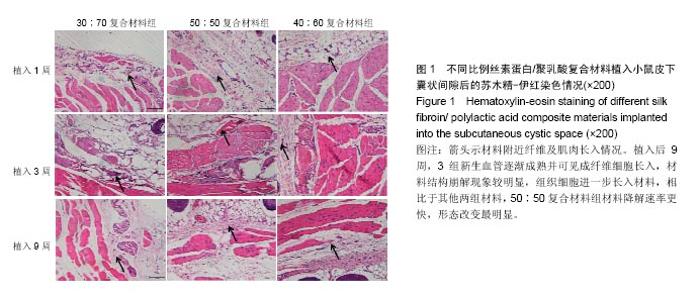
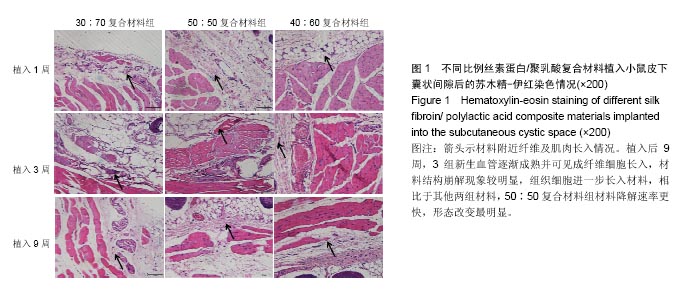
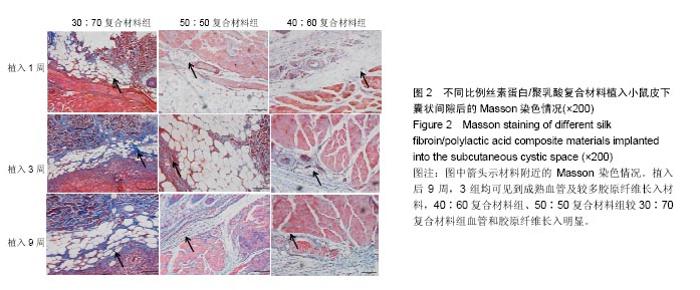
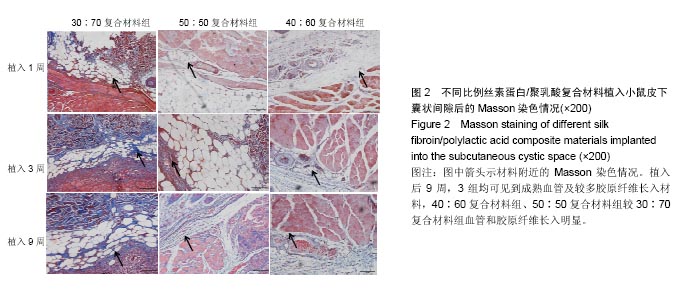
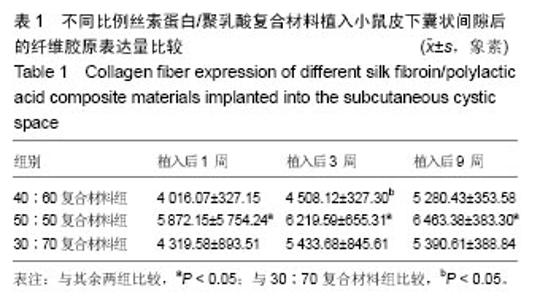
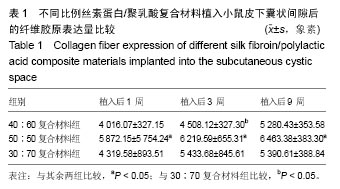
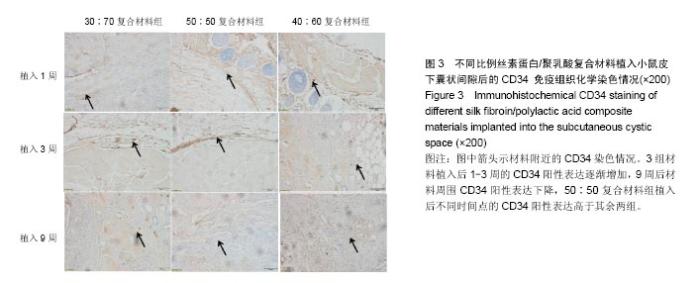
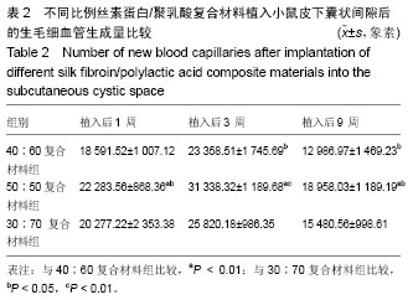
| [1]陈伟良,李劲松,杨朝晖,等.儿童口腔颌面部大面积血管瘤的整形手术治疗[C].中国广东深圳:全国口腔颌面部脉管性疾病学术研讨会,2004.[2]桂平,张兵,黄宇文.脱细胞异体组织补片修复口腔黏膜缺损16例[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(5):731-732.[3]刘玉丽.儿童口腔颌面部大面积血管瘤整形手术治疗[J].中国医疗美容,2016,6(4):12-13.[4]王红燕.口腔内游离皮片移植手术的护理[J].中国美容医学, 2000,9(1):46-47.[5]Fuchs JR,Nasseri BA,Vacanti JP.Tissue engineering: a 21st century solution to surgical reconstruction.Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72(2):577-591.[6]何静.胶原蛋白在生物医药工程中的应用研究进展[J].河南科技, 2015,31(10):104-105.[7]陈忠敏,陈枭,庞亚妮,等.丝胶蛋白应用于组织工程支架材料的研究进展[J].丝绸,2015,52(4):25-30.[8]王宗良.细菌纤维素组织工程支架材料的制备及其应用研究[D].吉林大学,2008.[9]周爱梅.利用重组人源胶原蛋白制备生物医学组织工程材料[D].南京理工大学,2015.[10]叶漫文,曾曙光.基于丝素蛋白和壳聚糖的骨组织工程材料研究进展[J].广东牙病防治,2013,21(2):108-112.[11]陶学强,祁全.组织工程材料在周围神经损伤修复中应用的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(4): 318-321.[12]Tang X,Xue C,Wang Y,et al.Bridging peripheral nerve defects with a tissue engineered nerve graft composed of an in vitro cultured nerve equivalent and a silk fibroin-based scaffold. Biomaterials.2012;33(15):3860-3867.[13]Wang S,Zhang Y,Wang H,et al.Fabrication and properties of the electrospun polylactide/silk fibroin-gelatin composite tubular scaffold.Biomacromolecules.2009;10(8):2240-224.[14]吕晓迎,黄炎,俞亚东,等.基因/蛋白质组学技术在生物材料生物相容性研究中的应用[J].无机材料学报,2013,28(1): 21-28.[15]金洹宇,刘星,银华,等.丝素蛋白在生物医用领域中的应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2014,31(1):228-232.[16]张笑.丝素蛋白/聚乳酸复合纤维支架生物相容性的初步研究[D].吉林大学,2013.[17]武欣.骨髓间充质干细胞与左旋聚乳酸/丝素蛋白支架复合修复兔口腔粘膜[D].吉林大学,2014.[18]寇琴.丝蛋白肽链/聚乳酸共聚改性的研究[D].南京林业大学, 2008.[19]孙莹.丝素蛋白/左旋聚乳酸支架材料与软骨细胞体外相容性研究[D].吉林大学,2015.[20]邢帅,夏亚一,袁凌伟,等.聚乳酸/丝素蛋白复合组织工程支架的制备及生物学性能的评价[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2008, 34(3):405-410.[21]张显华,左保齐.丝素蛋白/聚乳酸共混溶液的流变性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2010,26(2):47-49.[22]千建峰.不同孔径丝素蛋白材料体内降解的初步研究[D].复旦大学,2012.[23]Wang YL,Gu XM,Kong Y,et al.Electrospun and woven silk fibroin/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nerve guidance conduits for repairing peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(10):1635-1642.[24]Zhu H,Feng X,Zhang H,et al.Structural characteristics and properties of silk fibroin/poly(lactic acid) blend films.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2009;20(9):1259-1274.[25]Szpaderska AM,Walsh CG,Steinberg MJ,et al.Distinct patterns of angiogenesis in oral and skin wounds.J Dent Res. 2005; 84(4):309-314.[26]Eming SA,Werner S,Bugnon P,et al.Accelerated wound closure in mice deficient for interleukin-10.Am J Pathol. 2007;170(1):188-202.[27]Tamaki T,Okada Y,Uchiyama Y,et al.Synchronized reconstitution of muscle fibers, peripheral nerves and blood vessels by murine skeletal muscle-derived CD34(-)/45 (-) cells.Histochem Cell Biol.2007;128(4):349-360.[28]Barreiro O,Cibrian D,Clemente C,et al.Pivotal role for skin transendothelial radio-resistant anti-inflammatory macrophages in tissue repair.Elife. 2016;5.pii:e15251.doi:10.7554/eLife.15251.[29]Wells A,Nuschke A,Yates CC.Skin tissue repair: Matrix microenvironmental influences. Matrix Biol.2016;49:25-36.[30]Fu L,Zhang J,Yang G.Present status and applications of bacterial cellulose-based materials for skin tissue repair. Carbohydr Polym.2013;92(2):1432-1442. |