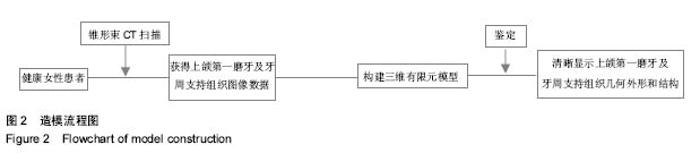
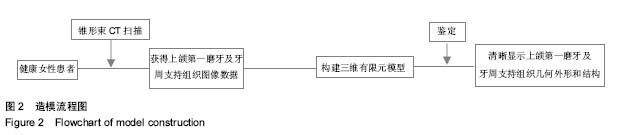
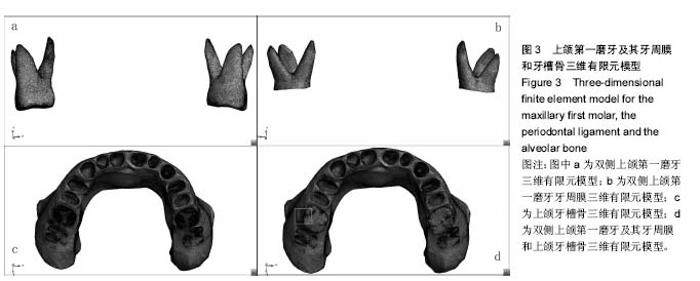
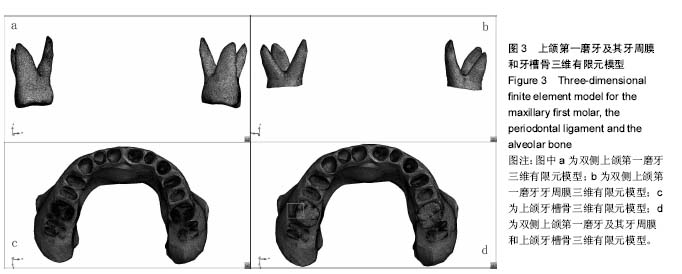
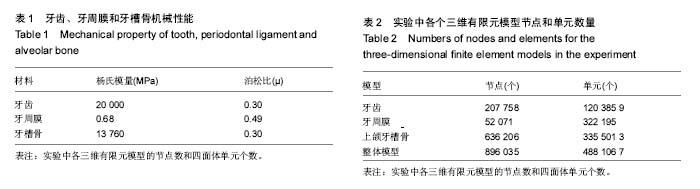
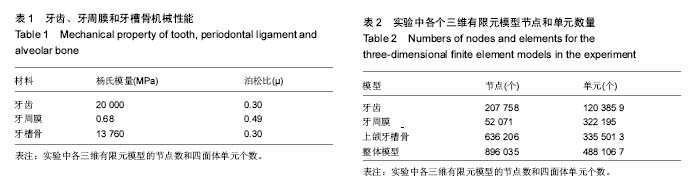
| [1] Zablocki HL, McNamara JA, Franchi L. Effect of the transpalatal arch during extraction treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;133(6):852-860.
[2] Fujisawa M. A modified transpalatal arch with customized bonding base. Orthodontic Waves. 2011;70(1):39-42.
[3] Arslan A, Ozdemir DN, Gursoy-Mert H. Intrusion of an overerupted mandibular molar using mini-screws and mini-implants: a case report. Aust Dent J. 2010;55(4): 457-461.
[4] Gunduz C. An improved transpalatal bar design. Part II. Clinical upper molar derotation-case report. Angle Orthod. 2003;73(3):244-248.
[5] Ma D, Wang XX, Jin SM. Comparison of two treatment method for maxillary incisors intrusion. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2013;22(2):206-209.
[6] Hourfar JB, Ludwig G. An active, skeletally anchored transpalatal appliance for derotation, distalization and vertical control of maxillary first molars. J Orthod. 2014;41 Suppl 1:S24-S32.
[7] Chisari JR, McGorray SP, Nair M. Variables affecting orthodontic tooth movement with clear aligners. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;145(4 Suppl):S82-S91.
[8] Jung GB, Kim KA, Han I. Biochemical characterization of human gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement using Raman spectroscopy. Biomed Opt Express. 2014;5(10):3508-3520.
[9] Kojima Y, Kawamura J, Fukui H, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of force directions on tooth movement in extraction space closure with miniscrew sliding mechanics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;142(4):501-508.
[10] Oh H, Herchold K, Hannon S. Orthodontic tooth movement through the maxillary sinus in an adult with multiple missing teeth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;146(4): 493-505.
[11] Farah JW, Craig RG, Sikarskie DL. Photoelastic and finite element stress analysis of a restored axisymmetric first molar. J Biomech. 1973;6(5):511-520.
[12] Fariba R, Sirous R, Somayyeh T. Stress analysis in the periodontium of the maxillary canine in translatory movement with a three dimensional finite element method. J Life Sci. 2013;10(2s):245-250.
[13] Geramy A. Alveolar bone resorption and the center of resistance modification (3-D analysis by means of the finite element method). Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000; 117(4):399-405.
[14] Harris DA, Jones AS, Darendeliler MA. Physical properties of root cementum: part 8. Volumetric analysis of root resorption craters after application of controlled intrusive light and heavy orthodontic forces: a microcomputed tomography scan study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130(5):639-647.
[15] Jing Y, Han XL, Cheng BH. Three-dimensional FEM analysis of stress distribution in dynamic maxillary canine movement. Shenjing Kexue Tongbao. 2013;58(20):2454-2459.
[16] Kojima Y, Fukui H, Numerical simulation of canine retraction by sliding mechanics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005 127(5):542-551.
[17] Largura LZ, Argenta MA, Sakima MT, et al.Bone stress and strain after use of a miniplate for molar protraction and uprighting: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;146(2):198-206.
[18] Cifter M, Sarac M. Maxillary posterior intrusion mechanics with mini-implant anchorage evaluated with the finite element method. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;140(5): 233-241.
[19] Ehsani S, Mirhashemi FS, Asgary S. Finite Element Reconstruction of a Mandibular First Molar. Iran Endod J. 2013;8(2):44-47.
[20] Lee HJ, Lee KS, Kim MJ. Effect of bite force on orthodontic mini-implants in the molar region: Finite element analysis. Korean J Orthod. 2013;43(5):218-224.
[21] Park JM. Three dimensional finite element analysis of the stress distribution around the mandibular posterior implant during non-working movement according to the amount of cantilever. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014;6(5):361-371.
[22] Yu IJ, Kook YA, Sung SJ. Comparison of tooth displacement between buccal mini-implants and palatal plate anchorage for molar distalization: a finite element study. Eur J Orthod. 2014; 36(4):394-402.
[23] Zhao Z, Fan Y, Bai D. The adaptive response of periodontal ligament to orthodontic force loading - a combined biomechanical and biological study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2008;23 Suppl 1:S59-S66.
[24] Magne P. Efficient 3D finite element analysis of dental restorative procedures using micro-CT data. Dent Mater. 2007;23(5):539-548.
[25] Ammar HH, Ngan P, Crout RJ. Three-dimensional modeling and finite element analysis in treatment planning for orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;139(1):59-71.
[26] Cattaneo PM, Dalstra M, Melsen B. The finite element method: a tool to study orthodontic tooth movement. J Dent Res. 2005;84(5):428-433.
[27] 魏洪涛,张天夫.牙颌三维有限元模型生成方法的探讨[J].白求恩医科大学学报,2000,26(2):150-151.
[28] 高勃,王忠义.牙冠表面形状测量造型方法[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 1999,15(4):299-301.
[29] 李志华,陈天云.上颌第一磨牙的三维有限元模型的建立[J].实用临床医学,2001,2(1):31-33.
[30] 李吉国,倪龙兴.运用Micro-CT技术建立上颌第一磨牙根管系统的有限元模型[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2007,17(6):320-323.
[31] 蔚一博,朱强,曹志中.Micro-CT技术结合逆向工程软件建立上颌第一前磨牙的三维有限元模型[J].第二军医大学学报,2011, 32(7): 745-748.
[32] 殷霄,张亚庆.用实体建模法建立上颌第一磨牙隐裂的三维有限元模型[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2010,20(3):143-146.
[33] GiD Reference manual, Pre and post processing system for Numerical Simulations. International Center For Numerical Methods In Engineering (CIMNE). 2014. |