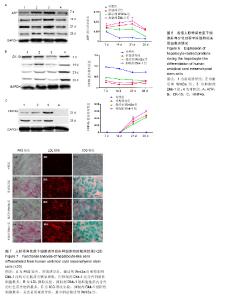
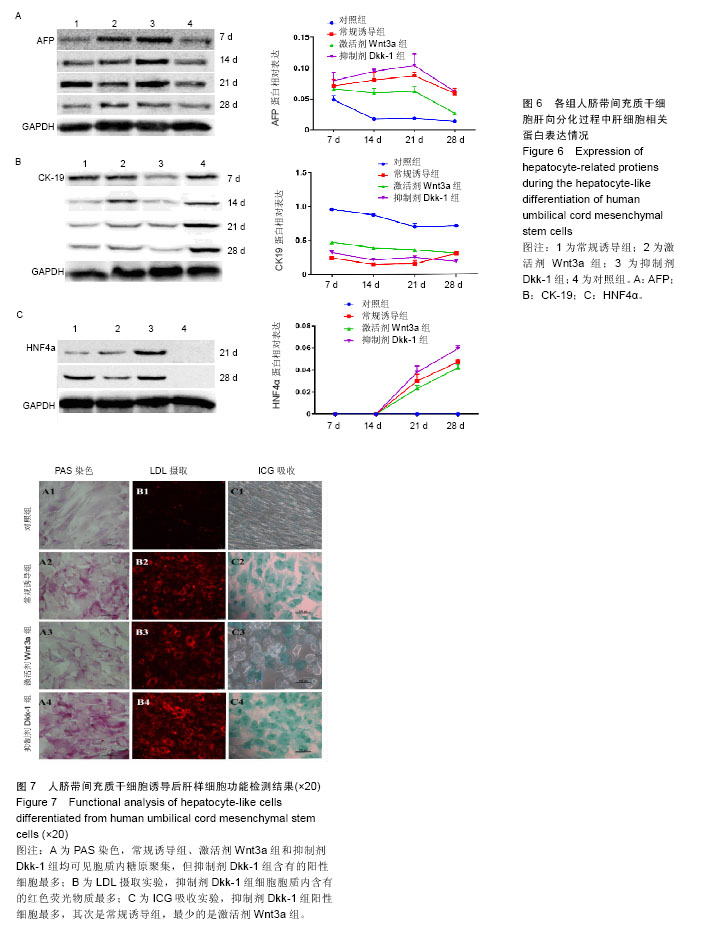
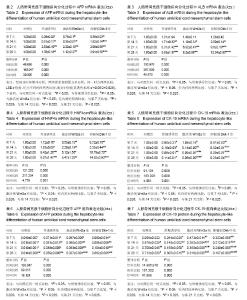
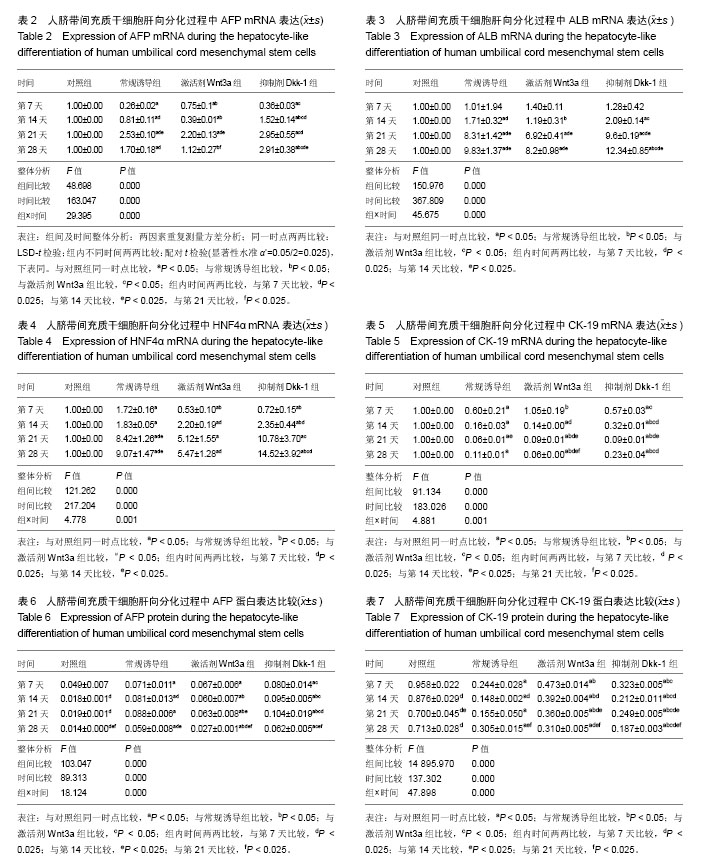
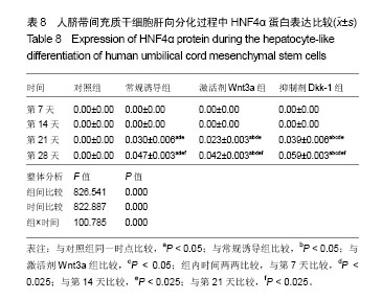
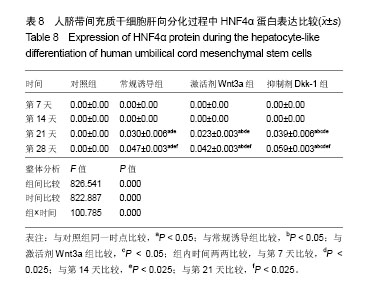
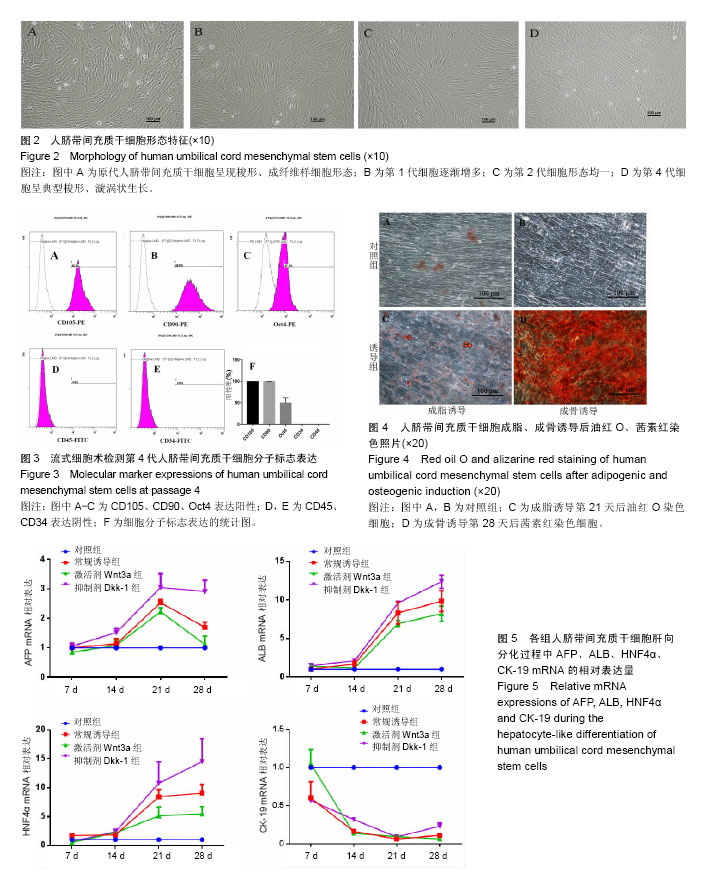
2.1 hUC-MSCs分离培养及流式鉴定结果 通过组织块贴壁法分离得到的hUC-MSCs在含有体积分数为10%胎牛血清的完全培养基中培养1周后开始有细胞爬出,经过第1次换液后,可见长梭形、纺锤形成纤维样贴壁生长的细胞(图2A),培养至80%融合,按1︰3传代(图2B)。传至第4代,大部分细胞呈典型梭形、漩涡状生长,排列规则紧密(图2D)。用流式细胞术检测第4代细胞分子标志CD105、CD90、Oct4、CD45、CD34的表达情况,结果显示细胞阳性表达CD105(99.3±0.57)%、CD90(99.5±0.73)%、Oct4(47.16±1.32)%,不表达造血干细胞特异分子标志CD45(0.00±0.00)%、CD34(0.01±0.03)%,符合脐带间充质干细胞特征(图3A-F)。 2.2 hUC-MSCs体外成脂、成骨分化能力 见图4。hUC- MSCs成脂诱导21 d,细胞由长梭形逐渐变短、变圆,呈不规则形态,细胞内开始出现折光性很强透明的圆形脂肪粒,逐渐增多变大,油红O染色可见橘红色脂滴(图4C)。hUC-MSCs成骨诱导28 d,细胞质内颗粒样物质逐渐增多,细胞呈向心性生长,细胞间可见钙盐沉积,结节中心的细胞相互融合,细胞结构消失,经茜素红染色呈橘红色致密钙结节(图4D)。 2.3 Wnt3a和Dkk-1对hUC-MSCs肝向分化过程中肝细胞特异mRNA表达的影响 常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt-3a组、抑制剂Dkk-1组除CK-19随时间表达下调且表达低于对照组外(F组间、时间、交叉,P值分别为91.134,0.000;183.026,0.000;4.881,0.001),AFP、ALB、HNF4α mRNA的表达水平整体高于对照组(F组间,P值分别为:48.698,0.000;150.976,0.000;121.262,0.000),并且随分化时间的延长而上升(F时间,P值分别为:163.047,0.000;367.809,0.000;217.204,0.000),上升幅度大于对照组(F交叉,P值分别为:29.395,0.000;45.675,0.000;4.778,0.001)。 对照组、常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt3a组和抑制剂Dkk-1组组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),组内不同时点差异有显著性意义(P < 0.025),见表2-5。抑制剂Dkk-1组AFP、ALB、HNF4α mRNA的表达高于常规诱导组和激活剂Wnt-3a组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。诱导后第21天常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt3a组、抑制剂Dkk-1组AFP mRNA的表达均达到最大值(P < 0.025),与诱导第7天比,3组差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.025),21 d后呈下调趋势,但仍高于第7,14天,且抑制剂Dkk-1组在第14,21,28天的表达均高于其他两组,其中第14,28天差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而激活剂Wnt-3a组AFP mRNA的表达在3组中则为最低,尤其在第14,21天两者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。对于ALB、HNF4α mRNA的表达,与第7天相比,3组均随时间延长表达上调,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.025),且抑制剂Dkk-1组ALB mRNA在4个时点上的表达均高于其他2组,尤其在诱导第28天,两者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),且在4个时间点上均高于激活剂Wnt3a组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),激活剂Wnt3a组表达则低于常规诱导组,诱导第14天,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。抑制剂Dkk-1组HNF4α mRNA的表达在第14,21,28天均高于其他两组,其中除了第21天与常规诱导组差异不显著外,其他两个时间点均高于常规诱导组和激活剂组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。激活剂Wnt3a组HNF4α mRNA在第7,21,28天的表达低于常规诱导组,且在第7天时差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.4 Wnt3a和Dkk1对hUC-MSCs肝向分化过程中肝细胞相关蛋白表达的影响 见表6-8。常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt-3a组、抑制剂Dkk-1组CK-19蛋白的表达低于对照组,且随时间延长表达下调(F组间、时间、交叉,P值分别为:14895.970,0.000;137.302,0.000;47.898,0.000),AFP、HNF4α蛋白的表达水平整体高于对照组(F组间,P值分别为:103.047,0.000;826.541,0.000),并且随分化时间的延长而上升(F时间,P值分别为:89.313;0.000;822.887),上升幅度大于对照组(F交叉,P值分别为:18.124,0.000;100.785,0.000)。其中,常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt3a组、抑制剂Dkk-1组AFP在诱导第7,14,21,28天的表达均与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),3组AFP的表达均由第7天开始上调,至21天为最高表达,随后开始下调,AFP表达量、上调幅度依次为Dkk-1组>常规诱导组>Wnt3a组(P < 0.05),且在4个时间点上,Dkk-1组的表达均高于Wnt3a组(P < 0.05)。而对于HNF4α蛋白则在诱导第7,14天时无论是实验组还是对照组均不表达,在第21天后才开始表达(P < 0.05),对照组则始终不表达HNF4α蛋白,常规诱导组、激活剂Wnt3a组、抑制剂Dkk-1组在诱导第21-28天呈上调趋势,上调幅度为Dkk-1组>常规诱导组> Wnt3a激活组(P < 0.05),且不同时间点两两比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图6,结果与qPCR基本一致。 2.5 诱导后细胞肝样功能检测结果 hUC-MSCs肝向分化诱导第28天进行PAS染色、LDL吞噬实验和ICG吸收实验,结果显示:Dkk-1抑制剂组细胞质中含有大量染成粉红色的糖原聚集(图7A4),荧光显微镜下也可见到胞质内含有大量红色荧光物质(图7B4),同时抑制剂Dkk-1组细胞质中也可见到大量绿色物质(图7C4),说明抑制剂Dkk-1组肝样细胞更早成熟,而激活剂Wnt3a组阳性细胞(图7A3,B3,B3)则少于抑制剂Dkk-1组和常规诱导组(图7A2,B2,B2),说明激活剂Wnt3a组肝样细胞功能相比正常诱导组细胞要更不成熟。对照组细胞几乎都为阴性(图7A1,B1,C1)。"
| [1] Yang JF, Cao HC, Pan QL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord ameliorate fulminant hepatic failure and increase survival in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14(2):186-193.[2] Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.[3] Hong SH, Gang EJ, Jeong JA, et al. In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330(4):1153-1161.[4] Campard D, Lysy PA, Najimi M, et al. Native umbilical cord matrix stem cells express hepatic markers and differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(3):833-848.[5] Zhang L, Zhao YH, Guan Z, et al. Application potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly in liver tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl): 137-143.[6] An SY, Han J, Lim HJ, et al. Valproic acid promotes differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells from whole human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Cell. 2014;46(2):127-135.[7] Zhang YN, Lie PC, Wei X. Differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly into hepatocyte-like cells. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):548-558.[8] Anzalone R, Lo Iacono M, Corrao S, et al. New emerging potentials for human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells: immunological features and hepatocyte-like differentiative capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):423-438.[9] Cui L, Zhou X, Li J, et al. Dynamic microRNA profiles of hepatic differentiated human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44737.[10] Liang XJ, Chen XJ, Yang DH, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells by hTERT gene transfection in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(2): 215-221.[11] Cui L, Shi Y, Zhou X, et al. A set of microRNAs mediate direct conversion of human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e918.[12] Xue G, Han X, Ma X, et al. Effect of Microenvironment on Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Hepatocytes In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8916534.[13] Herencia C, Martínez-Moreno JM, Herrera C, et al. Nuclear translocation of β-catenin during mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into hepatocytes is associated with a tumoral phenotype. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34656.[14] García-Castro MI, Marcelle C, Bronner-Fraser M. Ectodermal Wnt function as a neural crest inducer. Science. 2002;297(5582): 848-851.[15] Fagotto F. Looking beyond the Wnt pathway for the deep nature of β-catenin. EMBO Rep. 2013;14(5):422-433.[16] Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky-Shapiro II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381-390.[17] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[18] He H, Nagamura-Inoue T, Takahashi A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Int J Hematol. 2015;102(3): 368-378.[19] Zahari W, Hashim SN, Yusof MF, et al. Immunomodulatory Effect of Cytokines in the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(3):197-206.[20] Doan CC, Le TL, Hoang NS, et al. Differentiation of umbilical cord lining membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells into endothelial-like cells. Iran Biomed J. 2014;18(2):67-75.[21] Robinson AP, Foraker JE, Ylostalo J, et al. Human stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow enhance glial differentiation of rat neural stem cells: a role for transforming growth factor β and Notch signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(2): 289-300.[22] Pattabhi SR, Lehaf AM, Schlenoff JB, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell osteoblast differentiation, ECM deposition, and biomineralization on PAH/PAA polyelectrolyte multilayers. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(5):1818-1827.[23] Qian SW, Li X, Zhang YY, et al. Characterization of adipocyte differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow. BMC Dev Biol. 2010;10:47.[24] Esmaeli S, Allameh A, Adelipour M, et al. The impact of oxidative DNA changes and ATM expression on morphological and functional activities on hepatocytes obtained from mesenchymal stem cells. Biologicals. 2017;47:52-58.[25] Haegele L, Ingold B, Naumann H, et al. Wnt signalling inhibits neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells by controlling bone morphogenetic protein expression. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003; 24(3):696-708.[26] Aubert J, Dunstan H, Chambers I, et al. Functional gene screening in embryonic stem cells implicates Wnt antagonism in neural differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20(12):1240-1245.[27] Ke Z, Zhou F, Wang L, et al. Down-regulation of Wnt signaling could promote bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(2):342-348.[28] Yoshida Y, Shimomura T, Sakabe T, et al. A role of Wnt/beta-catenin signals in hepatic fate specification of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;293(5):G1089-1098.[29] Ren S, Johnson BG, Kida Y,et al. LRP-6 is a coreceptor for multiple fibrogenic signaling pathways in pericytes and myofibroblasts that are inhibited by DKK-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(47):E7643-E7644.[30] Yamamoto H, Sakane H, Yamamoto H, et al. Wnt3a and Dkk1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell. 2008;15(1):37-48. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||