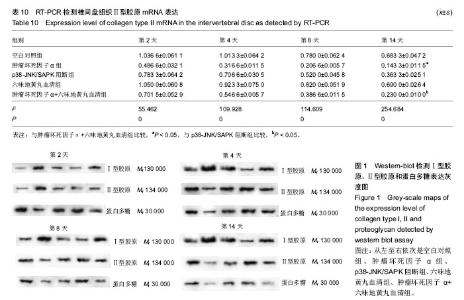
| [1] O'Connell GD, Leach JK, Klineberg EO. Tissue Engineering a Biological Repair Strategy for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Biores Open Access. 2015;4(1):431-445.[2] Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and internationally. Spine J. 2008;8(1):8-20. [3] Asche CV, Kirkness CS, McAdam-Marx C, et al. The societal costs of low back pain: data published between 2001 and 2007. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2007;21(4):25-33.[4] Haschtmann D, Stoyanov JV, Ettinger L, et al. Establishment of a novel intervertebral disc/endplate culture model: analysis of an ex vivo in vitro whole-organ rabbit culture system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(25):2918-2925.[5] 贺石林,王键,王净净.中医科研设计与统计学[M]. 长沙:湖南科学技术出版社,2008:49-50.[6] Baillet A, Grange L, Trocmé C, et al. Differences in MMPs and TIMP-1 expression between intervertebral disc and disc herniation. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(3):341-342.[7] 陶帅,姜宏,李晓春,等.基质金属蛋白酶与腰椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(2):162-164.[8] 关圆,倪家骧.椎间盘源性腰痛的细胞病理学研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(7):683-686.[9] 夏根,付斌,尚雁冰,等.Cathepsin G对人腰椎间盘退变的研究[J].宁夏医学杂志,2016,38(3):241-243.[10] Benz K, Stippich C, Fischer L, et al. Intervertebral disc cell- and hydrogel-supported and spontaneous intervertebral disc repair in nucleotomized sheep. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(9):1758-1768.[11] Lotz JC, Hadi T, Bratton C, et al. Anulus fibrosus tension inhibits degenerative structural changes in lamellar collagen. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(9):1149-1159.[12] 胡明,张传森.退变椎间盘细胞外基质的改变[J].局解手术学杂志, 2004,13(1):55-57.[13] 林建平,陈少清,林先钊,等.“三步五法”对椎间盘胞外基质系统的调控作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(11):4087-4090.[14] Vonk LA, Kroeze RJ, Doulabi BZ, et al. Caprine articular, meniscus and intervertebral disc cartilage: an integral analysis of collagen network and chondrocytes.Matrix Biol. 2010;29(3):209-218.[15] Ahsan R, Tajima N, Chosa E, et al. Biochemical and morphological changes in herniated human intervertebral disc. J Orthop Sci. 2001;6(6):510-518.[16] Smith LJ, Martin JT, Szczesny SE, et al. Altered lumbar spine structure, biochemistry, and biomechanical properties in a canine model of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5):616-622.[17] Kobayashi S, Baba H, Takeno K, et al. Fine structure of cartilage canal and vascular buds in the rabbit vertebral endplate. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;9(1):96-103.[18] Urano T, Narusawa K, Shiraki M, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1 (HAPLN1) gene is associated with spinal osteophyte formation and disc degeneration in Japanese women. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):572-577.[19] 陈伯华,郑洪军,吕振华,等.颈椎间盘蛋白多糖聚合体的分布及其意义[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2007,43(2):95-99.[20] Boden SD, Kang J, Sandhu H, et al. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 to achieve posterolateral lumbar spine fusion in humans: a prospective, randomized clinical pilot trial: 2002 Volvo Award in clinical studies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(23):2662-2673.[21] Kleeman TJ, Ahn UM, Talbot-Kleeman A. Laparoscopic anterior lumbar interbody fusion with rhBMP-2: a prospective study of clinical and radiographic outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24):2751-2756.[22] Chuang SY, Popovich JM Jr, Lin LC, et al. The effects of exogenous crosslinking on hydration and fluid flow in the intervertebral disc subjected to compressive creep loading and unloading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(24): E1362-1366.[23] Smith LJ, Nerurkar NL, Choi KS, et al. Degeneration and regeneration of the intervertebral disc: lessons from development. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4(1):31-41. [24] Shinmei M, Kikuchi T, Yamagishi M, et al. The role of interleukin-1 on proteoglycan metabolism of rabbit annulus fibrosus cells cultured in vitro. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13(11):1284-1290.[25] Yang SH, Wu CC, Shih TT, et al. Three-dimensional culture of human nucleus pulposus cells in fibrin clot: comparisons on cellular proliferation and matrix synthesis with cells in alginate. Artif Organs. 2008;32(1):70-73.[26] Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ. Studies of human intervertebral disc cell function in a constrained in vitro tissue culture system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(11): 1187-1195.[27] Chiba K, Andersson GB, Masuda K, et al. A new culture system to study the metabolism of the intervertebral disc in vitro. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(17):1821-1827.[28] Haschtmann D, Stoyanov JV, Ettinger L, et al. Establishment of a novel intervertebral disc/endplate culture model: analysis of an ex vivo in vitro whole-organ rabbit culture system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(25):2918-2925.[29] 梁倩倩,梁茂新,王拥军,等.古今中医药治疗腰椎间盘突出症的比较研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007,15(2):68-71.[30] 翟献斌.补肾活血方延缓腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中医正骨, 2009,21(5):18-22. |