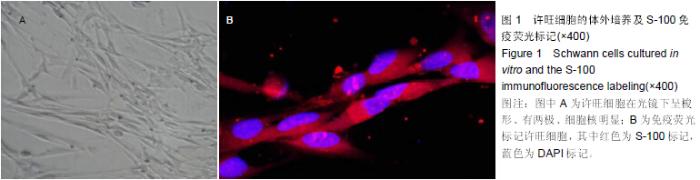
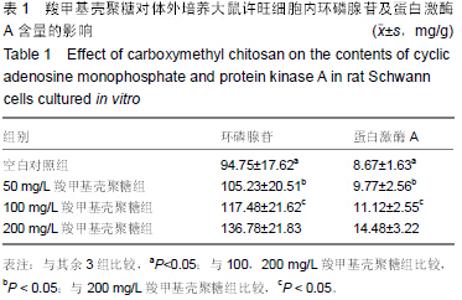
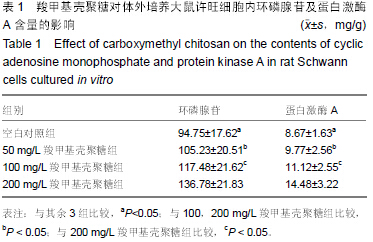
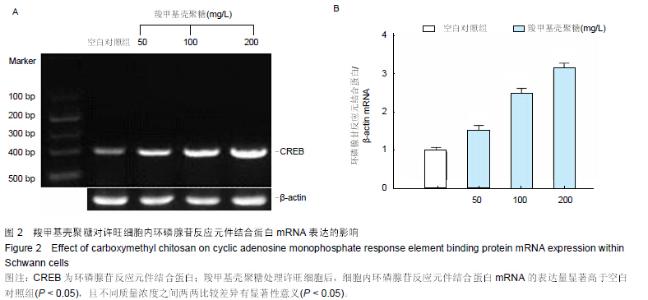
| [1] Wills TE,Batchelor PE,Kerr NF,et al.Corticospinal tract sprouting in the injured rat spinal cord stimulated by Schwann cell preconditioning of the motor cortex. Neurol Res.2013; 35(7):763-772.
[2] Allodi I,Mecollari V,Gonzalez-Perez F,et al.Schwann cells transduced with a lentiviral vector encoding Fgf-2 promote motor neuron regeneration following sciatic nerve injury.Glia. 2014;62(10):1736-1746.
[3] Chen Z,Chang R,Guan W,et al.Transplantation of porcine hepatocytes cultured with polylactic Acid-o-carboxymethylated chitosan nanoparticles promotes l iver regeneration in acute l iver failure rats.J Drug Deliv.2011; 2011:797503.
[4] Wang F,Chen Y,Zhang D,et al.Folate-mediated targeted and intracellular delivery of paclitaxel using a novel deoxycholic acid-Ocarboxymethylated chitosan-folic acid micelles.Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:325-337.
[5] Liu SQ,Qiu B,Chen LY,et al.The effects of carboxymethy- lated chitosan on metalloproteinase-1, -3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 gene expression in cartilage of experimental osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int.2005;26(1): 52-57.
[6] Chen Q,Liu SQ,Du YM,et al.Carboxymethyl-chitosan protects rabbit chondrocytes from interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol.2006;541(1-2):1-8.
[7] He B,Liu SQ,Chen Q,et al.Carboxymethylated chitosan stimulates proliferation of Schwann cells in vitro via the activation of the ERK and Akt signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.2011;667(1-3):195-201.
[8] Tao HY,He B,Liu SQ,et al.Effect of carboxymethylated chitosan on the biosynthesis of NGF and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the proliferation of Schwann cells.Eur J Pharmacol.2013;702(1-3):85-92.
[9] 贺斌,陶海鹰,卫爱林,等.羧甲基壳聚糖对体外培养雪旺细胞增殖周期及其分泌神经营养因子的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(8):923-927.
[10] 贺斌,陶海鹰,卫爱林,等.羧甲基壳聚糖对体外培养许旺细胞增殖及核因子κB表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3): 389-394.
[11] He B,Tao HY,Liu SQ,et al.Neuroprotective effects of carboxymethylated chitosan on hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis in Schwann cells. Eur J Pharmacol.2014;740: 127-134.
[12] 贺斌,陶海鹰,刘世清,等.羧甲基壳聚糖抗氧化损伤诱导雪旺细胞凋亡的作用及机制研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(22): 2095-2100.
[13] 贺斌,陶海鹰,刘世清.羧甲基壳聚糖对氧化应激诱导雪旺细胞凋亡及BDNF、GDNF表达的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014, 28(12):1530-1535.
[14] He B,Tao H,Liu S,et al. Protective effect of carboxymethylated chitosan on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Mol Med Rep.2015;11(3): 1629-1638.
[15] Zhang M,Fei XW,He YL,et al.Bradykinin inhibits the transient outward K+ current in mouse Schwann cells via the cAMP/PKA pathway.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2009; 296(6): C1364-1372.
[16] Salis C,Davio C,Usach V,et al.Iron and holotransferrin induce cAMP-dependent differentiation on Schwann cells. Neurochem Int.2012;61(5):798-806.
[17] Kim HA,DeClue JE,Ratner N.cAMP-dependent protein kinase A is required for Schwann cell growth: interactions between thecAMP and neuregulin/tyrosine kinase pathways. J Neurosci Res.1997;49(2):236-247.
[18] Monje PV,Athauda G,Wood PM.Protein kinase A-mediated gating of neuregulin-dependent ErbB2-ErbB3 activation underlies the synergistic action of cAMP on Schwann cell proliferation.J Biol Chem.2008;283(49):34087-34100.
[19] Liang W,Ge S,Yang L,et al.Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 promote proliferation and expression of neurotrophic factors in primarySchwann cell cultures. Brain Res.2010; 1357: 19-25.
[20] Bacallao K,Monje PV.Opposing roles of PKA and EPAC in the cAMP-dependent regulation of schwann cell proliferationand differentiation [corrected]. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82354.
[21] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[22] Brockes JP,Fields KP,Raff MC.Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. 1. Establishment of purified population from cultures of peripheral nerve.Brain Res. 1979;165(1):105-118.
[23] Jin YQ,Liu W,Hong TH,et al.Efficient Schwann cell purification by differential cell detachment using multiplex collagenase treatment.J Neurosci Methods.2008; 170(1):140.
[24] Koide M,Syed AU,Braas KM,et al.Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) dilates cerebellar arteries through activation of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated (BK) and ATP-sensitive (K ATP) K (+) channels.J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54(3):443-450.
[25] Harren K,Brandhoff B,Knödler M,et al. The high-affinity phosphodiesterase BcPde2 has impact on growth, differentiation and virulence of the phytopathogenic ascomycete Botrytis cinerea.PLoS One.2013;8(11):e78525.
[26] Dong CJ,Guo Y,Ye Y,et al.Presynaptic inhibition by α2 receptor/adenylate cyclase/PDE4 complex at retinal rod bipolar synapse. J Neurosci.2014;34(28):9432-9440.
[27] Bouizar Z,Ragazzon B,Viou L,et al.8Cl-cAMP modifies the balance between PKAR1 and PKAR2 and modulates the cell cycle, growth and apoptosis in human adrenocortical H295R cells.J Mol Endocrinol.2010;44(6):331-347.
[28] Ugland H,Boquest AC, Naderi S,et al.cAMP-mediated induction of cyclin E sensitizes growth-arrested adipose stem cells to DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell. 2008; 19(12):5082-5092.
[29] Blanchet E,Van de Velde S,Matsumura S,et al.Feedback Inhibition of CREB Signaling Promotes Beta Cell Dysfunction in Insulin Resistance.Cell Rep. 2015;10(7):1149-57.
[30] Wang Q,Dai X,Yang W,et al.Caffeine protects against alcohol-induced liver fibrosis by dampening the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in rat hepatic stellate cells.Int Immunopharmacol.2015;25(2):340-352. |