Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (23): 3457-3463.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.23.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, identification and transplantation combined with chemotherapy for lung cancer in mice
Zheng Tian-liang1, Zhao Song1, Guo Hai-zhou1, Cui Guang-hui1, Lin Da-wei2
- 1First Department of Thoracic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
2Medical College of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2016-05-05Online:2016-06-03Published:2016-06-03 -
Contact:Zheng Tian-liang, First Department of Thoracic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zheng Tian-liang, M.D., Attending physician, First Department of Thoracic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82541044
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Tian-liang, Zhao Song, Guo Hai-zhou, Cui Guang-hui, Lin Da-wei. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, identification and transplantation combined with chemotherapy for lung cancer in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(23): 3457-3463.
share this article
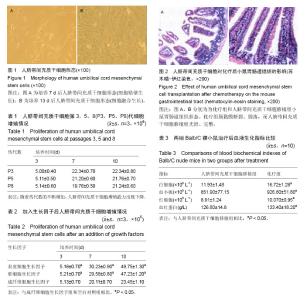
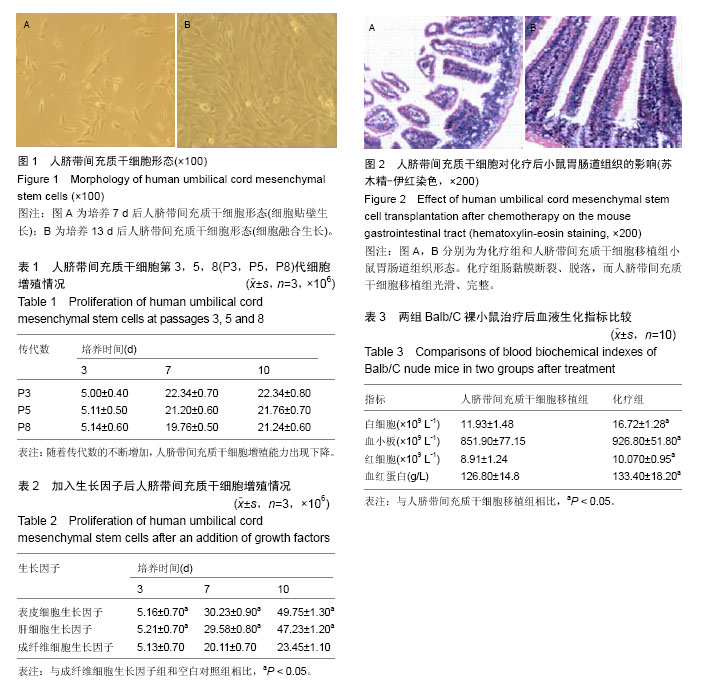
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验中的Balb/C裸小鼠20只全部进行结果分析数量,中途无脱落。 2.2 人脐带间充质干细胞形态:人脐带间充质干细胞培养7 d后细胞开始贴壁生长,到13 d融合80%-90%。在显微镜下细胞呈现长梭形,单核,传代后细胞形态趋于一致,呈现放射或旋涡状排列,见图1。 2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞生长情况 人脐带间充质干细胞第3,5,8代细胞总体呈现上升增殖现象,但是随着代数的不断增加,人脐带间充质干细胞增殖能力出现下降,见表1。 2.4 不同生长因子对人脐带间充质干细胞增殖的影响 人脐带间充质干细胞加入生长因子后,表皮细胞生长因子以及肝细胞生长因子能进一步促进细胞增殖(P < 0.05),而成纤维细胞生长因子和空白对照组的细胞增殖并不明显,见表2。 2.5 人脐带间充质干细胞对Balb/C裸小鼠肺癌生长的影响 在第21天时断颈处死小鼠,剥离腋下瘤体大小及肺癌生长曲线变化均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。化疗组瘤质量为(4.59±1.45) g,人脐带间充质干细胞移植组瘤质量为(4.16±1.13) g,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.6 人脐带间充质干细胞对化疗后小鼠胃肠道的影响 大体观察人脐带间充质干细胞移植组小鼠胃肠道红润、有光泽,而化疗组胃肠道苍白;病例切片苏木精-伊红染色下,化疗组肠黏膜断裂、脱落,而人脐带间充质干细胞移植组光滑、完整,见图2。 2.7 两组Balb/C裸小鼠治疗后血清学指标比较 人脐带间充质干细胞移植组经过化疗后Balb/C裸小鼠治疗后相关血清学指标均显著低于化疗组(P < 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] Tung A, Herrera S, Szafran MJ, et al. Effect of sleep deprivation on righting reflex in the rat is partially reversed by administration of adenosine A1 and A2 receptor antagonists. Anesthesiology. 2005;102: 1158-1164. [2] 唐欣,王岩,易海波,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为心肌细胞的特异性基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(27):4988-4991. [3] 马锡慧,冯凯,石炳毅.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及其研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(32): 6064-6067. [4] Xiong LZ, Zheng Y, Wu BI, et al. Preconditioning with isoflurane produces dose-dependent neuroprotection via activation of adenosinet triphosphate-regulated potassium channels after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Aneath Analg. 2003;96(1):233. [5] Karnieli O, Izhar-Prato Y, Bulvik S, et al. Generation of insulin-producing cells from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by genetic manipulation. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2837-2844. [6] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2011, 1(2):30-33. [7] 王娟,陆琰,何冬梅,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外分离、纯化及鉴定[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版,2009, 30(4):367-372. [8] 程建,袁涛,马勇,等.中医药及骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2012,32(7):1004-1007. [9] Gilpin DA, Weidenbecher MS, Dennis JE. Scaffold-free tissue-engineered cartilage implants for laryngotracheal reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(3):612-617. [10] Cool SM, Kenny B, Wu A, et al. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) composite biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration: in vitro performance assessed by osteoblast proliferation, osteoclast adhesion and resorption, and macrophage proinflammatory response. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;82(3):599-610. [11] 陈恩,祝加学,秦金保,等.人脐带间充质干细胞向血管内皮祖细胞诱导分化的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2009,5(6):310-313. [12] Kim SM, Moon SH, Lee Y, et al. Alternative xeno-free biomaterials derived from human umbilical cord for the self-renewal ex-vivo expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(22):3025-3038. [13] 杜磊.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗小鼠缺血性脑卒中的实验研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2008. [14] Lonne M, Lavrentieva A, Walter JG, et al. Analysis of oxygen-dependent cytokine expression in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;353(1):117-122. [15] 徐卉,田玉科,杨辉,等.丙泊酚反馈靶控输注静脉麻醉与异氟醚吸入麻醉的临床效果比较[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2003, 19(7):387-389. [16] Zhu S, Wildonger J, Barshow S, et al. The bHLH repressor deadpan regulates the self-renewal and specification of drosophila larval neural stem cells independently of notch. PLoS One. 2012,7(10):e46724. [17] 张彦刚,胡大海,张战凤,等.人表皮干细胞改良培养及其组织工程皮肤的构建[J].中国美容医学,2011,20(1):79-82. [18] Meng HB, Gong J, Zhou B, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rat severe acute pancreatitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(12):2703-2712. [19] 王跃春,李业霞,段阿林,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的快速分离、纯化及冻存[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(8): 1658-1661. [20] Wu KH, Tsai C, Wu HP, et al. Human application of ex vivo expanded umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: enhance hematopoiesis after cord blood transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(11):2041-2051. [21] 王阳,曹志强.绿色荧光蛋白转基因小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(37): 5923-5928. [22] 刘寿生,周敦华.间充质干细胞与移植物抗宿主病及移植物抗白血病的关系[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2012,27(1):69-72. [23] 王佃亮,张艳梅,杜娟.间充质干细胞过滤分离器制备人羊膜间充质干细胞的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2012, 32(10):63-66. [24] 李敏敏,邹亚伟,陈福雄.骨髓间充质干细胞与肿瘤耐药[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2011,26(10):792-794. [25] 孙源,吴子征,林红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导内皮细胞与自体骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后的成骨特性[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(33):68-71. [26] Moon HH, Joo MK, Mok H, et al. MSC-based VEGF gene therapy in rat myocardial infarction model using facial amphipathic bile acid-conjugated polyethyleneimine. Biomaterials. 2014;35(5):1744- 1754. [27] Oliveira-Sales EB, Maquigussa E, Semedo P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) prevented the progression of renovascular hypertension, improved renal function and architecture. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11): e78464. [28] 陈骅,施佳,罗良生,等.生物发光示踪技术在胶质瘤研究中的进展[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2014,29(2):107-110. [29] Noisa P, Urrutikoetxea-Uriguen A, Li M, et al. Generation of human embryonic stem cell reporter lines expressing GFP specifically in neural progenitors. Stem Cell Rev. 2010;6(3):438-449. [30] 崔向荣,朱静,田杰,等.STAT3过度表达和激活对骨髓间充质干细胞瘤样转化的作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志, 2013, 26(3):328-331. [31] 王力,徐小红,张宁坤,等.携带标记基因的慢病毒载体转染人脐带华通胶间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].天津医药, 2013,41(10):985-988. [32] 朱磊,李鲲鹏,马捷.VEGF基因转染间充质干细胞移植与单纯间充质干细胞移植对小鼠心肌梗死的疗效对比[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(9):9-11. [33] 管小俊,宋琳,郭雪君,等.携带绿色荧光蛋白基因慢病毒转染的小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的干细胞特性检测[J].诊断学理论与实践,2011,10(6):527-530. [34] 李佳成,郭燕珊,屠美,等.胚胎干细胞条件培养基对人脂肪干细胞增殖及分化能力的影响[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2014,35(2):169-176. [35] 金颖,任晓慧,刘晓帆.胚胎干细胞或诱导性全能干细胞自我更新和分化机制研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2012,32(9):1166-1170. [36] Wood JA, Chung DJ, Park SA, et al. Periocular and intra-articular injection of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: an in vivo imaging and migration study. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 28(3): 307-317. [37] Tanimura A, Nezu A, Morita T. Light microscopy techniques for live cell and animal imaging using fluorescent proteins. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013; 141(5):262-267. [38] 邹松平,王宇,李春雨,等.骨髓间充质干细胞旁分泌对急性心肌梗死心肌的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(23):3653-3659. [39] 樊艳,王建军,魏峰,等.脂肪间充质干细胞移植对心肌梗死后炎症反应及心室重构的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(6):900-905. [40] Hou LL, Gu F, Zhou C. 53P Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation ameliorates chemotherapy- induced bone marrow suppression in lung cancer patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(4 Suppl):S77. [41] Chen JJ, Gao XT, Yang L, et al. Disruption of Notch signaling aggravates irradiation-induced bone marrow injury, which is ameliorated by a soluble Dll1 ligand through Csf2rb2 upregulation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26003. [42] Sun M, Cheng J, Zhang Y, et al. Application value of diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression in monitoring the response to treatment of bone marrow involvement in lymphoma. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. [43] Malek E, de Lima M, Letterio JJ, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: the green light for myeloma immune escape. Blood Rev. 2016. [44] Men HT, Gou HF, Liu JY, et al. Prognostic factors of intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal carcinomatosis of gastric cancer: a retrospective study from a single center. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(5):3501-3507. [45] Zhe N, Chen S, Zhou Z, et al. HIF-1α inhibition by 2-methoxyestradiol induces cell death via activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016. [46] Berretta M, Caraglia M, Martellotta F, et al. Drug-Drug Interactions Based on Pharmacogenetic Profile between Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy and Antiblastic Chemotherapy in Cancer Patients with HIV Infection. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:71. [47] Feng L, Huang Q, Huang Z, et al. Optimized Animal Model of CTX-induced Bone Marrow Suppression. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. [48] Ma RM, Chen CZ, Zhang W, et al. Prognostic Value of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia at the First Cycle in Invasive Breast Cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(13):e3240. [49] Bellayr IH, Marklein RA, Lo Surdo JL, et al. Identification of Predictive Gene Markers for Multipotent Stromal Cell Proliferation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016. [50] Newman NB, Sidhu MK, Baby R, et al. Long-Term Bone Marrow Suppression During Postoperative Chemotherapy in Rectal Cancer Patients After Preoperative Chemoradiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;94(5):1052-1060. [51] Pavyde E, Usas A, Maciulaitis R. Regenerative pharmacology for the treatment of acute kidney injury: Skeletal muscle stem/progenitor cells for renal regeneration? Pharmacol Res. 2016. [52] Han Y, Li S, Holt HK, et al. Curative effect of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy in advanced or recurrent uterine sarcoma. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016;4(2):245-248. [53] Balakrishnan A, Ledford R, Jaglal M. Temozolomide- induced biliary ductopenia: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:33. [54] Araki N, Takahashi S, Sugiura H, et al. Retrospective inter- and intra-patient evaluation of trabectedin after best supportive care for patients with advanced translocation-related sarcoma after failure of standard chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 2016;56:122-130. [55] Wang Q, Ye T, Chen HL, et al. Correlation between intensity modulated radiotherapy and bone marrow suppression in breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(1):75-81. [56] Bi T, Jin F, Wu W, et al. Phase II clinical trial of two different modes of administration of the induction chemotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2015;37(9): 676-681. [57] Song SQ, Wang C, Zhang GN, et al. BEP for high-risk gestational trophoblastic tumor: results from a cohort of 45 patients. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2015;36(6): 726-729. [58] Somintara S, Leardkamolkarn V, Suttiarporn P, et al. Anti-Tumor and Immune Enhancing Activities of Rice Bran Gramisterol on Acute Myelogenous Leukemia. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146869. [59] Landry B, Gül-Uluda? H, Plianwong S, et al. Targeting CXCR4/SDF-1 axis by lipopolymer complexes of siRNA in acute myeloid leukemia. J Control Release. 2016;224:8-21. [60] 高延明,张路.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足过程中血管内皮生长因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(40):7169-7174. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||