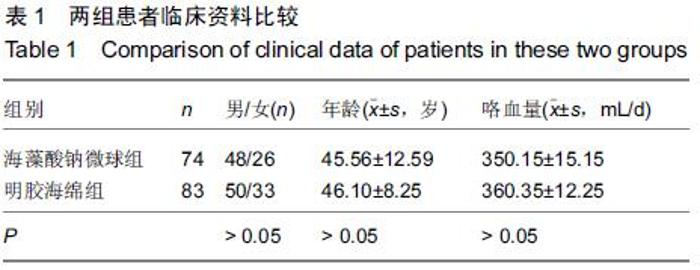
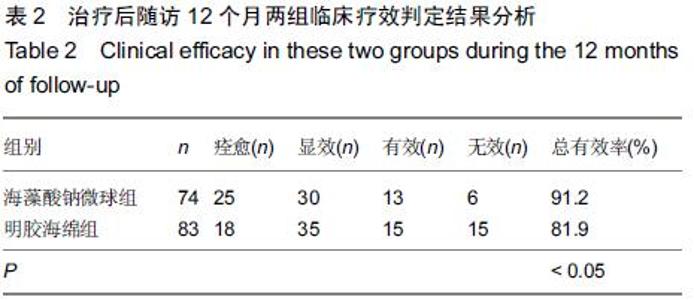
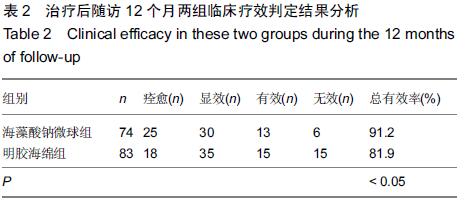
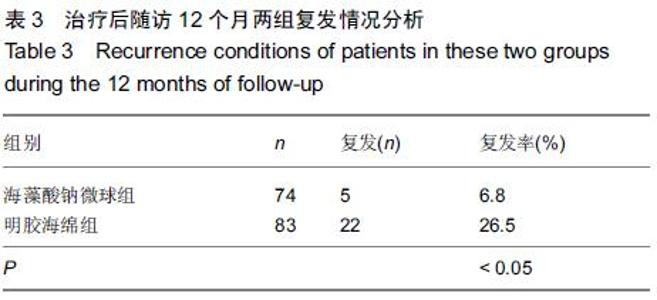
[1] 黄沁,田媛,敖国昆,等.海藻酸钠微球与明胶海绵栓塞肺结核大咯血的效果比较:143例分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(42):7959-7962.
[2] 祖庆泉,施海彬,杨正强,等.永久性颗粒栓塞治疗大咯血[J].介入放射学杂志,2011,20(2):108-111.
[3] 汪立明,王子彬.海藻酸钠微球支气管动脉栓塞治疗肺结核急性大咯血[C].//2007年全国医学影像(昆明)学术研讨会论文集, 2007:26-27.
[4] 张广宇,杨楠,敖国昆,等.海藻酸钠微球栓塞在甲状颈干动脉供血所致肺结核咯血中的临床应用[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2011,5(23):6910-6912.
[5] 于世平,徐克,张曦彤,等.肺外体循环动脉栓塞在治疗重症大咯血中的作用[J].中华放射学杂志,2008,42(1):89-92.
[6] 金鑫,施海彬,刘圣,等.采用不同栓塞材料的支气管动脉栓塞术治疗大咯血的疗效分析[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2012,9(3): 179-182.
[7] 温德泉,刘英峰,蔡成仕,等.支气管动脉栓塞术治疗咯血疗效观察[J].实用诊断与治疗杂志,2008,22(4):302-303.
[8] 侯国欣,张慧君,王以发,等.海藻酸钠微球支气管动脉栓塞治疗急性大咯血临床应用[J].河南外科学杂志,2007,13(3):28-29.
[9] 傅文宏,杜先懋,王家祥,等.急性大咯血责任血管来源的DSA分析及临床栓塞治疗[J].临床肺科杂志,2011,16(5):682-683.
[10] 吕朝阳,范菊意.大咯血的介入治疗[J].中国医药导报,2009, 6(11): 137-138.
[11] 江水.超选择性支气管动脉栓塞治疗大咯血的护理[J].基层医学论坛,2009,13(36):1076-1077.
[12] 史俊霞.对我院43例大咯血的介入治疗临床分析[J].中外医疗, 2011,30(8):87-87.
[13] 张玉新.支气管动脉栓塞术治疗大咯血17例分析[J].青岛医药卫生,2009,41(2):99-100.
[14] 布桂林.不同栓塞剂治疗大咯血的对比分析[J].中国现代医药杂志,2009,11(4):101-102.
[15] 陈一平.急性大咯血责任血管来源的DSA及其介入栓塞治疗的临床分析[C].//第十二次全国中西医结合医学影像学术研讨会论文集,2012:1051-1053.
[16] 江森,孙兮文,支文祥,等.应用明胶海绵和聚乙烯醇颗粒动脉栓塞治疗肺咯血疗效及复发原因分析[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志,2005,11(1):58-62.
[17] 李建军,翟仁友,戴定可,等.支气管动脉栓塞术治疗咯血的疗效分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2007,16(1):21-23.
[18] 曾晓华,邱怀明,易翠容,等.非肿瘤性肺咯血栓塞治疗后咯血复发:原因与对策[J].介入放射学杂志,2011,20(1):18-21.
[19] 刘凤永,段峰,王茂强,等.支气管动脉栓塞术治疗支气管扩张大咯血失败原因之一:膈下动脉参与供血[J].介入放射学杂志2008, 17(2):88-91.
[20] 陈平有,余刚,周选民,等.PVA颗粒联合明胶海绵栓塞治疗大咯血54例[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(17):2890-2891.
[21] 刘一之,倪才方,朱晓黎,等.支气管动脉栓塞-灌注法治疗反复咯血的临床研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2000,19(12):794-796.
[22] 张守民,李景英,王国兴,等.支气管动脉栓塞治疗肺结核咯血的疗效及复发原因分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(5):414-417.
[23] 解皓,李海涛,张玉杰,等.肋间支气管动脉栓塞治疗大咯血的疗效分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2008,24(3):359-361.
[24] 胡世兵,须可扬,傅晓明,等.明胶海绵胶浆及颗粒栓塞支气管动脉治疗支气管扩张大咯血19例[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2013,38(6):748-750.
[25] 陈绿娇,陈义雄,陈建业,等.2种材料支气管动脉栓塞治疗大咯血的临床分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2005,21(2):158-160.
[26] 屈国林,郭宝忱,徐晓明,等.超选择性支气管动脉栓塞治疗多发支气管扩张咯血14例[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(22):3563-3565.
[27] 何冰峰,曹振远,陈颖,等.不同栓塞剂治疗支扩大咯血的比较研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2005,14(6):580-581.
[28] 谭志斌,江宏志,朱纯生,等.不同栓塞剂对介入治疗咯血短期疗效的影响[J].临床肺科杂志,2010,15(3):334,339.
[29] 王草叶,王祁,何忠明,等.PVA颗粒联合金属弹簧圈栓塞治疗支气管扩张咯血临床价值分析[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(11): 1699-1702.
[30] 金桂云,梁元,邢丽,等.PVA颗粒超选择栓塞支气管动脉治疗急性大咯血[J].现代生物医学进展,2010,10(15):2924-2925.
[31] Yoon JY,Jeon EY,Lee IJ,et al.Coronary to bronchial artery fistula causing massive hemoptysis in patients with longstanding pulmonary tuberculosis.Korean J Radiol. 2012;13(1):102-106.
[32] Blyth DF,Soni MA,Moran NF.Massive hemoptysis in an immunocompromised pregnant woman with human immunodeficiency virus disease and active pulmonary tuberculosis.Ann Thorac Surg.2007;84(6):2085-2086.
[33] 季松,刘海日,张大忠,等.PVA颗粒和明胶海绵联合栓塞在支气管扩张咯血治疗中的价值探讨[J].医学理论与实践,2012,25(24): 3028-3030.
[34] 孟祥宇,张雪君.明胶海绵(GS)颗粒和聚乙烯醇(PVA)颗粒支气管动脉内栓塞治疗急性大咯血的近期疗效比较[J].继续医学教育,2014,28(4):9-13.
[35] 屈国林,强民,唐晖,等.支气管动脉介入治疗的栓塞剂选择和应用[J].实用诊断与治疗杂志,2007,21(3):164-167.
[36] 王武杰,李玉亮,王永正,等.无水乙醇在大咯血患者支气管动脉栓塞治疗中的应用[J].山东医药,2013,53(46):73-75.
[37] 李海涛,解皓,柴斌,等.采用不同栓塞剂行支气管动脉栓塞治疗大咯血的疗效[J].临床荟萃,2006,21(11):781-783.
[38] 张万壮,史继国,田素红,等.三丙烯微球联合明胶海绵动脉双重栓塞治疗大咯血的效果评价[J].中国综合临床,2014,30(6): 645-648.
[39] 任医民,伍筱梅,钱元新,等.食管固有动脉作为非支气管性体动脉参与咯血的介入诊断与治疗[J].介入放射学杂志,2013,22(9): 734-737.
[40] 吴金平,焦旭东,吴辉,等.肺结核大咯血多次栓塞治疗的远期疗效及安全性观察[J].临床放射学杂志,2008,27(6):833-836.