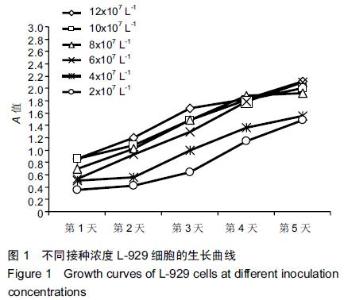
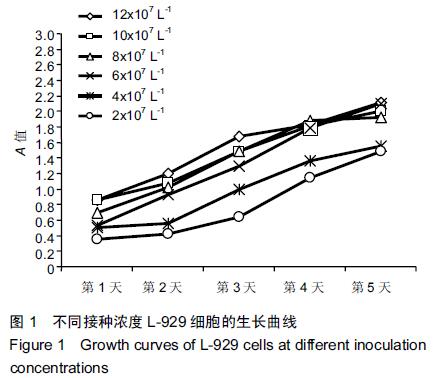
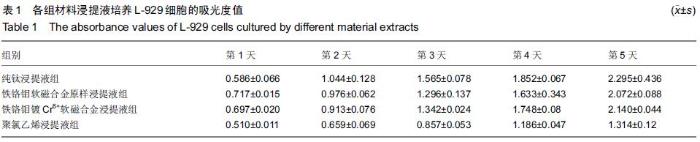
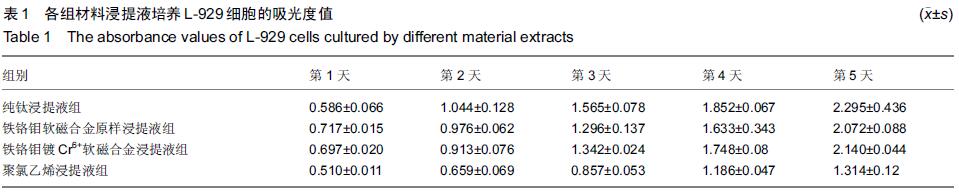
| [1] Gillings BR.Magnetic retention for overdentures.Part II.J Prosthet Dent. 1983;49(5):607-618.
[2] 陈启林,刘东艳,陈永吉,等.磁性附着体与改良杆卡式附着体对支持组织的应力分布[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2013,29(9):552-554.
[3] Nganbe M,Khan U,Louati H,et al.In vitro assessment of strength, fatigue durability, and disassembly of Ti6Al4V and CoCrMo necks in modular total hip replacements. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2011;97(1):132-138.
[4] Lavrentiev MY,Wróbel JS,Nguyen-Manh D,et al.Magnetic and thermodynamic properties of face-centered cubic Fe-Ni alloys.Phys Chem Chem Phys.2014;16(30): 16049- 16059.
[5] Kojima T, Ogiwara M, Mizuguchi M,et al.Fe-Ni composition dependence of magnetic anisotropy in artificially fabricated L1 0-ordered FeNi films.J Phys Condens Matter. 2014;26(6): 064207.
[6] Ekholm M, Zapolsky H, Ruban AV,et al.Influence of the magnetic state on the chemical order-disorder transition temperature in Fe-Ni permalloy.Phys Rev Lett. 2010; 105(16): 167208.
[7] 姜瑞,聂二民,张春元,等.新型材料磁性附着体设计模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):460-464.
[8] 奚延斐,辛仁东,薛淼,等.医疗器械生物学评价[M].北京:中国质检出版社,2012:105.
[9] 周群,苗磊,冯靖雯,等.钴铬钼合金对L929 细胞生物学行为的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(4):407-413.
[10] Mahshim N,Reza F,Omar NS.Physical properties and cytotoxicity comparison of experimental gypsum-based biomaterials with two current dental cement materials on L929 fibroblast cells.J Conserv Dent.2013;16(4):331-335.
[11] Li J,Chen S,Li W,et al.Toxicity of extracts from disposable chopsticks, toothpicks, and paper cups on L-929 cells.Can J Physiol Pharmacol.2015;93(4):223-226.
[12] Franz A,Spinell T,Graf A,et al.Cytotoxicity of post and core composites as a function of environmental conditions.Dent Mater.2014;30(10):1179-1186.
[13] Chen RS,Liu CC,Tseng WY,et al.Cytotoxicity of three dentin bonding agents on human dental pulp cells.J Dent.2003;31(3): 223-229.
[14] Issa Y,Watts DC,Brunton PA,et al.Resin composite monomers alter MTT and LDH activity of human gingival fibroblasts in vitro.Dent Mater.2004;20(1):12-20.
[15] McGinley EL,Fleming GJ,Moran GP.Development of a discriminatory biocompatibility testing model for non-precious dental casting alloys.Dent Mater.2011;27(12):1295-1306.
[16] Steele C,Leigh J,Swoboda R,et al.Growth inhibition of Candida by human oral epithelial cells.J Infect Dis.2000; 182(5):1479-1485.
[17] Franz A,Cong F,Skolka A,et al.Cytotoxicity of resin composites as a function of interface area.Dent Mater.2007; 23(11):1438-1446.
[18] Cheung HS,Haak MH.Growth of osteoblasts on porous calcium phosphate ceramic: an in vitro model for biocompatibility study.Biomaterials.1989;10(1):63-67.
[19] Bernd W,Birte S,Sandra U,et al.Microstrucure, cytotoxicity and corrosion of powder-metallurgical iron alloys for biodegrad- able bone replacement materials.Mater Sci Eng. 2011;176(20):1789-1796.
[20] Ristic L, Vucevic D, Radovic L, et al.Corrosive and Cytotoxic Properties of Compact Specimens and Microparticles of Ni-Cr Dental Alloy. J Prosthodont. 2014;23(3):221-226.
[21] Kunwar A,Barik B,Mishra B,et al.Quantitative cellular uptake, localization and cytotoxicity of curcuminin normal and rumor celles. Biochim Biophys Acta.2008;1780(4):673-679.
[22] Roesems G,Hoet PH,Dinsdale D,et al.In vitro cytotoxicity of various forms of cobalt for rat alveolar macrophages and type II pneumocytes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2000;162(1):2-9. |