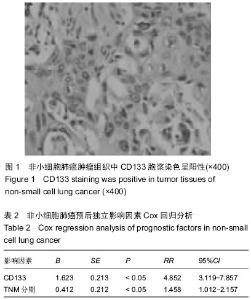
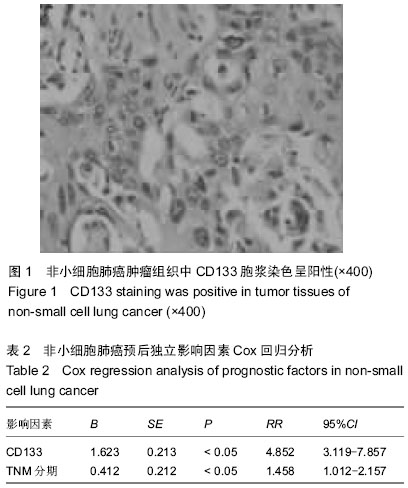
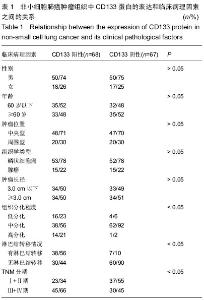
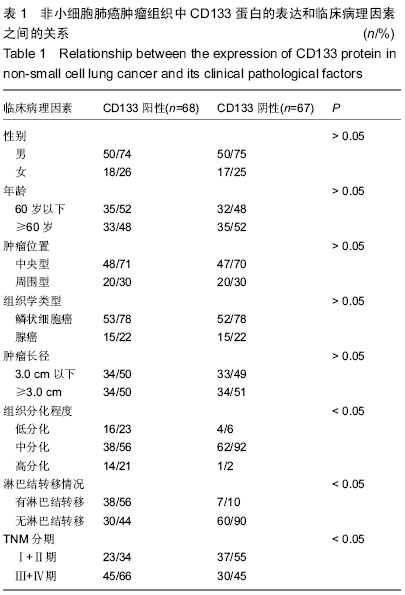
| [1] 周蕾,武世伍,俞岚,等.非小细胞肺癌中CD133和Notch1的表达及其临床病理意义[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(2):196-201.
[2] 梁洪享,钟弦,罗勇,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133、CD44、SOX2、OCT4、ALDH1在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].肿瘤防治研究,2013,40(12):1138-1142.
[3] 梁洪享,钟竑,罗勇,等.肿瘤干细胞标记物CD133、CD44、SOX2、OCT4、ALDH1在NSCLC中的表达及临床意义[J].实用癌症杂志,2013,28(5):472-475.
[4] 苟云久,何晓东,谢定雄,等.非小细胞肺癌组织中CD133表达及临床意义的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4292- 4298.
[5] Hilbe W, Dirnhofer S, Oberwasserlechner F, et al. CD133 positive endothelial progenitor cells contribute to the tumour vasculature in non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57(9):965-969.
[6] 秦勇,韩宏光.肿瘤干细胞标记物CD133在肺癌组织中的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4334-4339.
[7] 顾宇平,朱一蓓,张光波,等.CD133、TROP-2在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及相关性研究初探[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版, 2012,32(10):1396-1400.
[8] 蒋娟,易亭伍,张瑜,等.非小细胞肺癌的肿瘤干细胞与非肿瘤干细胞中表皮生长因子受体基因异质性的研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2012,34(20):2039-2042.
[9] 丁曼,张岸梅,朱波.人肺癌细胞系NCI-H1650中肿瘤干细胞的分离及鉴定[J].重庆医学,2015,44(12):1588-1591.
[10] 王树岗,曾志勇,杨胜生,等.CD133在83例人肺腺癌细胞中的表达研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2012,31(6):727-729.
[11] 倪静怡,杨磊,朱兴华,等.基因OCT4、CD133在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].实用临床医药杂志,2012,16(19):19-22.
[12] 王树岗,曾志勇,杨胜生,等.CD133+肺癌细胞的干细胞特性研究[J].临床肺科杂志,2012,17(5):871-872.
[13] 任涟萍,王佳,郭雪君. CD133+A549肺癌细胞的分选及其肿瘤干细胞和间质化相关基因的表达[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2012,32(6):736-740.
[14] 程继荣,邹静,祖木热提•穆沙江.CD133和CD45在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].肿瘤基础与临床,2011,24(4): 284-286.
[15] 曹志飞,陈志欣,张祖斌,等.人肺腺癌细胞系SPCA1边缘细胞亚群的初步分析[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2011,31(5):709-712.
[16] 姚杰,王志刚,童文先,等.肿瘤干细胞标记物CD133和CD44在肺癌原发灶及转移淋巴结中的表达情况[J].西南国防医药,2010, 20(12):1300-1303.
[17] 魏益平,王梅,华平,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及临床意义[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2008,29(3): 312-316.
[18] Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, et al. Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(38):16281-16286.
[19] Salnikov AV, Gladkich J, Moldenhauer G, et al. CD133 is indicative for a resistance phenotype but does not represent a prognostic marker for survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(4):950-958.
[20] Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432(7015):396-401.
[21] 张惠忠,魏益平,王梅,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133和内皮素转化酶对非小细胞肺癌预后的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2007, 27(5):696-699.
[22] Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, et al. The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 36(3):446-453.
[23] Liu D, Li WM, Mo XM, et al. Multiparametric flow cytometry analyzes the expressions of immunophenotype CD133, CD34, CD44 in lung cancer naive cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008;39(5):827-831.
[24] Cui F, Wang J, Chen D, et al. CD133 is a temporary marker of cancer stem cells in small cell lung cancer, but not in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;25(3):701-708.
[25] Meng X, Li M, Wang X, et al. Both CD133+ and CD133- subpopulations of A549 and H446 cells contain cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(6):1040-1046.
[26] Janikova M, Skarda J, Dziechciarkova M, et al. Identification of CD133+/nestin+ putative cancer stem cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2010;154(4):321-326.
[27] Salnikov AV, Gladkich J, Moldenhauer G, et al. CD133 is indicative for a resistance phenotype but does not represent a prognostic marker for survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(4):950-958.
[28] Vroling L, Lind JS, de Haas RR, et al. CD133+ circulating haematopoietic progenitor cells predict for response to sorafenib plus erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(2):268-275.
[29] Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, et al. Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(38):16281-16286.
[30] 顾永平,孙茂民,顾丽琴,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133、ABCG2、p75NTR在非小细胞肺癌组织的表达及其生物学意义[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2010,30(3):513-516,572.
[31] 郑少秋,李书华,王红艳,等.CD133阳性/阴性肺癌细胞的分选、鉴定及差异基因的筛选[J].中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(3):123-130.
[32] 文加斌,张阳,王丽萍,等.NCI-H446人小细胞肺癌细胞株细胞亚群克隆与肿瘤干细胞的实验研究[J].实用癌症杂志,2009,24(2): 114-116.
[33] 伍伫,刘丹,李为民,等.多参数流式细胞术分析肺癌幼稚细胞免疫表型CD133、CD34、CD44的表达[J].四川大学学报:医学版, 2008,39(5):827-831.
[34] Zhao P, Li Y, Lu Y. Aberrant expression of CD133 protein correlates with Ki-67 expression and is a prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:218.
[35] Woo T, Okudela K, Mitsui H, et al. Prognostic value of CD133 expression in stage I lung adenocarcinomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2010;4(1):32-42.
[36] Immervoll H, Hoem D, Sakariassen PØ, et al. Expression of the "stem cell marker" CD133 in pancreas and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:48.
[37] Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514.
[38] Schneider M, Huber J, Hadaschik B, et al. Characterization of colon cancer cells: a functional approach characterizing CD133 as a potential stem cell marker. BMC Cancer. 2012; 12:96.
[39] Salnikov AV, Gladkich J, Moldenhauer G, et al. CD133 is indicative for a resistance phenotype but does not represent a prognostic marker for survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(4):950-958.
[40] Xu YH, Zhang GB, Wang JM, et al. B7-H3 and CD133 expression in non-small cell lung cancer and correlation with clinicopathologic factors and prognosis. Saudi Med J. 2010; 31(9):980-986. |