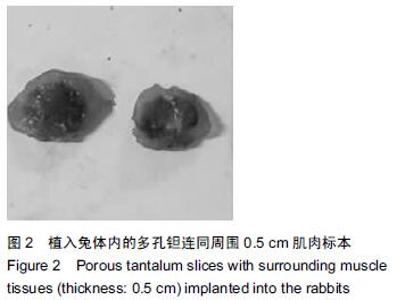
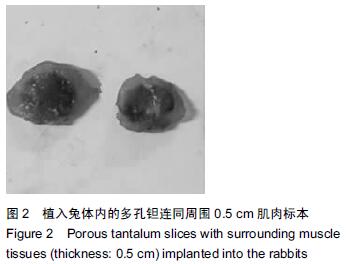
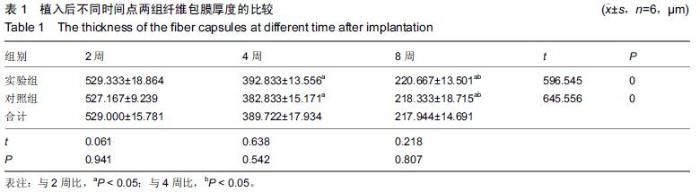
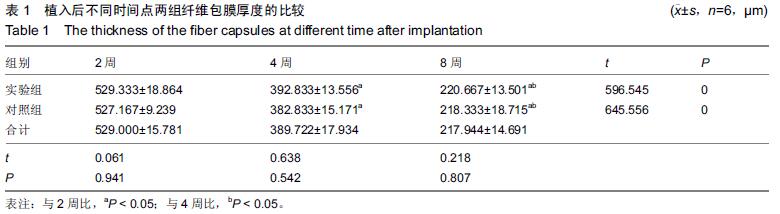
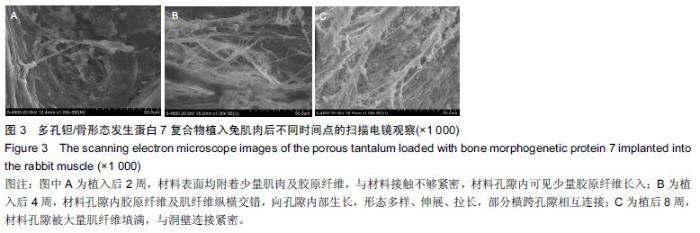
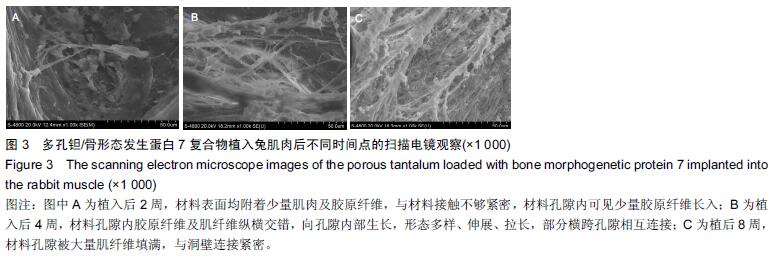
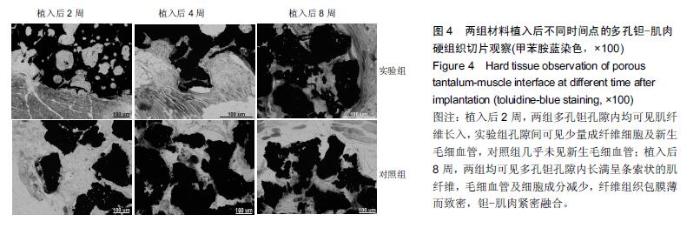
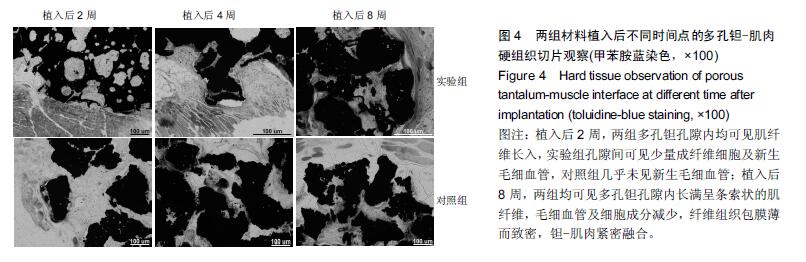
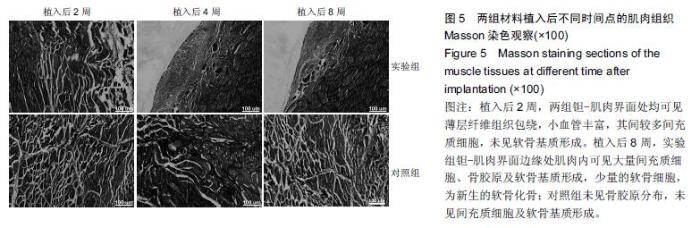
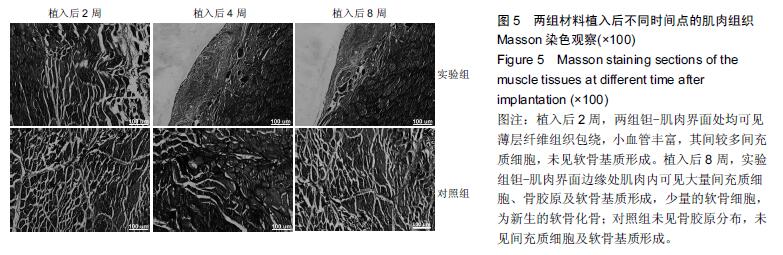
| [1] Bobyn JD,Stackpool GH,Hacking SA,et al. Characteristics of bone ingrowth and interface mechanics of a new porous tantalum biomatcrial.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999;81(5):907-914. [2] Periasamy K,Watson WS,Mohammed A,et al.A randomised study of peri-prosthetic bone density after cemented versus trabecular fixation of a polyethylene acetabular component.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011; 93(8):1033-1044. [3] Amanatullah DF,Farac R,McDonald TJ,et al. Subtrochanteric Fracture following Removal of a Porous Tantalum Implant.Case Rep Orthop.2013;2013: 946745. [4] Sinclair SK,Konz GJ,Dawson JM,et al.Host bone response to polyetheretherketone versus porous tantalum implants for cervicalspinal fusion in a goat model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2012;37(10):E571-580. [5] 武垚森,池永龙.小梁金属(多孔钽)在骨科的应用现状[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(12): 939-941. [6] 倪滨,李明.BMP生物活性的研究现状[J].重庆医学, 2007, 36(10):970-973. [7] Gillogly SD.Treatment of large full-thickness chondral defects of the knee with autologous chondrocyte implantation.Arthroscopy.2003;19(Suppl 1):147-153. [8] Imai Y,Miyamoto K,An HS,et al.Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 upregulates proteoglycan metabolism of human anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(12): 1303-1309. [9] Chubinskaya S,Kawakami M,Rappoport L,et al. Anti-catabolic effect of OP-1 in chronically compressed intervertebral discs.J Ortho Res. 2007; 25(4):517-530. [10] Mason JM,Breitbart AS,Barcia M,et al.Cartilage and bone regeneration using gene enhanced tissue engineering.Clin Orthop.2000;(379Suppl):S171-S178. [11] 李丹,孔迅,李葚煦,等.骨形态发生蛋白与关节软骨修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2008,12(28):5525-5529. [12] Clokie CM,Urist MR.Bone morphogenetic protein excipients: comparative observation on poloxamer. Plast Reconstr Surg.2000;105(2):628-637. [13] Maccauro G,Iommetti PR,Muratori F,et al.An overview about biomedical applications of micron and nano size tantalum.Recent Pat Biotechnol.2009;3(3):157-165. [14] 甘洪全,刘鑫,李琪佳.医用多孔金属钽材料的基础研究与应用[J].中外医疗,2014,34(14):191-192. [15] 耿丽鑫,李琪佳.多孔钽的生物学特性与关节重建[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(14): 2328-2330. [16] 王茜,张辉,耿丽鑫,等.国产多孔钽复合MG63细胞培养Col-1、OC和OPN蛋白表达及意义[J]. 2015,23(5):441- 449. [17] Henricson A,Rösmark D,Nilsson KG.Trabecular metal tibia still stable at 5 years: an RSA study of 36 patients aged less than 60 years.Acta Orthop. 2013;84(4): 398-405. [18] Sandiford NA,Skinner JA,Muirhead-Allwood SK.Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with a Tapered Trabecular Metal™ Coated Femoral Component: Experience with a Minimum 24-Month Follow-up.Surg Technol Int.2013;23:239-242. [19] 赵阳,李亮,王志强.多孔钽在关节融合中的历史与前景[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014,3(5):370-373. [20] 柴雷子,丁亮,薛锋.多孔钽棒治疗早期股骨头坏死的文献回顾[J].医学综述,2014,20(4):714-716. [21] 张宇,张永兴,赵庆华.多孔钽金属在临床骨关节修复中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2015, 36(1):36-39. [22] 李亮,赵阳,王志强.多孔金属钽髋臼在全髋关节置换术后髋臼翻修中的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2013,2(8): 470-473. [23] 孙新君,王正国,朱佩芳,等.脱细胞骨基质材料的特性及生物安全性观察[J].中华创伤杂志,2005,21(11):833-837. [24] Hacking SA,Bobyn JD,Toh K,et al.Fibrous tissue ingrowth and at tachment to porous tantalum.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;52(4):631-638. [25] Yuan H,Kurashina K,de Bruijn JD,et al.A preliminary study on oste- oinduction of two kinds of calcium phosphate ceramics.Biomaterials. 1999;20(19): 1799-1806. [26] Wang Q,Zhang H,Li Q,et al.Biocompatibility and osteogenic properties of porous tantalum.Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(3):780-786. [27] 王茜,张辉,耿丽鑫,等.MG63 细胞与国产多孔钽材料共培养后成骨相关因子的表达研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(11):1393-1398. [28] 李琪佳,王茜,甘洪全,等.多孔钽材料细胞毒性、生物相容性及体内成骨性研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2014,34(9): 954-961. [29] Ekelund A,Brosjo O,Nilsson OS.Experimental induction of heterotopic bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;263(2):102-112. [30] Goebel EA,Walsh JC.Heterotopic Bone in the Distal Esophagus.Int J Surg Pathol. 2016. pii: 1066896916632299.[Epub ahead of print] No abstract available. [31] Chryssikos T,Crandall KM,Sansur CA.Imaging symptomatic bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced heterotopic bone formation within the spinal canal: case report.J Neurosurg Spine.2016:1-5.[Epub ahead of print] [32] Kraft CT,Agarwal S,Ranganathan K,et al.Trauma-induced heterotopic bone formation and the role of the immune system: A review.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016;80(1):156-165. [33] Qiao C,Zhang K,Sun B,et al.Sustained release poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres of bone morphogenetic protein 2 plasmid/calcium phosphate to promote in vitro bone formation and in vivo ectopic osteogenesis.Am J Transl Res.2015;7(12):2561-2572. [34] Zhang X,Guo J,Wu G,et al.Effects of heterodimeric bone morphogenetic protein-2/7 on osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells.Cell Prolif.2015; 48(6):650-660. [35] He Y,Dong Y,Cui F,et al.Ectopic osteogenesis and scaffold biodegradation of nano-hydroxyapatite- chitosan in a rat model.PLoS One.2015;10(8): e0135366. [36] Cvetkovi? VJ,Najdanovi? JG,Vukeli?-Nikoli? M?,et al. Osteogenic potential of in vitro osteo-induced adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma in an ectopic model.Int Orthop.2015;39(11):2173-2180. [37] Simon Z,Deporter DA,Pilliar RM,et al.Heterotopic bone formation around sint- ered porous-surfaced Ti-6Al-4V implants coated with native bonemorphogenetic proteins. Implant Dent.2006;15(3):265-274. |