Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (16): 2515-2520.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.16.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Flow shear stress promotes the endothelialization of small diameter tissue-engineered vessels
Zhang Wei1, Song Ai-jing2
- 1Guanhao Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative and Implantable Medical Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Provincial Institute of Sport Science, Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-05-05Online:2017-06-08Published:2017-07-06 -
Contact:Song Ai-jing, Ph.D., Associate researcher, Guangdong Provincial Institute of Sport Science, Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Wei, Master, Intermediate engineer, Guanhao Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative and Implantable Medical Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2010A080407005; the Major Project of National Key Research Plan for the Biomedical Materials Research and Tissues/Organs Repair, Replacement, No. 2016YFC1103202
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Wei, Song Ai-jing. Flow shear stress promotes the endothelialization of small diameter tissue-engineered vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(16): 2515-2520.
share this article
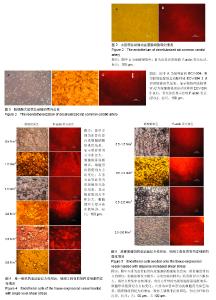
2.1 大鼠颈总动脉的形态 硝酸银染色法和F-actin荧光标记染色结果显示,大鼠颈动脉血管内壁上无血管内皮细胞,但血管结构保留完整(图2)。 2.2 脱细胞大鼠颈总动脉的内皮化 硝酸银染色和血管内皮细胞 F-actin荧光标记结果表明,血管内皮细胞已完全覆盖血管内壁表面,生长状态良好,并融合成细胞单层;细胞呈椭圆形,细胞间连接紧密;细胞膜周边出现F-actin(图3)。 2.3 流动剪切力对组织工程血管内皮化的作用 2.3.1 单一水平的流动剪切力 硝酸银染色结果表明,0.5 N/m2作用24 h,细胞无明显变化;1.0 N/m2作用24 h,部分细胞变得紧缩,有少许细胞脱落;1.5,2.0 N/m2作用2 h,部分细胞呈梭形,局部有细胞脱落;2.5 N/m2作用2 h,细胞形态呈明显的梭形,细胞的长轴与液体流动方向一致,细胞脱落较多,细胞膜受到不同程度的损伤;3.0 N/m2作用2 h,细胞几乎全部脱落,仅存的个别细胞形态为椭圆形,可清晰看到血管壁内弹性层(图4)。 荧光染色结果显示,0.5 N/m2作用24 h,微丝主要分布在细胞膜的周边;1.0 N/m2作用24 h,细胞膜周边微丝减少,核周边微丝数量增多;1.5,2.0 N/m2作用2 h,核周微丝逐渐增多;2.5 N/m2作用2 h,微丝主要分布在核周边,能清晰看到应力纤维;3.0 N/m2作用2 h,细胞几乎全部脱落,观察不到微丝的存在(图4)。 2.3.2 成梯度增加的流动剪切力 硝酸银染色结果表明,经0.5-1.5 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,多数细胞保持原状,极少细胞脱落;0.5-2.0 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,部分细胞变为梭形,细胞长轴与液流方向一致;细胞间连接紧密,无细胞脱落;0.5-2.5 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,多数细胞变为梭形,有明显的轴向排列;细胞间连接紧密,极少数细胞脱落;0.5-3.0 N/m2成梯度作用后,细胞呈梭形,沿液流方向被拉长,有明显的轴向排列,内皮细胞层较为完整(图5)。 荧光染色结果显示,经0.5-1.5 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,微丝主要分布在膜周边;0.5-2.0 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,部分细胞变为梭形,细胞长轴与液流方向一致,细胞间连接紧密;核周边微丝明显增多;0.5-2.5 N/m2成梯度增加的剪切力作用后,细胞多为梭形,有明显的轴向排列;微丝主要集中在核周边,有应力纤维的出现;0.5-3.0 N/m2成梯度作用后,细胞有明显的轴向排列,微丝主要分布在核周边,有应力纤维的出现(图5)。"
| [1] Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(2):115-126.[2] Li S, Henry JJ. Nonthrombogenic approaches to cardiovascular bioengineering. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2011; 13:451-475. [3] Lytle BW, Loop FD, Cosgrove DM, et al. Long-term (5 to 12 years) serial studies of internal mammary artery and saphenous vein coronary bypass grafts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1985;89(2):248-258.[4] Jensen LP, Lepäntalo M, Fossdal JE, et al. Dacron or PTFE for above-knee femoropopliteal bypass. a multicenter randomised study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007;34(1):44-49. [5] L'Heureux N, McAllister TN, de la Fuente LM. Tissue-engineered blood vessel for adult arterial revascularization. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(14):1451-1453.[6] 王秋兰.脑血管支架种类及材料学特点与支架置入后的补体反应及干预[J].中国医学工程,2016,24(2):6-9.[7] Wang F, Guan X, Wu T, et al. Acellular Endocardium as a Novel Biomaterial for the Intima of Tissue-Engineered Small-Caliber Vascular Grafts. Artif Organs. 2016;40(12): E253-E265. [8] Sankaran KK, Subramanian A, Krishnan UM, et al. Nanoarchitecture of scaffolds and endothelial cells in engineering small diameter vascular grafts. Biotechnol J. 2015;10(1):96-108. [9] Wilhelmi M, Jockenhoevel S, Mela P. Bioartificial fabrication of regenerating blood vessel substitutes: requirements and current strategies. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2014;59(3):185-195. [10] Jaspan VN, Hines GL. The Current Status of Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts. Cardiol Rev. 2015; 23(5):236-239. [11] 姜力,陈思原,王园园,等.小口径人工血管构建研究现状与展望[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2016,35(3):357-364.[12] 关颖,关国平,林婧,等.小口径人工血管顺应性的影响因素和改善方法[J].材料导报,2014,28(10):125-129.[13] Yeager RA, Hobson RW 2nd, Jamil Z, et al. Differential patency and limb salvage for polytetrafluoroethylene and autogenous saphenous vein in severe lower extremity ischemia. Surgery. 1982;91(1):99-103.[14] Weinberg CB, Bell E. A blood vessel model constructed from collagen and cultured vascular cells. Science. 986;231(4736): 397-400.[15] Quint C, Kondo Y, Manson RJ, et al. Decellularized tissue-engineered blood vessel as an arterial conduit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(22):9214-9219. [16] Gui L, Muto A, Chan SA, et al. Development of decellularized human umbilical arteries as small-diameter vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(9):2665-2676. [17] Mitchell SL, Niklason LE. Requirements for growing tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2003; 12(2):59-64.[18] 姜力,陈思原,王园园,等.小口径血管构建研究现状与展望[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2016,35(3):357-364.[19] Koobatian MT, Row S, Smith RJ Jr, et al. Successful endothelialization and remodeling of a cell-free small-diameter arterial graft in a large animal model. Biomaterials. 2016;76:344-358. [20] 王甩艳,赖琛,奚廷斐.小口径人工血管及制备方法的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2013,32(6):723-730.[21] 何艳平,马德春,李磊,等.人工血管材料血液相容性及表面改性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1272-1276.[22] 汪涛,赵珺,张健,等.多巴胺处理聚四氟乙烯人工血管对体外种植内皮细胞的影响[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2016,19(1):11-15.[23] 王园园.双重修饰的小口径人工血管的快速内皮化[D].天津:南开大学,2016.[24] Kang TY, Lee JH, Kim BJ, et al. In vivo endothelization of tubular vascular grafts through in situ recruitment of endothelial and endothelial progenitor cells by RGD-fused mussel adhesive proteins. Biofabrication. 2015;7(1):015007.[25] Chlupá? J, Filová E, Riedel T, et al. Attachment of human endothelial cells to polyester vascular grafts: pre-coating with adhesive protein assemblies and resistance to short-term shear stress. Physiol Res. 2014;63(2):167-177.[26] Montini-Ballarin F, Calvo D, Caracciolo PC, et al. Mechanical behavior of bilayered small-diameter nanofibrous structures as biomimetic vascular grafts. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;60:220-233. [27] 覃素华,潘君,吴科达.促进内皮细胞在小口径人工血管表面的黏附方法探讨[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2005,22(3):629-632.[28] Ahn H, Ju YM, Takahashi H, et al. Engineered small diameter vascular grafts by combining cell sheet engineering and electrospinning technology. Acta Biomater. 2015;16:14-22. [29] 陈满军,洪文娟,洪志鹏.血液剪切力诱导的血管内皮细胞形态学变化和信号通路[J].山东医药,2014,54(40): 99-102.[30] 任长辉,刘肖,康红艳,等.剪切力条件下血管内皮细胞与平滑肌细胞的相互作用[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(2):185-191.[31] 柴守栋,顾承雄.血流剪切力对静脉桥血管再狭窄影响的研究紧张[J].心肺血管病杂志,2016,35(6):495-497.[32] 曹雪飞.剪切力对血管内皮功能影响及机制研究进展[J].中国实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016,30(10):956-958.[33] 吴科达,王远亮,覃素华,等.超低温处理后的兔颈总动脉血管支架内皮化的实验研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2005,24(5):382-384.[34] 叶志义.鼠颈总动脉超低温处理后的血管力学性能及衬里人脐静脉内皮细胞研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2001.[35] Amensag S, Goldberg LA, O'Malley KA, et al. Pilot assessment of a human extracellular matrix-based vascular graft in a rabbit model. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(3):839-847.e1. [36] Lim SH, Cho SW, Park JC, et al. Tissue-engineered blood vessels with endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;85(2):537-546.[37] G N, Tan A, Gundogan B, et al. Tissue engineering vascular grafts a fortiori: looking back and going forward. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(2):231-244. [38] Zhou M, Liu Z, Liu C, et al. Tissue engineering of small-diameter vascular grafts by endothelial progenitor cells seeding heparin-coated decellularized scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(1):111-120. [39] Tressel SL, Huang RP, Tomsen N, et al. Laminar shear inhibits tubule formation and migration of endothelial cells by an angiopoietin-2 dependent mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27(10):2150-2156.[40] Shaik E, Hoffmann KA, Dietiker JF. Numerical simulations of pulsatile flow in an end-to-side anastomosis model. Mol Cell Biomech. 2007;4(1):41-53.[41] Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987;238(4826): 491-497.[42] 张西正.组织工程研究的现状与进展[J].医用生物力学,2010, 25(1):1-3.[43] Ahn H, Ju YM, Takahashi H, et al. Engineered small diameter vascular grafts by combining cell sheet engineering and electrospinning technology. Acta Biomater. 2015;16:14-22.[44] Ercolani E, Del Gaudio C, Bianco A. Vascular tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels: reviewing the electrospinning approach. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015; 9(8):861-888.[45] Ercolani E, Del Gaudio C, Bianco A. Vascular tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels: reviewing the electrospinning approach. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015; 9(8):861-888. [46] Teebken OE, Bader A, Steinhoff G, et al. Tissue engineering of vascular grafts: human cell seeding of decellularised porcine matrix. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000;19(4): 381-386.[47] Kato N, Yamagishi M, Kanda K, et al. First Successful Clinical Application of the In Vivo Tissue-Engineered Autologous Vascular Graft. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102(4):1387-1390.[48] Laschke MW, Menger MD. Bioengineered vascular grafts off the shelf. Lancet. 2016;387(10032):1976-1978. [49] Meza D, Abejar L, Rubenstein DA, et al. A Shearing-Stretching Device That Can Apply Physiological Fluid Shear Stress and Cyclic Stretch Concurrently to Endothelial Cells. J Biomech Eng. 2016;138(3):4032550.[50] Hunt JA. Regenerative medicine: Materials in a cellular world. Nat Mater. 2008;7(8):617-618. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | Bai Zixing, Cao Xuhan, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Chen Si, Wen Jianmin, Lin Xinxiao, Sun Weidong. Construction and biomechanical analysis of ankle joint finite element model in gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366. |
| [4] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [5] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [9] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [12] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [13] | Zheng Yongze, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Li Pengfei, Lin Ziling. Extended finite element modeling analysis of femoral neck fracture based on ABAQUS software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 853-857. |
| [14] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [15] | Duan Chao, Shang Xiaoqiang, Duan Xianglin, Yang Ping, Tao Shengxiang. Stability of patellar claw versus loop plate combined with patellar claw for the treatment of comminuted fractures of the lower pole of the patella [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 934-937. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||