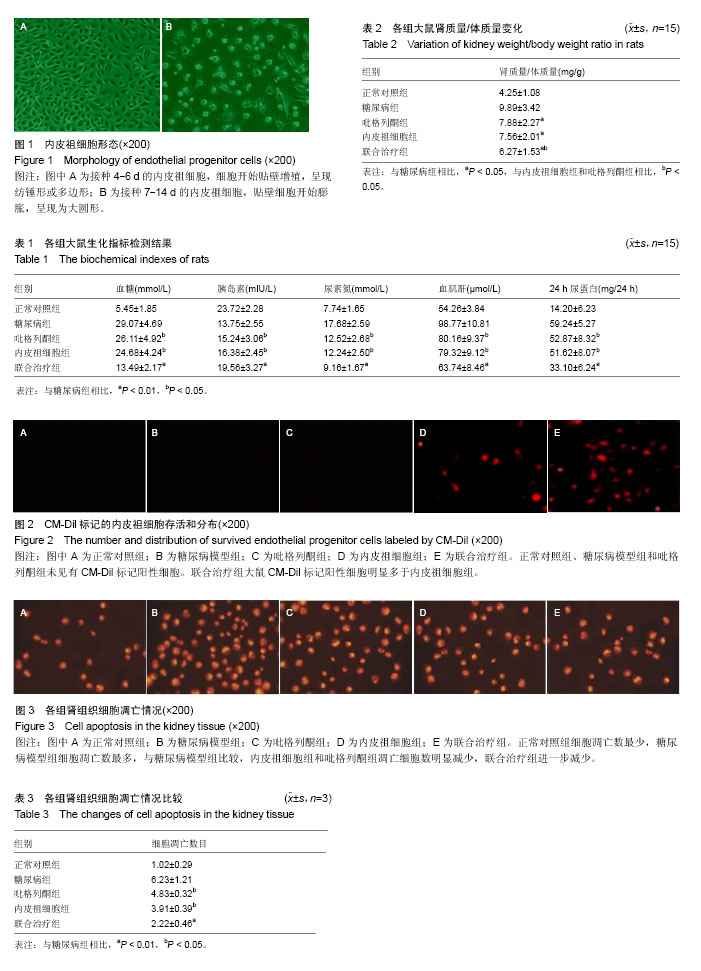
| [1] 代庆红,王忠东.中国糖尿病的现状调查[J].中国医药指南,2011, 9(13):206-208.[2] Bassetti M, Trecarichi EM, Mesini A, et al. Risk factors and mortality of healthcare-associated and community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(9):862-869.[3] Pozzilli P. Type 1 diabetes mellitus in 2011: Heterogeneity of T1DM raises questions for therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8(2):78-80.[4] 赵子粼,许顶立.内皮祖细胞治疗急性心肌梗死后心功能改变的研究进展[J].临床急诊杂志,2011,12(2):142-144.[5] 刘隽炜,董念国.内皮祖细胞研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2011, 32(4):528-531.[6] 宋一萌,李明真,马潞林.肾移植患者外周血来源的血管内皮祖细胞的促血管新生作用研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2016,37(1):57- 61.[7] 姜萌,王彬尧,王长谦,等.静脉注射携带缺氧诱导因子的内皮祖细胞对裸鼠缺血下肢血管新生的作用[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2007, 15(8):580-584.[8] 朱光旭,宋明宝,潘兴华,等.骨髓源性内皮祖细胞与内皮细胞共培养促进其向成熟内皮细胞分化的研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2013, 32(5):641-645.[9] 胡洋,郝兰坡,赵炳飞,等.骨髓源性血管内皮祖细胞体外分离?培养及分化为内皮细胞的研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2015, 24(22):2421-2424.[10] 孟刘坤,刘成珪.内皮祖细胞在肺动脉高压治疗中的应用[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2009,15(2):155-158.[11] 万钧,王辰,王军.内皮祖细胞在肺动脉高压的作用[J].国际呼吸杂志,2009,29(22):1393-1396.[12] 农慧,盛庆寿,梁健,等.STZ诱导糖尿病大鼠模型的研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(1):69-72.[13] 吴艳萍,张妍,朱久新,等.大明胶囊对STZ诱导的1型糖尿病大鼠胰腺microRNA表达谱的影响及其靶点分析[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2015,49(1):1-7.[14] 于萍,李强,刘颖,等.内皮祖细胞移植对糖尿病兔下肢缺血的病理及血管内皮生长因子的影响[J].中国实用内科杂志,2007,27(15): 1207-1209.[15] 郑曦,张弛.内皮祖细胞与骨髓单个核细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢缺血大鼠的比较研究[J].医学临床研究,2014,31(12): 2329-2331, 2336.[16] Oikonomou D, Kopf S, von Bauer R, et al. Influence of insulin and glargine on outgrowth and number of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in type 2 diabetes patients: a partially double-blind, randomized, three-arm unicenter study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:137.[17] 邓亚萍,赵婷,倪敏,等. eNOS:糖尿病内皮祖细胞功能失调的一个关键因素[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2012,28(7): 901-903.[18] 覃媛,何艳华,张根水,等.激活Sonic hedgehog 通路改善1型糖尿病小鼠内皮祖细胞功能[J].中国药理学通报, 2015,31(8): 1066-1071.[19] 王晓荣. MicroRNA let-7f调节1型糖尿病内皮祖细胞功能的作用和机制研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2011.[20] Patelarou E, Girvalaki C, Brokalaki H, et al. Current evidence on the associations of breastfeeding, infant formula, and cow's milk introduction with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Nutr Rev. 2012;70(9):509-519.[21] Noble JA, Valdes AM. Genetics of the HLA region in the prediction of type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2011;11(6): 533-542.[22] Tang ST, Tang HQ, Zhang Q, et al. Association of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen 4 gene polymorphism with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2012;508 (2):165-187.[23] Hamad AR, Arcara K, Uddin S, et al. The potential of Fas ligand (apoptosis-inducing molecule) as an unconventional therapeutic target in type 1 diabetes. Front Immunol. 2012;3: 196.[24] 李华,王军,崔张新,等.1型糖尿病患者发生肾功能损害的危险因素分析[J].山东医药,2007,47(17):10.[25] 庞烨锋.吡格列酮对1型糖尿病大鼠胰岛素抵抗的改善及机制研究[D].长沙:湖南大学,2013.[26] 周文静.吡格列酮对外周血内皮祖细胞数量与增殖能力的影响[D].杭州:浙江大学,2008.[27] 陈立东,肖敏,张绪国,等.吡格列酮对不稳定型心绞痛合并糖尿病患者内皮祖细胞数量及脂联素水平的影响[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2015,7(1):69-71.[28] Cao Y, Hao Y, Li H, et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis of differentiated mouse podocytes induced by high glucose. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(4):809-816.[29] Palm F, Cederberg J, Hansell P, et al. Reactive oxygen species cause diabetes-induced decrease in renal oxygen tension. Diabetologia. 2003;46(8):1153-1160.[30] Gilbert RE, Zhang Y, Yuen DA. Cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy: is the future, now. Semin Nephrol. 2012;32(5): 486-493.[31] Arya A, Yadav HN, Sharma PL. Involvement of vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase in development of experimental diabetic nephropathy in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;354(1-2):57-66.[32] Ibegbulem C,Chikezie P. Levels of Acute Blood Indices Disarrangement and Organ Weights of Wistar Rats Fed with Flavour Enhancer-and Contraceptive-Containing Diets. Journal of Investigational Biochemistry. 2016;5(1):1-9.[33] Bi B, Schmitt R, Israilova M, et al. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(9):2486-2496.[34] Zhang Y, Yuen DA, Advani A, et al. Early-outgrowth bone marrow cells attenuate renal injury and dysfunction via an antioxidant effect in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(8):2114-2125.[35] Yuen DA, Connelly KA, Advani A, et al. Culture-modified bone marrow cells attenuate cardiac and renal injury in a chronic kidney disease rat model via a novel antifibrotic mechanism. PLoS One. 2010;5(3):e9543.[36] Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu W, et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(2):34.[37] An S, Zang X, Yuan W, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) may play a protective role against rats ischemia/reperfusion renal injury via inhibiting tubular epithelial cell apoptosis. Ren Fail. 2013;35(1):143-149.[38] Redondo S, Hristov M, Gümbel D, et al. Biphasic effect of pioglitazone on isolated human endothelial progenitor cells: involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and transforming growth factor-beta1. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(6):979-987.[39] Sorrentino SA, Bahlmann FH, Besler C, et al. Oxidant stress impairs in vivo reendothelialization capacity of endothelial progenitor cells from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: restoration by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist rosiglitazone. Circulation. 2007; 116(2):163-173. |