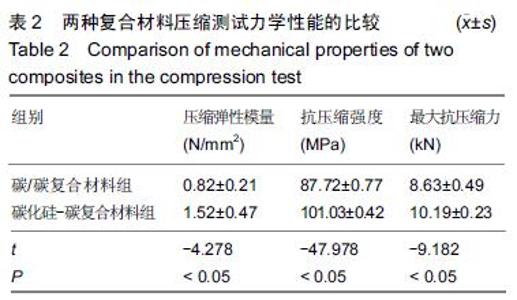
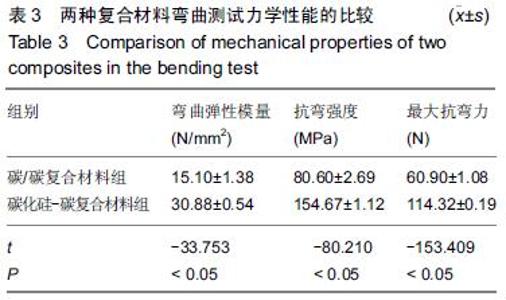
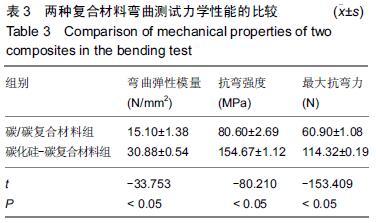
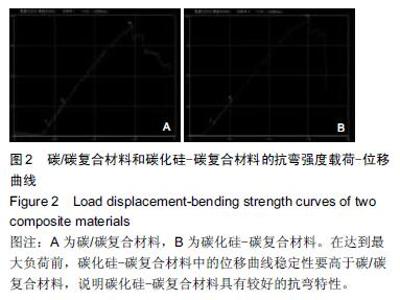
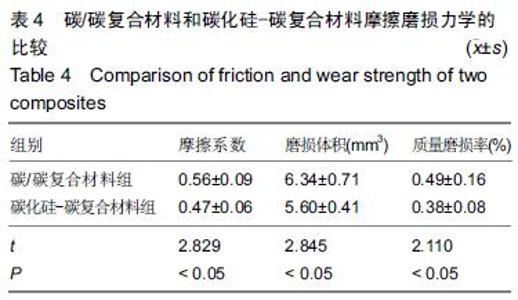
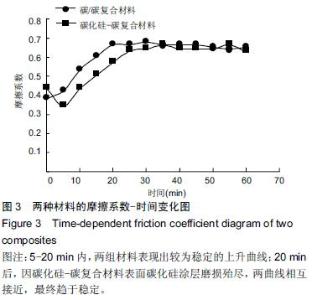
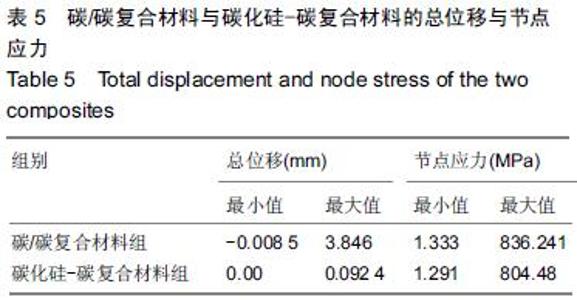
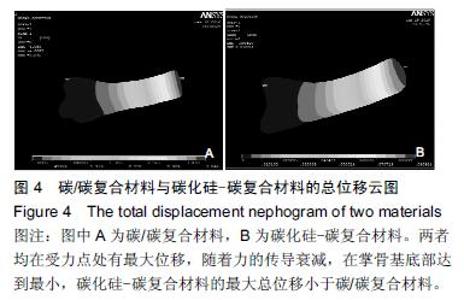
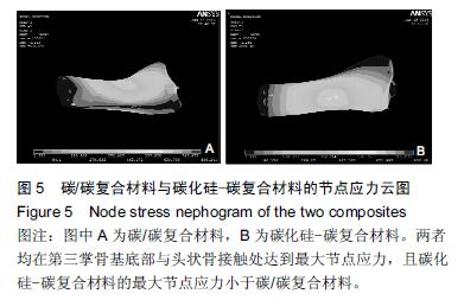
| [1] 王伟,刘迎曦,周礼荣.手部掌指关节损伤的手术方式及其疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2006,21(8):653-654. [2] 付海燕,陈逊文,高峻青.手部骨关节缺损关节重建治疗的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(20): 3939-3942. [3] 林浩东,方有生,陈德松.人工关节置换术治疗手部关节损伤[J].实用骨科杂志,2006,12(4): 293-295. [4] 李贺军,薛晖,付前刚,等.C/C复合材料高温抗氧化涂层的研究现状与展望[J].无机材料学报,2010,25(4):337-343. [5] 陈洁,熊翔,肖鹏.高导热C/C复合材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2006,20(s2):431-435. [6] 卢雪峰.原位生长纳米纤维改性C/C复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[D].中南大学, 2012. [7] 王雅雷.C/C复合材料HfC抗烧蚀涂层的制备, 结构及性能研究[D].中南大学,2012. [8] 余惠琴,陈长乐.C/C-SiC复合材料的制备与性能[J].宇航材料工艺,2001,31(2):28-32. [9] 张智,郝志彪,闫联生.C/C-SiC复合材料制备方法及应用现状[J].炭素,2008,27(2):29-35. [10] 樊志强,徐永清,李晶,等.正常腕关节运动时腕中关节运动学在体研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(1):5-8. [11] 贾雪峰,戴月.掌骨骨折损伤程度及法医学鉴定[J].中国法医学杂志,2001,16(3): 152-153. [12] 张晓南,徐瑞泽,吴刚,等.不同生物材料假体在人工关节置换中的应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(47): 8869-8874. [13] Ziaee H,Daniel J,Datta A,et al.Transplacental transfer of cobalt and chromium in patients with metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty A CONTROLLED STUDY. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2007;89(3):301-305. [14] Dunstan E,Sanghrajka A,Tilley S,et al.Metal ion levels after metal-on-metal proximal femoral replacements A 30-YEAR FOLLOW-UP.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(5): 628-631. [15] 郭欢,翁正阳,刘想梅,等.钛合金骨植入体表面改性进展[J].中国科技论文在线,2012, 11(6):1-12. [16] Ku Y,Chung CP,Jang JH.The effect of the surface modification of titanium using a recombinant fragment of fibronectin and vitronectin on cell behavior. Biomaterials.2005;26(25):5153-5157. [17] Del Bravo V,Graci C,Spinelli M,et al.Histological and ultrastructural reaction to different materials for orthopaedic application.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.2011;24(1 suppl2):91-94. [18] 王晓庆,朱振安,薛秀君.聚乙烯颗粒诱导假体周围骨溶解中TNF-α变化的实验研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2004,1(4):14-l6. [19] Nagao T,Pamies-Teixeira J,Suh N.Behavior of medium carbon steel under combined fatigue and wear.Wear. 1977;44(1):101-108. [20] Sharma S,Lakkad S.Effect of CNTs growth on carbon fibers on the tensile strength of CNTs grown carbon fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites.Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manufac.2011;42(1):8-15. [21] Cao N,Dong J,Wang Q,et al.Plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on carbon/carbon composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and related tests in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;92(3):1019-1027. [22] Xiong XB,Zeng XR,Zou CL,et al.Strong bonding strength between HA and (NH4)2S2O8-treated carbon/carbon composite by hydrothermal treatment and induction heating.Acta Biomater. 2009;5(5): 1785-1790. [23] Cao S,Li H,Li K,et al.In vitro mineralization of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells on collagen/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds coated carbon/carbon composites.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(2):533-543. [24] Miaoling L, Lehua Q, Hejun L.An imaging technique using rotational polarization microscopy for the microstructure analysis of carbon/carbon composites.Microsc Res Tech.2012;75(1):65-73. [25] Li Y,Qi L,Song Y,et al.Quantitative characterization of carbon/carbon composites matrix texture based on image analysis using polarized light microscope. Microsc Res Tech.2015;78(10):908-917. [26] Wang GH,Yu S,Zhu SH,et al.Biological properties of carbon/carbon implant composites with unique manufacturing processes.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(12):2487-2492. |