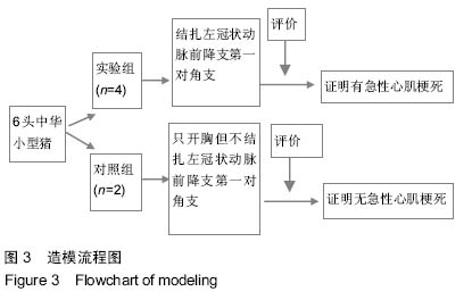
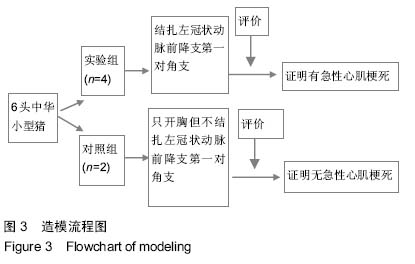
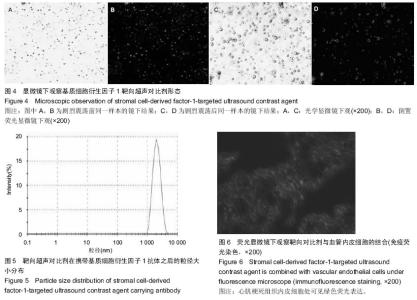
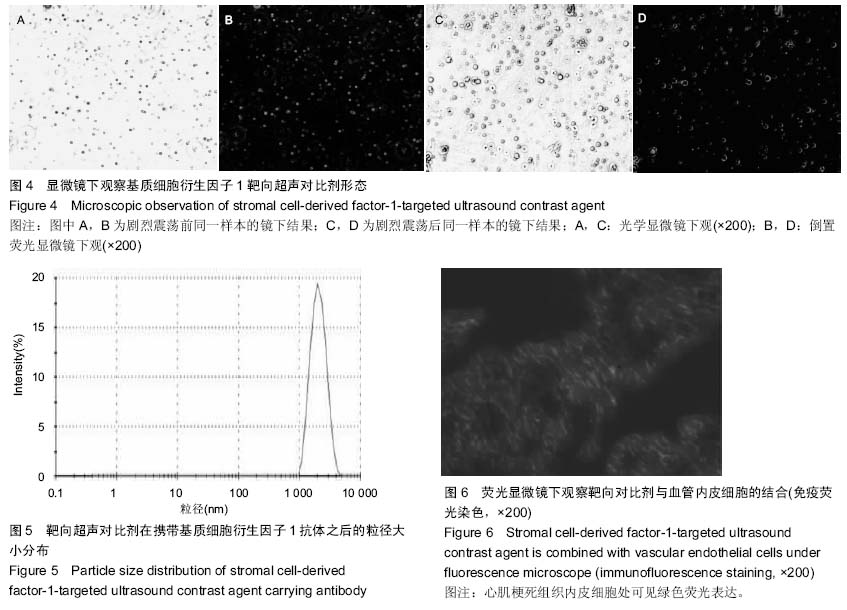
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (20): 3188-3194.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.20.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stromal cell-derived factor-1-targeted ultrasound contrast agent tightly binds to vascular endothelial cells
Wang Meng, Shi Qi, Mu Yu-ming, Tuerxunnayi Adi
- Department of Ultrasound, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2015-05-14Published:2015-05-14 -
Contact:Mu Yu-ming, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Department of Ultrasound, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Meng, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Ultrasound, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271590
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Meng, Shi Qi, Mu Yu-ming, Tuerxunnayi Adi. Stromal cell-derived factor-1-targeted ultrasound contrast agent tightly binds to vascular endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(20): 3188-3194.
share this article
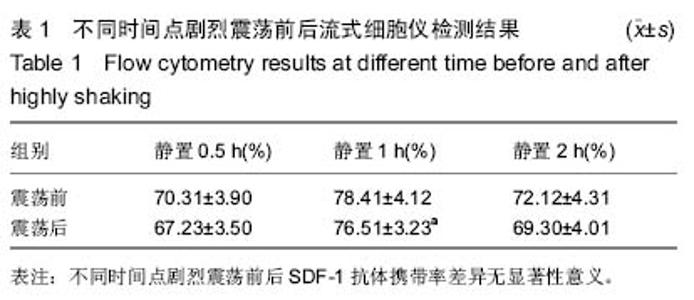
| [1] Lasala GP, Minguell JJ. Bone marrow-derived stem/progenitor cells: their use in clinical studies for the treatmentof myocardial infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 2009; 18(3):171-180. [2] 曹桂秋,穆玉明,李艳红,等.彩色编码参数量化技术结合靶向微泡对比剂评价干细胞移植后微血管新生[J].中华超声影像学杂志, 2011,20(11):983-987. [3] Takagi H, Umemoto T. Intracoronary stem cell injection improves left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction: an updated meta-analysis of randomized trials. Int J Cardiol. 2011;151(2):226-228. [4] Strauer BE, Yousef M, Schannwell CM. The acute and longterm effects of intracoronary Stem cell Transplantation in 191 patients with chronic heARt failure: the STAR-heart study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010;12(7):721-729. [5] Gao XR, Tan YZ, Wang HJ, et al. Overexpression of Csx/Nkx2.5 and GATA-4 Enhances the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation After Myocardial Infarction. Circ J. 2011;75(11):2683-2691. [6] Ling ZY, Shu SY, Zhong SG, et al. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction promotes angiogenesis and heart function by inducing myocardial microenvironment change. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013;39(11):2001-2010. [7] Marcello R. SDF-1 axis and myocardial repair. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299(5):H1307-H1308. [8] Tang JM, Wang JN, Zhang L, et al. VEGF/SDF-1 promotes cardiac stem cell mobilization and myocardial repair in the infarcted heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(3):402-411. [9] Tsuji H, Miyoshi S, Ikegami Y, et al. Xenografted human amniotic membrane- derived mesenchymal stem cells are immunologically tolerated and transdiffere-ntiated into cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2010;106(10):1613-1623. [10] Huber BC, Brunner SA, Nathan P, et al. Parathyroid hormone is a DPP-IV inhibitor and increases SDF-1-driven homing of CXCR4+ stem cells into the ischaemic heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;90(3):529-537. [11] Segers VF, Revin V, Wu W, et al. Protease-resistant stromal cellderived factor1 for the treatment of experimental peripheral artery disease. Circulation. 2011;12(123): 1306-1315. [12] Inaba Y, Lindner JR. Molecular imaging of disease with targeted contrast ultrasound imaging. Transl Res. 2012; 159(3):140-148. [13] Gessner R, Dayton PA. Advances in molecular imaging with ultrasound. Mol Imaging. 2010;9(3):117-127. [14] 陈智毅,谢明星.超声靶向破坏微泡技术的应用进展[J].中国医学影像技术,2010,26(9):1790-1792. [15] 刘腾,洪玉蓉,董鑫,等.靶向纳米液态氟碳球囊超声对比剂的制备及体外靶向研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2014,23(1):71-75. [16] Decano JL, Moran AM, Ruiz-Opazo N, et al. Molecular Imaging of Vasa Vasorum Neovascularization via DEspR-targeted Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound Micro- imaging in Transgenic Atherosclerosis Rat Model. Mol Imaging Biol. 2011;13:1096-1106. [17] Muramoto T, Shimoya R, Yoshida K, et al. Evaluation of the specific adsorption of biotinylated microbubbles using a quartz crystal microbalance. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014; 40(5):1027-1033. [18] 刘世清,冉海涛,王志刚,等.携sialyl lewisx配基的靶向脂质微泡的构建及体外寻靶的试验研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2013, 29(6):561-564. [19] Hunziker PR, Imsand C, Keller D, et al. Bedside quantification of atherosclerosis severity for cardiovascular risk stratification: a prospective cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39: 702-709. [20] 刘兴钊,任建丽,王志刚.携抗P-选择素单抗靶向超声对比剂的制备及体外寻靶实验研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2013,22(4): 349-354. [21] Schaar JA, de Korte CL, Mastik F, et al. Characterizing vulnerable plaque features with intravascular elastography. Circulation. 2003;108:2636-2641. [22] 徐秀霞,宋竹清,徐健蓉,等.RGD靶向微泡对比剂的制备及其黏附效能[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2015,(2):87-90. [23] Yang CH, Sheu JJ, Tsai TH, et al. Effect of tacrolimuson myocardial infarction is associated with inflammation, ROS, MAP kinase and Akt pathways in mini-pigs. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013;20(1):9-22. [24] 宋桂仙,李小荣,张凤祥,等.猪心肌梗死后室性心律失常模型建立方法的比较[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志,2012,26(3): 246-249. [25] Munz MR, Faria MA, Monteiro JR, et al. Surgical porcine myocardial infarction model through permanent coronary occlusion. Comp Med. 2011;61(5):445-452. [26] Mu Y, Cao G, Zeng Q, et al. Transplantation of induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the cardiac function of rabbits with dilated cardiomyopathy via upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Exp Biol Med. 2011;236(9):1100-1107. [27] Hu G, Liu C, Liao Y, et al. Ultrasound molecular imaging of arterial thrombi with novel microbubbles modified by cyclic RGD in vitro and in vivo. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(1): 172-183. [28] Ling ZY, Shu SY, Zhong SG, et al. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction promotes angiogenesis and heart function by inducing myocardial microenvironment change. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013;39(11):2001-2010. [29] Zhong S, Shu S, Wang Z, et al. Enhanced homing of mesenchymal stem cells to the ischemic myocardium by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction. Ultrasonics. 2012;52(2):281-286. [30] Sun L, Huang CW, Wu J, et al. The use of cationic microbubbles to improve ultrasound-targeted gene delivery to the ischemic myocardium. Biomaterials. 2013;34(8): 2107-2116. [31] 王潇,郭瑞强,周青,等.携抗ICAM-1靶向微泡定向转染Ang-1基因治疗急性心肌梗死的实验研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2011, 20(5):436-440. [32] Kuvat SV, Keklik B, Özden BC, et al. Major donor area complication after a mandibular reconstruction with an osseous fibular free flap: pseudo-compartment syndrome. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(2):499-501. [33] Leung K. Microbubbles-echistatin. Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). 2005. [34] Piedra M, Allroggen A, Lindner JR. Molecular imaging with targeted contrast ultrasound. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;27 Suppl 2:66-74. [35] Lafaras C, Mandala E, Verrou E, et al. Non-thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in multiple myeloma, after thalidomide treatment: a pilot study. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(10): 1765-1769. [36] Debourdeau P, Chahmi DK, Zammit C, et al. Venous thromboembolism associated with long-term use of central venous catheters in cancer patients. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2008; 56(4):211-219. [37] Kaufmann BA, Lindner JR. Molecular imaging with targeted contrast ultrasound. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18(1):11-16. [38] Linenberger ML. Catheter-related thrombosis: risks, diagnosis, and management. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2006;4(9): 889-901. [39] Behm CZ, Lindner JR. Cellular and molecular imaging with targeted contrast ultrasound.Ultrasound Q. 2006;22(1):67-72. [40] Hach-Wunderle V. Diagnosis and treatment of venous thrombosis. Hamostaseologie. 2005;25(4):356-366. [41] Lindner JR. Molecular imaging with contrast ultrasound and targeted microbubbles. J Nucl Cardiol. 2004;11(2):215-221. [42] Lindner JR. Evolving applications for contrast ultrasound. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90(10A):72J-80J. [43] Van den Noortgate N, Michielsen W, Afschrift M, et al. Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis: primary manifestation of a colorectal adenocarcinoma in a very old woman. Acta Clin Belg. 2000;55(2):94-96. [44] Taheri SA, Lazar L, Haddad G, et al. Diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis by use of soluble necrosis factor receptor. Angiology. 1998;49(7):537-541. [45] Steiner RE, Bydder GM. Nuclear magnetic resonance in gastroenterology. Clin Gastroenterol. 1984;13(1):265-279. [46] 肖云彬,宾建国,宾建平.靶向超声对比剂的修饰与生物连接技术[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2010,19(4):359-361. [47] 叶露薇,王志刚,冉海涛,等.携抗CD34和抗ICAM-1双抗体的靶向超声对比剂的制备及鉴定[C].中国超声医学工程学会第十一届全国超声医学学术大会论文汇编,2012:278-279.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||