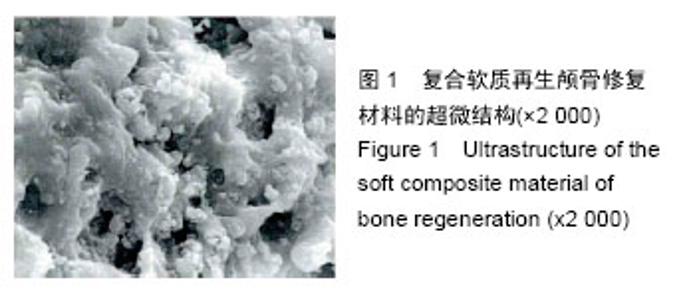
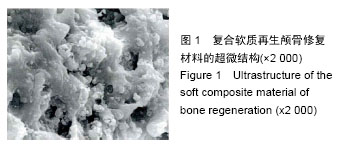
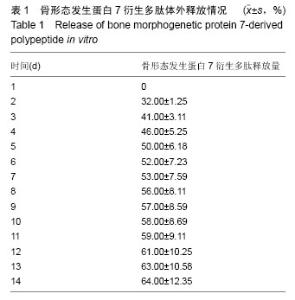
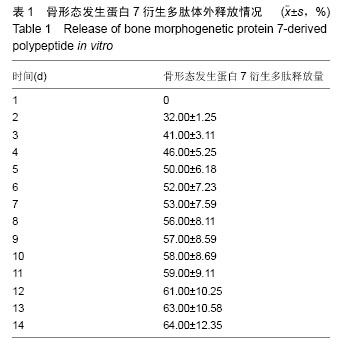
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (25): 3706-3712.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.25.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Soft composite materials for bone regeneration in vitro in skull repair
Zhang Tong-xing, Gao Hua
- Department of Neurosurgery, Jizhou Hospital, Jizhou 053200, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2016-04-17Online:2016-06-17Published:2016-06-17 -
About author:Zhang Tong-xing, Attending physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Jizhou Hospital, Jizhou 053200, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Tong-xing, Gao Hua. Soft composite materials for bone regeneration in vitro in skull repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(25): 3706-3712.
share this article
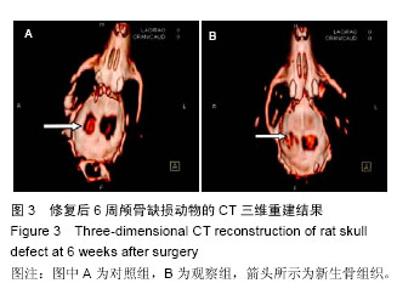
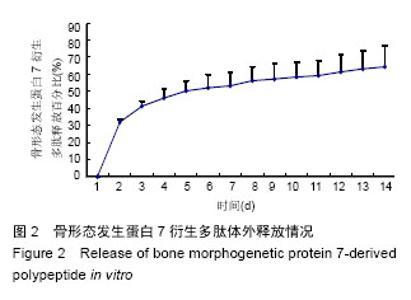
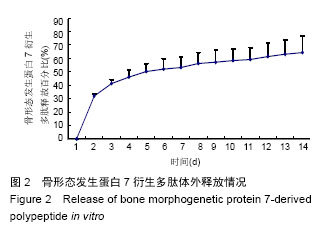
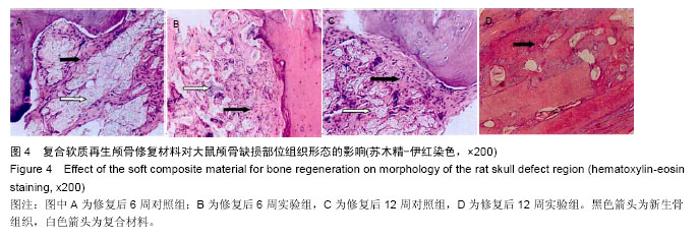
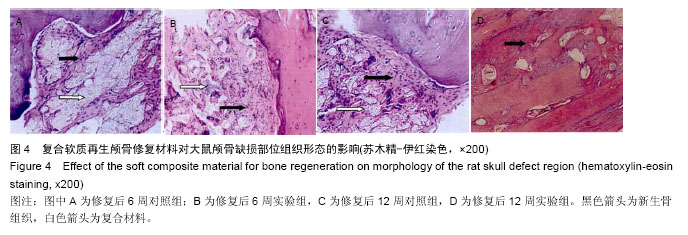
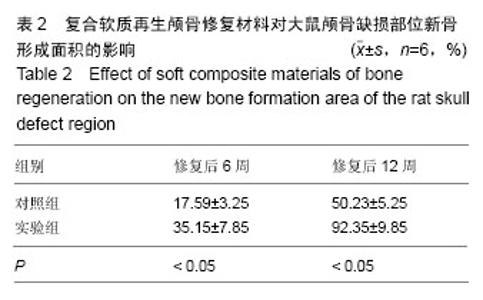
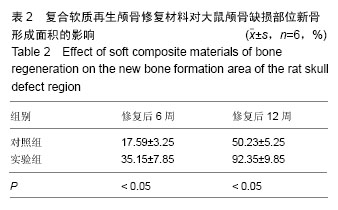
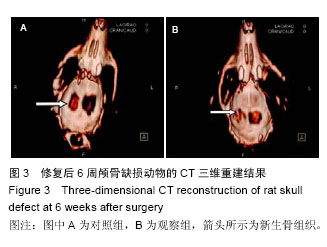
2.3 实验动物数量分析 大鼠颅骨缺损区切口均良好愈合,未出现组织坏死或者感染。纳入的所有大鼠均进入最终的结果分析,未出现中途死亡或者脱落现象。2.4 颅骨缺损动物的CT三维重建和组织变化 修复后6周,CT三维重建可见对照组缺损区存在轻微片状致密影,与正常骨密度相比相对偏低(图3A);实验组缺损区可观察到存在片状高密度影,且密度与正常骨组织十分接近(图3B)。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,对照组材料内部仅有少量成骨细胞长入现象(图4A),实验组材料内部出现大量成骨细胞长入,且部分材料开始发生降解(图4B)。修复后12周,CT三维重建结果可见对照组骨缺损区域的高密度影出现一定的增强情况,面积也出现增大,大约为骨缺损面积的50%;实验组大则可观察到骨缺损区骨缺损完全愈合的情况(图3B)。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,对照组部分材料发生了降解,并存在未成熟编织骨分散分布的情况(图4C)。实验组大部分材料均发生降解,并被成熟板层骨替代,仅存少量编织骨(图4D)。"
| [1] 王冠聪.具有二级三维网络结构的壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石骨组织工程复合支架材料的构建及其生物性能研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012. [2] 郭晓东,王明波,黎维勇,等.BMP2活性肽/PLGA复式微球及仿生支架材料的研制[C]//第九届中国南方骨质疏松论坛暨江西省骨质疏松学术会论文集.2013:198.[3] 李丹.PLGA/羟基磷灰石复合支架的制备及其用于骨修复的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2011.[4] 杨大志,罗惠莉,易伟宏,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2/胶原/掺锶羟基磷灰石材料修复颅骨缺损[J].中华实验外科杂志, 012,29(7):1250-1253. [5] 李均荣.羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸—聚羟乙酸/2型骨形态发生蛋白(HA-PLGA-BMP-2)颅骨修复材料的组织相容性及成骨性研究[D].张家口:河北北方学院,2013.[6] 张艳红.羟基磷灰石/丝素复合支架负载BMP-2的制备及其生物相容性研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2011.[7] Cao N, Dong J, Wang Q, et al. An experimental bone defect healing with hydroxyapatite coating plasma sprayed on carbon/carbon composite implants. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;205(4):1150-1156.[8] Zhu W, Lu W, Zhang XJ, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite/ fibrin glue/recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 artificial bone for repair of bone defect in an animal model. Micro Nano Lett. 2012;7(5):467-471.[9] Dong JL, Li LX, Mu WD, et al. Bone Regeneration with BMP-2 Gene-modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Seeded on Nano-hydroxyapatite/Collagen/ Poly(L-Lactic Acid) Scaffolds. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2010;25(6):547-566.[10] 吴斌.胶原矿化仿生骨联合骨形态发生蛋白2相关多肽促进骨再生的实验研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2009.[11] 赵峰,尹玉姬,姚康德,等.壳聚糖-明胶网络/羟基磷灰石复合材料支架的研究--成骨细胞培养[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(2):130-133.[12] 杨为中,周大利,尹光福,等.BMP/α-磷酸三钙生物活性骨水泥的BMP释放动力学及成骨性能研究[J].无机材料学报,2004,19(6):1359-1366.[13] 熊莹帆,邱建华,楚胜华,等.不同颅骨成型材料的选择及评价[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2011,5(17): 5119-5121.[14] Nitzsche H, Lochmann A, Metz H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of a biomimetic composite scaffold for bone defect repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(1):298-307.[15] Jung UW, Song KY, Kim CS, et al. Effects of a chitosan membrane coated with polylactic and polyglycolic acid on bone regeneration in a rat calvarial defect. Biomed Mater. 2007;2(3):S101-105.[16] Zhang X, Zhu L, Lv H, et al. Repair of rabbit femoral condyle bone defects with injectable nanohydroxyapatite/chitosan composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(8):1941-1949.[17] 徐建军,丁华山,瞿鸿义,等.计算机三维重建EH复合型颅骨预制体修复额颞顶大面积颅骨缺损[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2006,11(12):748-749.[18] 章浩伟,周思远,刘颖,等.基于增材制造技术修复缺损颅骨的研究和应用[J].生物医学工程学进展, 2014,35(4): 219-222.[19] Dinarvand P, Seyedjafari E, Shafiee A, et al. New approach to bone tissue engineering: simultaneous application of hydroxyapatite and bioactive glass coated on a poly(L-lactic acid) scaffold. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2011;3(11):4518-4524.[20] Nakasa T, Ishida O, Sunagawa T, et al. Feasibility of prefabricated vascularized bone graft using the combination of FGF-2 and vascular bundle implantation within hydroxyapatite for osteointegration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;85(4):1090-1095.[21] 王新.纳米羟基磷灰石-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的研究[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2007.[22] 杨耀武,毛天球,侯锐,等.鸵鸟骨转化羟基磷灰石支架复合骨膜修复颅骨极限缺损实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2007,23(3):317-320.[23] 徐建军,丁华山,瞿鸿义,等.颅骨成形术三种不同材料的临床分折[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2003,8(1):67-68.[24] 叶迅,赵元立,朱琳等.颅骨修补材料钛金属表面梯度生物活性涂层的生物相容性研究[J].北京医学, 2008,30(1): 8-12.[25] Florczyk SJ, Leung M, Li Z, et al. Evaluation of three-dimensional porous chitosan-alginate scaffolds in rat calvarial defects for bone regeneration applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(10): 2974-2983.[26] 孙春明,崔岗,周岱.EH复合材料人工颅骨的生物力学研究[J].苏州医学院学报,1999,19(9):969-970.[27] 唐晓军.天然羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料生物学特性的实验研究[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2006.[28] 施恒军,曹胜武.医用树脂和羟基磷灰石复合材料在修补大面积颅骨缺损中的应用体会(附42例报告)[J].实用临床医药杂志,2011,15(19):153-154.[29] Bi L, Jung S, Day D, et al. Evaluation of bone regeneration, angiogenesis, and hydroxyapatite conversion in critical-sized rat calvarial defects implanted with bioactive glass scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(12):3267-3275.[30] 田轶.颗粒状羟基磷灰石与纤维蛋白凝胶复合人工骨的可塑性和生物相容性的实验研究[D].大连:大连医科大学, 2007.[31] Ma X, Wang Y, Guo H, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite/ chitosan sponge-like biocomposite for repairing of rat calvarial critical-sized bone defect. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2011;26(4): 335-346.[32] Wang YY, Shi R, Gong P, et al. Bioelectric effect of a chitosan bioelectret membrane on bone regeneration in rabbit cranial defects. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2012; 27(2):122-132.[33] 傅德皓.骨形态发生蛋白-2诱导成骨过程中血管内皮生长因子的表达及意义[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2006.[34] Datta P, Ghosh P, Ghosh K, et al. In vitro ALP and osteocalcin gene expression analysis and in vivo biocompatibility of N-methylene phosphonic chitosan nanofibers for bone regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(5):870-879.[35] Cui ZW, Wright LD, Guzzo R, et al. Poly(D-lactide)/ poly(caprolactone) nanofiber thermogelling chitosan gel composite scaffolds for osteochondral tissue regeneration in a rat model. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2013;28(2):115-125.[36] Fricain JC, Schlaubitz S, Le Visage C, et al. A nano-hydroxyapatite--pullulan/dextran polysaccharide composite macroporous material for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2013;34(12):2947-2959. [37] Lü YM, Cheng LM, Pei GX, et al. Experimental study of repairing femoral bone defects with nHA/RHLC/PLA scaffold composite with endothelial cells and osteoblasts in canines. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;93(17):1335-1340. [38] Oliveira JM, Rodrigues MT, Silva SS, et al. Novel hydroxyapatite/chitosan bilayered scaffold for osteochondral tissue-engineering applications: Scaffold design and its performance when seeded with goat bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2006; 27(36):6123-6137. [39] Kim SS, Sun Park M, Jeon O, et al. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(8):1399-1409. [40] Laschke MW, Strohe A, Menger MD, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel nanosize hydroxyapatite particles/poly(ester-urethane) composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(6):2020-2027. [41] Xue D, Zheng Q, Zong C, et al. Osteochondral repair using porous poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/ nano-hydroxyapatite hybrid scaffolds with undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(1):259-270. [42] Zhang W, Walboomers XF, van Osch GJ, et al. Hard tissue formation in a porous HA/TCP ceramic scaffold loaded with stromal cells derived from dental pulp and bone marrow. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(2):285-294.[43] 车向新.诱导型人工骨材料修复兔颅骨缺损的实验研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2008.[44] 胡鹏.犬甲状软骨缺损应用骨形态发生蛋白材料修复的实验研究[D].昆明:昆明医学院,2001. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||