Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (50): 7557-7564.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.50.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on behavior and transplanted neural stem cells in rats with chronic stress depression
Mi Kun1, Guo Qiang2, Sang Wen-hua1, Wang Hai-bo2, Li Le3
- 1Department of Affective Disorder, Sixth People’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
3Baoding First Central Hospital, Boading 071028, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-09-28Online:2016-12-02Published:2016-12-02 -
Contact:Guo Qiang, Attending physician, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Mi Kun, Attending physician, Department of Affective Disorder, Sixth People’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mi Kun, Guo Qiang, Sang Wen-hua, Wang Hai-bo, Li Le. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on behavior and transplanted neural stem cells in rats with chronic stress depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(50): 7557-7564.
share this article
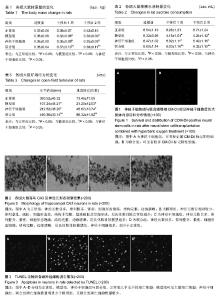
2.1 实验动物数量分析 造模成功的45只SD大鼠均进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠行为学改变 体质量变化:造模前,4组大鼠体质量比较差异无显著性意义。给予外源性干预后,4组大鼠体质量变化比较差异有显著性意义(F=5.05,P < 0.05)。与正常组相比,模型组大鼠体质量下降(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,神经干细胞组、联合组大鼠体质量显著升高(P < 0.01);联合组体质量高于神经干细胞组(P < 0.05),见表1。 蔗糖水消耗量的变化:造模前,4组蔗糖水消耗量比较差异无显著性意义。给予不同的干预后,4组间蔗糖水消耗量比较差异有显著性意义(F=11.82,P < 0.01)。与正常组相比,模型组蔗糖水消耗量降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,神经干细胞组、联合组蔗糖水消耗量显著增高(P < 0.01);联合组蔗糖水消耗量高于神经干细胞组(P < 0.05),见表2。 旷场实验评分:造模前,4组水平运动次数和垂直运动距离比较差异均无显著性意义。给予外源性干预后,4组大鼠水平运动次数和垂直运动距离比较差异均有显著性意义(F水平=13.59,F垂直=67.67,P < 0.01)。与正常组相比,模型组大鼠各项行为学水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,神经干细胞组、联合组各项行为学水平显著增高(P < 0.05);联合组各项行为学水平高于神经干细胞组(P < 0.05),见表3。 2.3 CM-Dil标记神经干细胞的存活和分布情况 用CM-Dil进行标记后,在荧光显微镜观察神经干细胞发出红色荧光。与模型组相比,神经干细胞组海马CA3区可见CM-Dil阳性细胞,联合组可见较多CM-Dil阳性细胞,见图1,两组间阳性细胞数量比较差异有显著性意义(17.29±4.01,33.64±5.17,P < 0.01)。 2.4 尼氏染色法检测大鼠海马神经元的大小、形态和数目变化 尼氏染色中,尼氏体受染后呈块状或颗粒状,核周围尼氏体颗粒较大,近边缘处较小而细长;生理情况下,尼氏体大而数量多;神经元受损时,尼氏体的数量可减少或消失。图2显示了4组大鼠海马CA3区尼氏染色图,通过比较可以看出正常组CA3区神经元数目多,排列整齐、紧密,细胞形态饱满,结构完整,边缘清晰,尼氏体数目较模型组多;模型组CA3区神经元数目相对较少,排列紊乱、疏松,细胞形态差,结构不完整,基质疏松及空泡形成,尼氏体数目减少;神经干细胞组及联合组CA3区神经元数目多,排列整齐、紧密,细胞形态饱满,结构完整,边缘清晰,尼氏体数目较模型组多;联合组CA3区神经元数目较神经干细胞组多,但少于正常组。 2.5 TUNEL法测定神经细胞凋亡情况 TUNEL阳性信号为绿色荧光,位于胞核。正常组中,几乎见不到TUNEL阳性细胞,细胞凋亡率为(3.52±1.08)%;模型组能见到更多TUNEL阳性细胞,细胞凋亡率为(61.7± 2.21)%;神经干细胞组、联合组细胞凋亡率明显降低,分别为(49.23±3.28)%、(19.56±3.31)%,且两组间细胞凋亡率比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。"

| [1] Henderson SE,Johnson AR,Vallejo AI,et al.A preliminary study of white matter in adolescent depression: relationships with illness sever Ity,anhedonia, and irritability.Front Psychiatry. 2013; 4(152):1-10.[2] Ouyang X,Tao HJ,Liu HH,et al.White matter integrity deficit in treatment-naive adult patients with major depressive disorder.East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2011;21(1):5-9.[3] Colloby SJ,Firbank MJ,Thomas AJ,et al.White matter changes in late-life depression:A diffusion tensor imaging study.J Affect Disord.2011;135(1-3):216-220.[4] Yang P,Gao ZY,Zhang HD,et al.Changes in proinflammatory cyto-kines and white matter in chronically stressed rats.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:597-607.[5] Judd LL,Schettler PJ,Coryell W,et al.Overt irritability/anger in unipolar major depressive episodes:past and current char-acteristics and implications for long- term course.JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(11):1171-1180.[6] Saveanu RV,Nemereff CB.Etiology of depression:genetic and environmental factors. Psychiatr Clin Noah Am.2012;35(1):51-71.[7] Teng HK,Teng KK,Lee R,et al.ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci. 2005; 25(22):5455-5463. [8] Krishnan V,Nestler EJ.The molecular neurobiology of depression.Nature.2008; 455(7215):894-902. [9] Duman RS,Voleti B.Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents.Trends Neurosci. 2012;35(10):47-56. [10] Yu H,Wang DD,Wang Y,et al.Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism alters vulnerability to stress and response to antidepressants. J Neurosci.2012;32(12):4092-4101.[11] McEwen BS.Glucocorticoids,depression,and mood disorders:structural remodeling in the brain. Metabolism.2005;54(5 Suppl 1):20-23.[12] Drevets WC,Price C,Furey ML.Brain structural and functional ab-normalities in mood disorders: implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Brain Struct Funct. 2008;213(1-2):93-118.[13] Fournier NM,Duman RS.Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in adult hippocampal neurogenesis: implications for the pathophysiology and treatment of depression.Behav Brain Res.2012; 227(2):440-449.[14] Malberg JE,Schechter LE.Increasing hippocampal neurogenesis: a novel mechanism for antidepressant drugs.Curr Pharm Des.2005;11(2):145-155. [15] Zheng H,Ma GY,Xu CT,et al. Phenytoin reverse the chronic stress-induced impariment of memory consolidation for water maze training and depression of LTP in rat hippocampal CA1 region,but does not affect motor activity.Brain Res Cogn Brain Res.2005; 24(3):380-385. [16] Reddy PH,Beal MF.Amyloid beta,mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage:implications for cognitive decline in aging and Al• zheimer’s disease.Trends M01 Med.2008;14(2):45-53.[17] Toni N,Teng EM,Bushong EA,et al.Synapse formation on neurons born in the adult hippocampus. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(6):727-734.[18] Jindal A,Mahesh R,Bhatt S.Etazolate rescues behavioral deficits in chronic unpredictable mild stress model: modulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and brain•-derived neurotrophic factor level.Neurochem Int.2013; 63(5):465-475.[19] 付燕燕,宋远见,杨宜华,等.芒果苷对慢性应激抑郁小鼠行为及海马脑源性神经营养因子表达的影响[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2013,22(10):883-885.[20] 王国栋,董娇,李晏,等.慢性应激抑郁模型大鼠海马组织SIOOB表达及氟西汀的干预作用[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2013,22(11):978-981.[21] 余鸽鸽,王艺明.艾司西酞普兰对抑郁模型大鼠海马胶质细胞源性神经营养因子及细胞凋亡相关因子表达的影响[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2013,22(8):688 -691.[22] 王玉婷,丁虹,邱春玉,等.山腊梅叶醇提物对慢性应激抑郁模型小鼠行为学及脑内单胺类神经递质的影响[J].中成药,2015,37(5):1087-1090.[23] Cox BM,Alsawah F,McNeill PC,et al.Neurochemical, hormonal, and behavioral effects of chronic unpredictable stress in the rat.Behav Brain Res. 2011; 220(1):106-111. [24] Valente KD,Busatto Filho G.Depression and temporal lobe epilepsy represent an epiphenomenon sharing similar neural networks: clinical and brain structural evidences.Arq Neuropsiquiatr.2013;71(3):183-190. [25] Frazer A,Morilak DA.What should animal models of depression model.Neurosi Biobehav Rev.2005; 29(4-5):515-523.[26] Sullivan PF,Neale MC,Kendler KS.Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review andmeta analysis.Am J Psychiatry.2000;157(10):1552-1562.[27] Gao F,Wang S,Guo Y,et al.Protective effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in a rat model of transient cerebral ischaemia: A microPET study.Eur J Nuclear Med Molecular Imaging.2010; 37(5):954-961.[28] 李功迎,曹龙飞.精神障碍诊断与统计手册第5版解读[J].中华诊断学电子杂志,2014,2(4):310-312. [29] 张磊,章军建.丰富环境对慢性应激大鼠抑郁样行为的影响[J].中华行为学学与脑科学杂志,2011,20(11):970-972.[30] You ZL,Luo CM,Zhang WZ,et al.Pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines expression in rat’s brain and spleen exposed to chronic mild stress:Involvement in depression.Behav Brain Res.2011;225(1):135-141. [31] Hannestad J,DellaGioia N,Bloch M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on senlm levels of inflammatory eytokines:a meta analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology.2011;36(12):2452-2459.[32] Hemanth Kumar BS,Mishra SK,Trivedi R,et al. Demyelinating evidences in CMS rat model of depression:a DTI study at 7T. Neuroscience. 2014; 275:12-21.[33] Kemmotsu N,Kucukboyaci NE,Cheng CE,et al. Alterations in functional connectivity between the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex as a correlate of depressive symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav.2013;29(3):552-559.[34] 王国栋,董娇,王长虹,等.慢性应急大学抑郁模模型大鼠海马组织SIOOB表达及氟西汀的干预作用[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2013,22(11):978-981.[35] 季建林.抗抑郁药物治疗的起效与疗效评价[J].世界临床医药,2012,33(7):385-387.[36] Green DR.Apoptotic pathways:ten minutes to dead. Cell. 2005;121(5):671-674. [37] Kempton MJ,Salvador Z,Munafo MR,et al.Structural neuroimaging studies in major depressive disorder with bipolar disorder.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(7): 675-680 [38] Schermuly I,Wolf D,Lieb K,et al.State dependent posterior hippocampal volume increases in patients with major depressive disorder.J Affect Disord.2011; 135(1-3):405-409. [39] Lucassen PJ,Meerlo P,Naylor AS, et al.Regulation of adult neurogenesis by stress, sleep disruption, exercise and inflammation: lmplications for depression and antidepressant action.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;20(1):1-17.[40] ucassen PJ,Pruessner J,Sousa N,et al. Neuropathology of stress.Acta Neuropathol. 2014; 127(1):109-135.[41] Moreines JL,Owrutsky ZL,Grace AA.Involvement of Infralimbic Prefrontal Cortex but Not Lateral Habenula in Dopamine Attenuation after Chronic Mild Stress.Neuropsychopharmacology.2016.doi:10.1038/npp.2016.249.[Epub ahead of print][42] Ghosal S,Hare B,Duman RS.Prefrontal Cortex GABAergic Deficits and Circuit Dysfunction in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Chronic Stress and Depression.Curr Opin Behav Sci.2017;14:1-8.[43] Ghosal S,Packard AE,Mahbod P,et al.Disruption of glucagon-like peptide 1 signaling in Sim1 neurons reduces physiological and behavioral reactivity to acute and chronic stress.J Neurosci.2016 pii:1104-16. [Epub ahead of print][44] Lomazzo E,König F,Abassi L,et al.Chronic stress leads to epigenetic dysregulation in the neuropeptide-Y and cannabinoid CB1 receptor genes in the mouse cingulate cortex.Neuropharmacology.2016;113(Pt A): 301-313.[45] Zhou L,Chen P,Peng Y,et al.Role of Oxidative Stress in the Neurocognitive Dysfunction of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome.Oxid Med Cell Longev.2016; 2016: 9626831.[46] Dalvi PS,Chalmers JA,Luo V,et al.High-fat induces acute and chronic inflammation in the hypothalamus: Effect of HFD, palmitate and TNF-α on appetite-regulating NPY neurons.Int J Obes (Lond).2016.doi: 10.1038/ijo.2016.183.[Epub ahead of print][47] Luo Y,Kuang S,Xue L,et al.The mechanism of 5-lipoxygenase in the impairment of learning and memory in rats subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress.Physiol Behav. 2016;167:145-153.[48] Kiss A,Majercikova Z.Repeated asenapine treatment does not participate in the mild stress induced FosB/ΔFosB expression in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons.Neuropeptides.2016. pii: S0143-4179(16)30088-9. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2016.10.003. [Epub ahead of print][49] Li J,Li HX,Shou XJ,et al.Effects of chronic restraint stress on social behaviors and the number of hypothalamic oxytocin neurons in male rats.Neuropeptides. 2016 Sep 30. pii: S0143-4179(16)30015-4.doi:10.1016/j.npep.2016.08.011.[Epub ahead of print] |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||